J Korean Med Assoc.
2007 Aug;50(8):725-728. 10.5124/jkma.2007.50.8.725.
Visceral Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Korea. yooyoo1@kornet.net
- KMID: 2184900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2007.50.8.725
Abstract
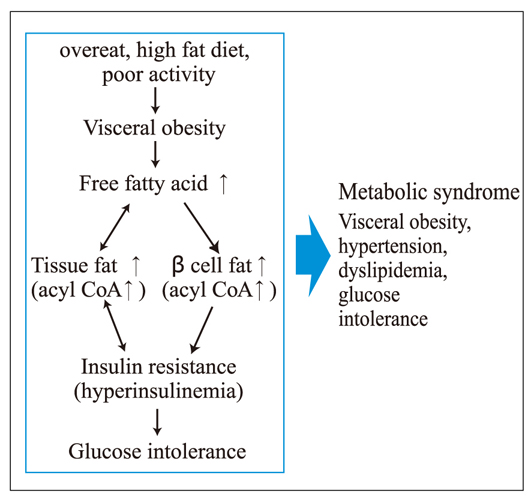
- Multiple lines of evidence support the thesis that visceral adiposity is causally related to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Visceral adipose tissue is biochemically quite distinct from subcutaneous adipose tissue. It has become increasingly evident that the effects of visceral adiposity must be mediated by multiple factors. The release of free fatty acid from visceral adipose tissue in obese individuals has been reported to account for 20% of that delivered to the liver, and it is unlikely that the contribution of visceral fat to the free fatty acid flux in the circulation is the major mechanism of insulin resistance. Adiponectin and other newly discovered adipokines are likely to contribute to attenuate the effects of visceral obesity onto insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance and the metabolic impacts are the consequence of the metabolic effects of the products being released from the adipose tissue rather than an effect of the absolute mass of the fat. Adipose tissue releases free fatty acids and cytokines and modulates the secretion of a large number of metabolically active adipokines. Abdominal circumference is one of indicators for visceral obesity. The abdominal circumference values among Koreans are discussed by active groups.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Consumption of Added Sugars and Lipid Profiles in Korean Population from a Cohort Study
Sang Yeun Kim, Sun Ha Jee
J Lipid Atheroscler. 2015;4(1):17-25. doi: 10.12997/jla.2015.4.1.17.
Reference
-
1. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Metabolic syndrome-pathological molecular biolocy. 2005. Seoul: Euihakmunhwasa;by Matsuzawa. (Korean version).2. Kim JY, Shin HW, Jeong IK, Yoo HJ, et al. Correlation among adiponectin, leptin, ghrelin, insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors according to the degree of obesity. Korean J of Internal Medicine. 2005. 69:631–641.3. Matsuzawa Y. Pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms of visceral fat syndrome. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1997. 13:3–13.4. Raven GM. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988. 37:1595–1607.
Article5. Grundy SM. Hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 83:25–29.
Article6. Miyazaki Y, Mahankali A, Matsuda M, Mahankali S, Hardies J, Cusi K, Mandarino LJ, DeFronzo RA. Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:2784–2791.
Article7. Lee SY, Park HS, Kim DJ, Han JH, Kim MS, Cho GJ, Kim DY, Kwon HS, Kim SR, Lee CB, Oh SJ, Park CY, Yoo HJ. Appro priate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity as main component of the new International Diabetes Federation definition in Korean adults. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 75:72–80. (accepted, 24 April 2006).
Article8. Park HS, Park CY, Oh SW, Yoo HJ. Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults. Obesity Reviews. 2007. (in press).
Article9. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Metabolic syndrome practical guide. 2005. Seoul: Euihakmunhwasa.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of Waist Circumference Measurement Site on Visceral Fat and Metabolic Risk in Youth
- The Accuracy of the Assessment of Visceral Obesity by InBody 4.0 and Waist Circumference
- Impact of Visceral Obesity on the Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome in Metabolically Healthy Normal Weight and Overweight Groups: A Longitudinal Cohort Study in Korea
- Association of Visceral Fat Area Measured by InBody 720 with the Results Measured by CT, DEXA and Anthropometric Measurement
- The Relationship between Abdominal Visceral Fat Area and Regional Subcutaneous Skinfold Thickness in Korean Adults