J Korean Med Assoc.
2005 May;48(5):472-478. 10.5124/jkma.2005.48.5.472.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tingling Sensation on Hands and Feet
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine and Hospital, Korea. kimsh1@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2183553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2005.48.5.472
Abstract
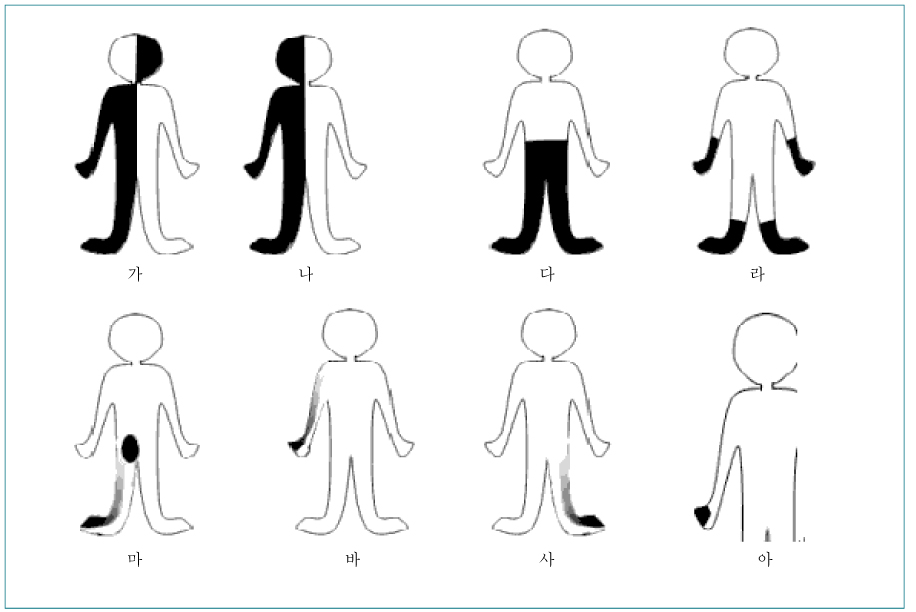
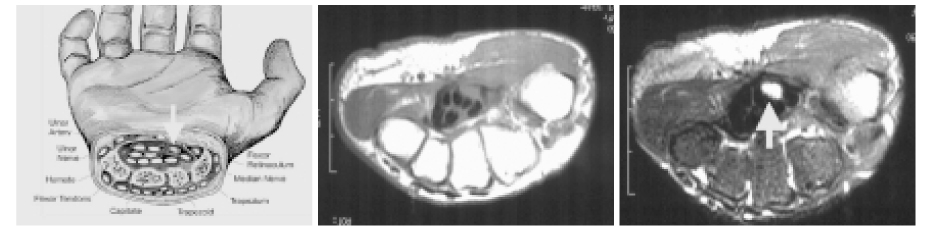
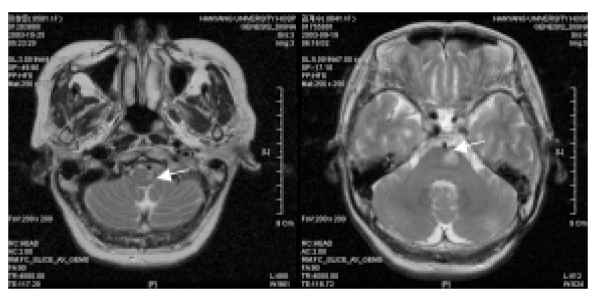
- Tingling Sensation on Hands and Feet is one of common sensory symptoms, which is frequently associated with not only peripheral nerve disorders, including polyneuropathies, entrapment neuropathies(carpal tunnel syndrome or tarsal tunnel syndrome) and radiculopathies, but also stroke or peripheral vascular diseases. Despite numerous conditions causing acroparesthesia, characteristic symptoms and signs of each category can afford to inform the critical differentiating clues like followings glove-stocking paresthesia in polyneuroapthy, dermatomal radiating paresthesia in radiculopathy, sensory level in myelopathy, and crossed paresthesia in brainstem lesion. In this review, diagnostic and therapeutic approach to acroparesthesia is schematically described. In addition, neuropathic pain, a special type of pain or unpleasant feeling caused by partial/complete denervation of sensory nervous systems, as one of common causes of acroparesthesia, will be discussed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Merskey H. Prepared by the IASP subcommittee on taxonomy. Classification of chronic pain syndromes and definition of pain terms. Pain. 1986. 3:S1–S226.2. Bowsher D. Neurogenic pain syndromes and their management. Br Med Bull. 1991. 47:644–666.
Article6. Kim JS. Restricted acral sensory syndorme following minor stroke: further observation with special reference to differential severity of symptoms among individual digits. Stroke. 1994. 25:2497–2502.
Article7. Sacco RL. Wallenbergs lateral medullary syndrome. clinical-magnetic resonance imaging correlation. Arch Neurol. 1993. 50:609–614.8. Schott GD. From thalamic syndrome to central poststroke pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995. 61:560–560.
Article9. Buchthal F. Sensory conduction from digit to palm and from palm to wrist in the carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971. 34:243–252.
Article10. Hunter JC, Gogas KR, Hedley LR, Jacobson LO, Kassotakis L, Fontana DJ, et al. The effect of novel anti-epileptic drugs in rat experimental models of acute and chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997. 324:153–160.
Article11. England JD, Happel LT, Kline DG, Gamboni F, Thouron CL, Liu ZP, Levinson SR. Sodium channel accumulation in humans with painful neuromas. Neurology. 1996. 47:272–276.
Article12. Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ. Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 1999. 353:1959–1964.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tingling Sensation and Difficulty in Daily Living of Clients Treated FOLFOX Chemotherapy after Colon Resection
- A Case of Podophyllum Toxicity with Peripheral Polyneuropathy
- Clinical Evaluation of Diabetic Neuropahty
- Abnormal Nocturnal Sensation of Hands in the Patient with Hyperthyroidism
- The Prevelance of Diagnosis as Raynaud's Disease among the People Complaint of Abnormal Sensation on Hands and Feet