J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Apr;50(4):588-593. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.4.588.
The Effects of Wnt Protein on Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of Corneal Limbal Stem Cells (CLSCs)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, College of Medicine and Laboratory of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Catholic Research Institutes of Medical Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ckjoo@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2212261
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.4.588
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the effects of the Wnt protein on proliferation and stemness maintenance of cultured corneal limbal stem cells.
METHODS
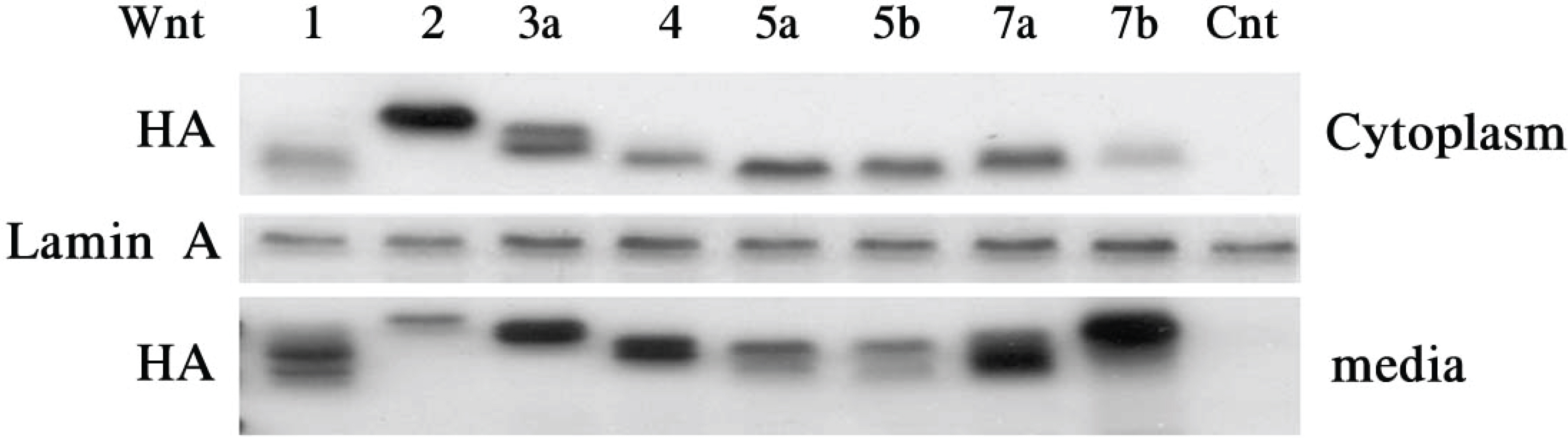
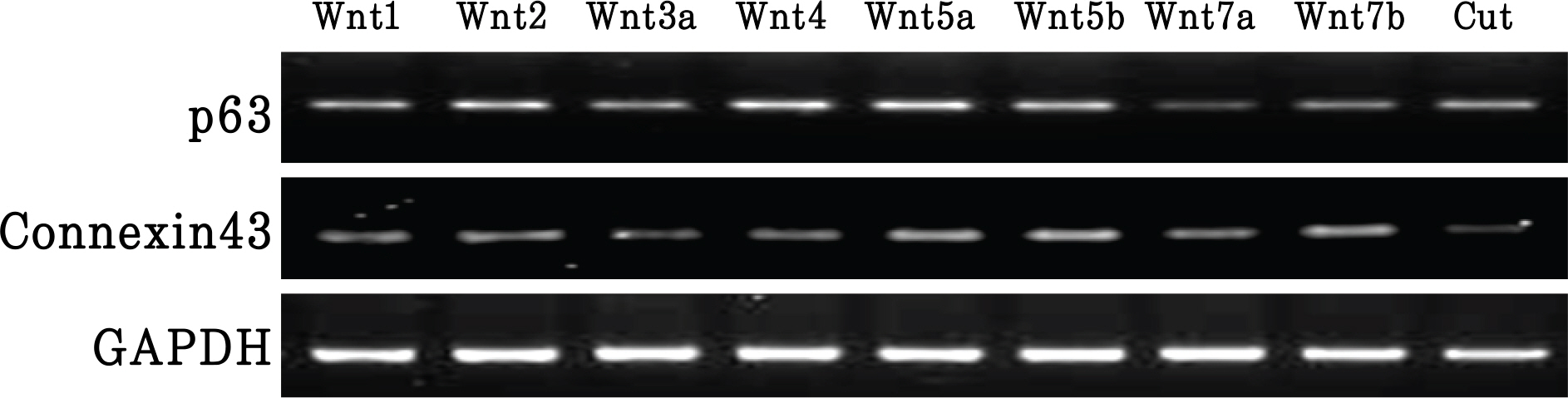
We examined the expression of Wnt proteins by Western blot analysis. We then evaluated the effects of Wnt on cell proliferation by colony forming efficiency. beta-catenin activation using Wnt proteins was examined by immunocytochemistry. We also examined the effects of Wnt on proliferation and stemness maintenance by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of p63 and connexin43.
RESULTS
Wnt has a different effect on corneal epithelial stem cells. Colony forming efficiency was also significantly higher in treated Wnt2 and Wnt4 cells compared with controls. The Wnt2 and Wnt4 treated cells showed nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin. In addition, the limbal stem cell marker p63 was strongly expressed in Wnt2, Wnt4 Wnt5a, and Wnt5b. Connexin43 mRNA was also strongly expressed in Wnt5a, Wnt5b and Wnt7b cells.
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that Wnt2 and Wnt4 could lead to more effective proliferation and stemness maintenance for human corneal epithelial stem cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Davanger M, Evensen A. Role of the pericorneal papillary structure in renewal of corneal epithelium. Nature. 1971; 229:560–1.
Article2. Daniels JT, Dart JK, Tuft SJ, et al. Corneal stem cells in review. Wound Repair Regen. 2001; 9:483–94.
Article3. Revoltella RP, Papini S, Rosellini A, et al. Epithelial stem cells of the eye surface. Cell Prolif. 2007; 40:445–61.
Article4. Kenyon KR, Tseng SC. Limbal autograft transplantation for ocular surface disorders. Ophthalmology. 1989; 96:709–22.
Article5. Frucht-Pery J, Siganos CS, Solomon A. Limbal cell autograft transplantation for severe ocular surface disorders. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1998; 236:582–7.
Article6. Kim MK, Lee JL, Shin KS, et al. Isolation of putative corneal epithelial stem cells from cultured limbal tissue. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2006; 20:55–61.
Article7. Park KS, Lim CH, Min BM, et al. The side population cells in the rabbit limbus sensitively increased in response to the central cornea wounding. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:892–900.
Article8. Dogru M, Tsubota K. Current concepts in ocular surface reconstruction. Semin Ophthalmol. 2005; 20:75–93.
Article9. Shortt AJ, Secker GA, Notara MD, et al. Transplantation of ex vivo cultured limbal epithelial stem cells: a review of techniques and clinical results. Surv Ophthalmol. 2007; 52:483–502.
Article10. Liu J, Song G, Wang Z, et al. Establishment of a corneal epithelial cell line spontaneously derived from human limbal cells. Exp Eye Res. 2007; 84:599–609.
Article11. Chee KY, Kicic A, Wiffen SJ. Limbal stem cells: the search for a marker. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:64–73.
Article12. Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Kruse FE. Identification and characterization of limbal stem cells. Exp Eye Res. 2005; 81:247–64.
Article13. Ivekovic R, Tedeschi-Reiner E, Novak-Laus K, et al. Limbal graft and/or amniotic membrane transplantation in the treatment of ocular burns. Ophthalmologica. 2005; 219:297–302.
Article14. Vossmerbaeumer U, Kuehl S, Bieback K, et al. Cultivation and differentiation characteristics of human limbal progenitor cells. Tissue Cell. 2008; 40:83–8.
Article15. Zhao B, Allinson SL, Ma A, et al. Targeted cornea limbal stem/ progenitor cell transfection in an organ culture model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:3395–401.16. Moon RT, Brown JD, Torres M. Wnts modulate cell fate and behaviour during vertebrate development. Trends Genet. 1997; 13:157–62.17. Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004; 20:781–810.
Article18. Nusse R. Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Cell Res. 2008; 18:523–7.
Article19. Willert K, Nusse R. Beta-catenin: a key mediator of Wnt signaling. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998; 8:95–102.20. Gordon MD, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:22429–33.
Article21. Hoppler S, Kavanagh CL. Wnt signalling: variety at the core. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120:385–93.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transplantation of in vivo Cultivated Limbal Corneal Epithelial Cells with Total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency
- Probiotic-Derived P8 Protein: Promoting Proliferation and Migration in Stem Cells and Keratinocytes
- Peripheral Blood As a Source of Stem Cells for RegenerativeMedicine: Emphasis Towards Corneal EpithelialReconstruction—An In Vitro Study
- Combined Surgery of the Penetrating Keratoplasty and the Limbal Cell Transplantation
- Migration of Normal Corneal Epithelial Cells in Rats