J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2011 Apr;49(2):120-127. 10.4047/jkap.2011.49.2.120.
Effects of chromium chloride addition on coloration and mechanical properties of 3Y-TZP
- Affiliations
-
- 1BK21 Project, Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2R&D Center for Titanium and Special Alloys, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Division of Materials Science and Engineering, Research Institute for Functional Surface Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. djlee8283@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2196118
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2011.49.2.120
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of chromium chloride addition on coloration, mechanical property and microstructure of 3Y-TZP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chromium chloride was weighed as 0.06, 0.12, and 0.25 wt% and each measured amount was dissolved in alcohol. ZrO2 powder was mixed with each of the individual slurry to prepare chromium doped zirconia specimen. The color, physical properties and microstructure were observed after the zirconia specimen were sintered at 1450degrees C. In order to evaluate the color, spectrophotometer was used to analyze the value of L*, C*, a* and b*, after placing the specimen on a white plate, and measured according to the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) standard, Illuminant D65 and SCE system. The density was measured in the Archimedes method, while microstructures were evaluated by using the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and XRD. Fracture toughness was calculated Vickers indentation method and indentation size was measured by using the optical microscope. The data were analyzed with 1-way ANOVA test (alpha= 0.05). The Tukey multiple comparison test was used for post hoc analysis.
RESULTS
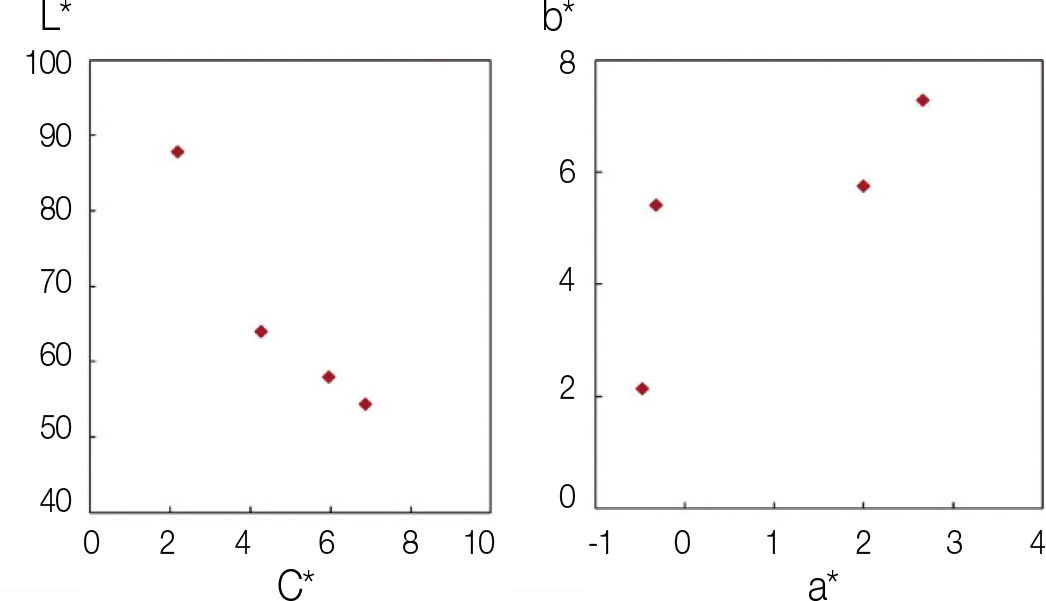
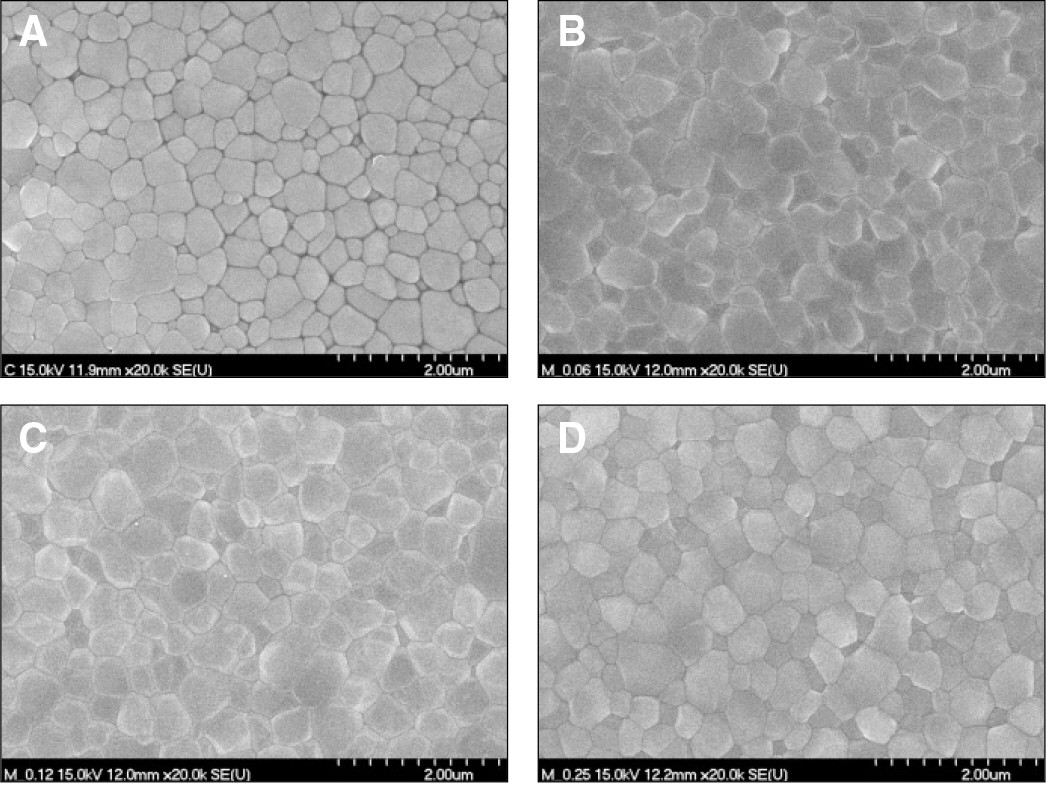
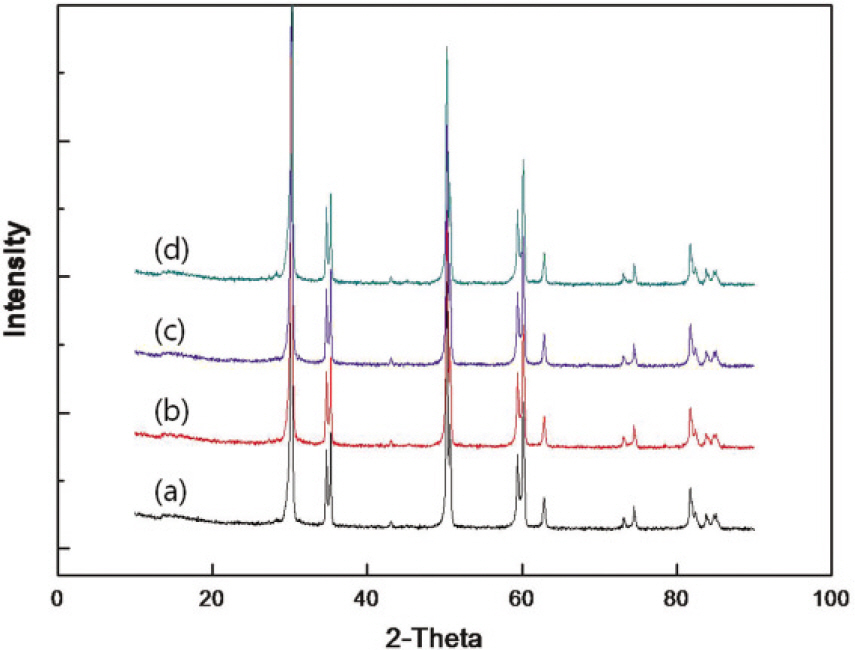
1. Chromium chloride rendered zirconia a brownish color. While chromium chloride content was increased, the color of zirconia was changed from brownish to brownish-red. 2. Chromium chloride content was increased; density of the specimen was decreased. 3. More chromium chloride in the ratio showed increase size of grains. 4. But the addition of chromium chloride did not affect the crystal phase of zirconia, and all specimens showed tetragonal phase. 5. The chromium chloride in zirconia did not showed statistically significant difference in fracture toughness, but addition of 0.25 wt% showed a statistically significant difference (P<.05).
CONCLUSION
Based on the above results, this study suggests that chromium chlorides can make colored zirconia while adding in a liquid form. The new colored zirconia showed a slight difference in color to that of the natural tooth, nevertheless this material can be used as an all ceramic core material.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Meyenberg KH., Lu¨thy H., Scha¨rer P. Zirconia posts: a new all-ceramic concept for nonvital abutment teeth. J Esthet Dent. 1995. 7:73–80.
Article2.Luthardt R., Weber A., Rudolph H., Scho¨ne C., Quaas S., Walter M. Design and production of dental prosthetic restorations: basic research on dental CAD/CAM technology. Int J Comput Dent. 2002. 5:165–76.3.Wohlwend A., Studer S., Scha¨rer P. The zirconium oxide abutment: An all-ceramic abutment for the esthetic improvement of implant superstructures. Quintessence Dent Technol. 1997. 1:63–74.4.Keith O., Kusy RP., Whitley JQ. Zirconia brackets: an evaluation of morphology and coefficients of friction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994. 106:605–14.
Article5.Sundh A., Sjo¨gren G. Fracture resistance of all-ceramic zirconia bridges with differing phase stabilizers and quality of sintering. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:778–84.
Article6.Aboushelib MN., de Jager N., Kleverlaan CJ., Feilzer AJ. Microtensile bond strength of different components of core veneered all-ceramic restorations. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:984–91.
Article7.Heffernan MJ., Aquilino SA., Diaz-Arnold AM., Haselton DR., Stanford CM., Vargas MA. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part II: core and veneer materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 88:10–5.
Article8.Shah K., Holloway JA., Denry IL. Effect of coloring with various metal oxides on the microstructure, color, and flexural strength of 3Y-TZP. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008. 87:329–37.
Article9.Bhushan S., Pober R., Giodano R. Coloration of partially stabilized zirconia. 83rd General Session & Exhibition of the IADR;Baltimore, MD: 2005. abstract no. 1775.10.Chantikul P., Anstis GR., Lawn BR., Marshall DB. A critical evaluation of indentation techniques for measuring fracture toughness: II Strength method. J Am Ceram Soc. 1981. 64:539–43.
Article11.Yan G., Qiang ZF., Hui H., Yuan LZ., Ying L. Sintering behavior of Y-doped ZrO2 ceramics: the effect of additive rare earth oxides. J Ceram Process Res. 2008. 14:270–6.12.Cales B. Colored zirconia ceramics for dental applications. Bioceramics. 1998. 11:591–4.13.Chiang YM., Birnie III D., Kingery WD. Chapter 2: Defects in ceramics, in physical ceramics: principles for ceramic science and engineering,. Wiley MIT, New York;1997. p. 101–84.14.O'Brien WJ., Groh CL., Boenke KM. One-dimensional color order system for dental shade guides. Dent Mater. 1989. 5:371–4.15.Shim DH., Lee YB., Kim YW., Oh KD., Park HC. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3/t-ZrO2 particulate composites. J Korean Ceram Soc. 1999. 36:734–41.16.Ranjbar K., Rao BT., Mohan TRM. Effect of zirconia allotropes on fracture toughness α -alumina. Am Ceram Soc. 1993. 38:473–84.17.Denry I., Kelly JR. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:299–307.
Article18.Sato K., Yugami H., Hashida T. Effect of rare-earth oxides on fracture properties of ceria ceramics. J Mater Sci. 2004. 39:5765–70.
Article19.Gorman CM., McDevitt WE., Hill RG. Comparison of two heat-pressed all-ceramic dental materials. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:389–95.
Article20.Yilmaz H., Aydin C., Gul BE. Flexural strength and fracture toughness of dental core ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 98:120–8.
Article21.Guazzato M., Albakry M., Ringer SP., Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part I. Pressable and alumina glass-infiltrated ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:441–8.
Article22.Guazzato M., Albakry M., Ringer SP., Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:449–56.
Article23.Wagner WC., Chu TM. Biaxial flexural strength and indentation fracture toughness of three new dental core ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 1996. 76:140–4.
Article24.Piconi C., Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999. 20:1–25.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mechanical behavior and microstructural characterization of different zirconia polycrystals in different thicknesses
- Effect of connector configuration on the fracture load in conventional and translucent zirconia three-unit fixed dental prostheses
- The effects of heat treatment on mechanical properties and metal release from heat-treated orthodontic archwires
- Physico-mechanical properties and prosthodontic applications of Co-Cr dental alloys: a review of the literature
- Analysis of osteogenic potential on 3mol% yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals and two different niobium oxide containing zirconia ceramics