J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Jun;78(6):390-397. 10.4174/jkss.2010.78.6.390.
Impaired Cation Transport May Lead to Bioelectrical Impedance Changes during Hepatic Ischemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Institute of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. ssyun@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2211970
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.78.6.390
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury is a major cause of hepatic failure after liver surgery, but there is no direct method to monitor it in real-time (like an electrocardiogram in heart disease) during surgery. Recently we found the possible role of bioelectrical impedance (BEI) to monitor I/R injury in liver. But the mechanism responsible for ischemia-related BEI changes has not been clearly determined.
METHODS
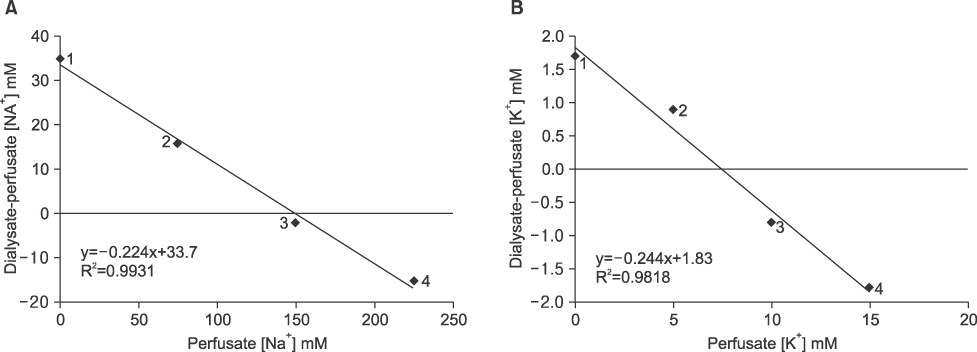
The authors used an LCR meter to quantify BEI changes at 0.12 KHz. Livers were subjected to 70% partial ischemia for 120 minutes, and ATP contents, cation changes in extracellular fluid (ECF; determined using an in vivo intracellular microdialysis technique), hepatocyte sizes, and histological changes were then examined.
RESULTS
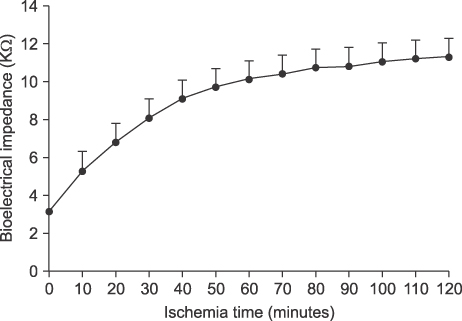
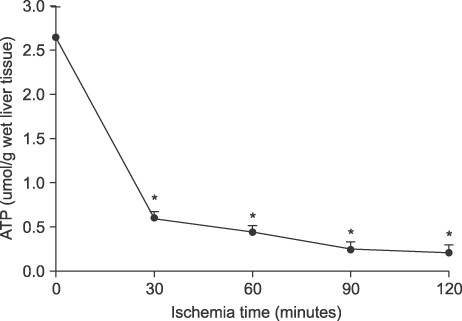
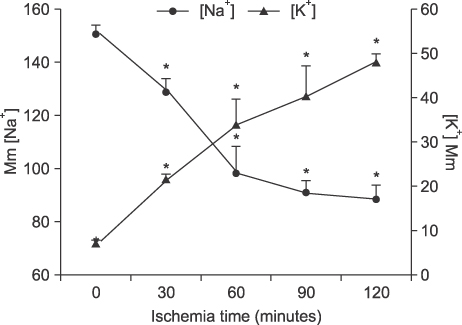
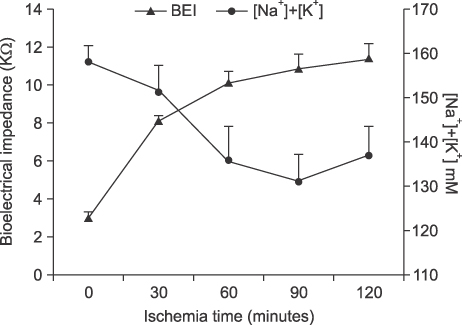
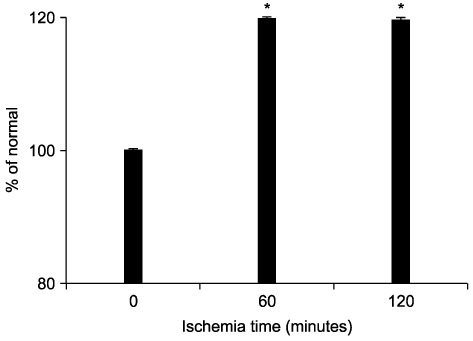
Liver tissue BEI was found to increase gradually during the first 60 minutes of ischemia and then tended to plateau. During the same period, intracellular ATP contents decreased to below 20% of the baseline level, [Na+] in ECF decreased from 150.4+/-3.8 to 97.8+/-10.6 mmol/L, and [K+] in ECF increased from 7.5+/-0.3 to 34.3+/-5.5 mmol/L during the first 60 minutes of ischemia. Hepatocyte diameter increased by ~20% during the first 60 minutes of ischemia.
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that BEI changes during hepatic ischemia are probably caused by sodium and potassium concentration changes in the ECF due to reduced intracellular ATP contents.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Significance of Bioelectrical Impedance Change after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Liver and What it Causes?
Sung Su Yun
Hanyang Med Rev. 2013;33(3):154-159. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2013.33.3.154.
Reference
-
1. Kun S, Ristic B, Peura RA, Dunn RM. Algorithm for tissue ischemia estimation based on electrical impedance spectroscopy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2003. 50:1352–1359.2. Konishi Y, Morimoto T, Kinouchi Y, Iritani T, Monden Y. Electrical properties of extracted rat liver tissue. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1995. 195:183–192.3. Cho YS, Yun SS, Shin HJ, Ahn HS, Lee DS, Kim HJ. Significance of bioelectrical impedance during ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rabbit's liver. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006. 10:29–33.4. Cui ML, Ahn HS, Kim JY, Shin HJ, Lee DS, Kim HJ, et al. Bioelectrical impedance may predict cell viability during ischemia and reperfusion in rat liver. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:577–582.5. Park SH, Yun SS, Lee DS, Kim HJ, Choi JH, Kim JY. Estimation of liver cell viability after ischemia and reperfusion injury in rat liver. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:1–7.6. Rees AE, Ward LC, Cornish BH, Thomas BJ. Sensitivity of multiple frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis to changes in ion status. Physiol Meas. 1999. 20:349–362.7. Camargo CA Jr, Madden JF, Gao W, Selvan RS, Clavien PA. Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology. 1997. 26:1513–1520.8. Khan HA. Bioluminometric assay of ATP in mouse brain: Determinant factors for enhanced test sensitivity. J Biosci. 2003. 28:379–382.9. Grubb BR, Chadburn JL, Boucher RC. In vivo microdialysis for determination of nasal liquid ion composition. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. 282:C1423–C1431.10. Gersing E. Impedance spectroscopy on living tissue for determination of the state of organs. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg. 1998. 45:145–149.11. Haemmerich D, Ozkan R, Tungjitkusolmun S, Tsai JZ, Mahvi DM, Staelin ST, et al. Changes in electrical resistivity of swine liver after occlusion and postmortem. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2002. 40:29–33.12. Elmquist WF, Sawchuk RJ. Application of microdialysis in pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm Res. 1997. 14:267–288.13. Tian Y, Fukuda C, Schilling MK. Interstitial accumulation of Na+ and K+ during flush-out and cold storage of rat livers: implications for graft survival. Hepatology. 1998. 28:1327–1331.14. Ungerstedt U. Marsden CA, editor. Measurement of neurotransmitter release by intracranial dialysis. Measurement of Neurotransmitter Release in vivo. 1984. New York: Wiley;81–105.15. Fleischhauer J, Lehmann L, Kleber AG. Electrical resistances of interstitial and microvascular space as determinants of the extracellular electrical field and velocity of propagation in ventricular myocardium. Circulation. 1995. 92:587–594.16. Yan GX, Chen J, Yamada KA, Kleber AG, Corr PB. Contribution of shrinkage of extracellular space to extracellular K+ accumulation in myocardial ischaemia of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1996. 490:215–228.17. del Rio CL, McConnell PI, Clymer BD, Dzwonczyk R, Michler RE, Billman GE, et al. Early time course of myocardial electrical impedance during acute coronary artery occlusion in pigs, dogs, and humans. J Appl Physiol. 2005. 99:1576–1581.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Bioelectrical Impedance Change after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Liver and What it Causes?
- Significance of Bioelectrical Impedance during Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the Rabbit's Liver
- Bioelectrical Impedance May Predict Cell Viability During Ischemia and Reperfusion in Rat Liver
- The Clinical Significance of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for The Diagnosis of Obesity on Elementary Students
- Percent of Body Fat by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Healthy Children