J Clin Neurol.
2015 Oct;11(4):319-330. 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.4.319.
EEG Source Imaging in Partial Epilepsy in Comparison with Presurgical Evaluation and Magnetoencephalography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sbhong@skku.edu
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute (SBRI), Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA.
- 5Center for Biosignals, Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Daejeon, Korea.
- 6Department of Medical Physics, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2179751
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.4.319
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the usefulness of three-dimensional (3D) scalp EEG source imaging (ESI) in partial epilepsy in comparison with the results of presurgical evaluation, magnetoencephalography (MEG), and electrocorticography (ECoG).
METHODS
The epilepsy syndrome of 27 partial epilepsy patients was determined by presurgical evaluations. EEG recordings were made using 70 scalp electrodes, and the 3D coordinates of the electrodes were digitized. ESI images of individual and averaged spikes were analyzed by Curry software with a boundary element method. MEG and ECoG were performed in 23 and 9 patients, respectively.
RESULTS
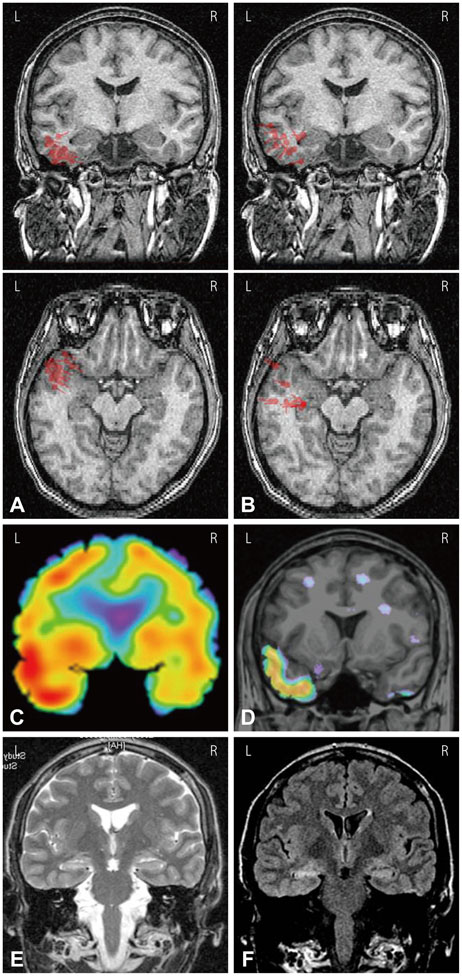
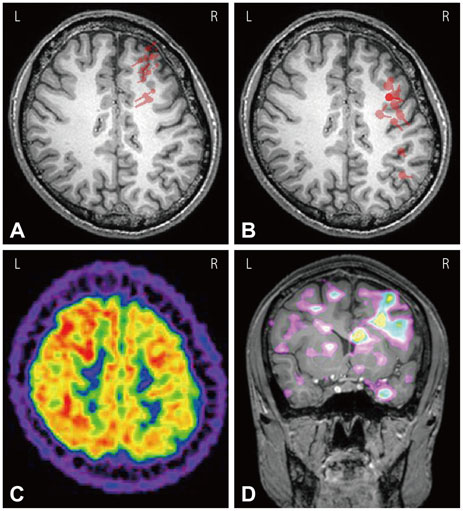
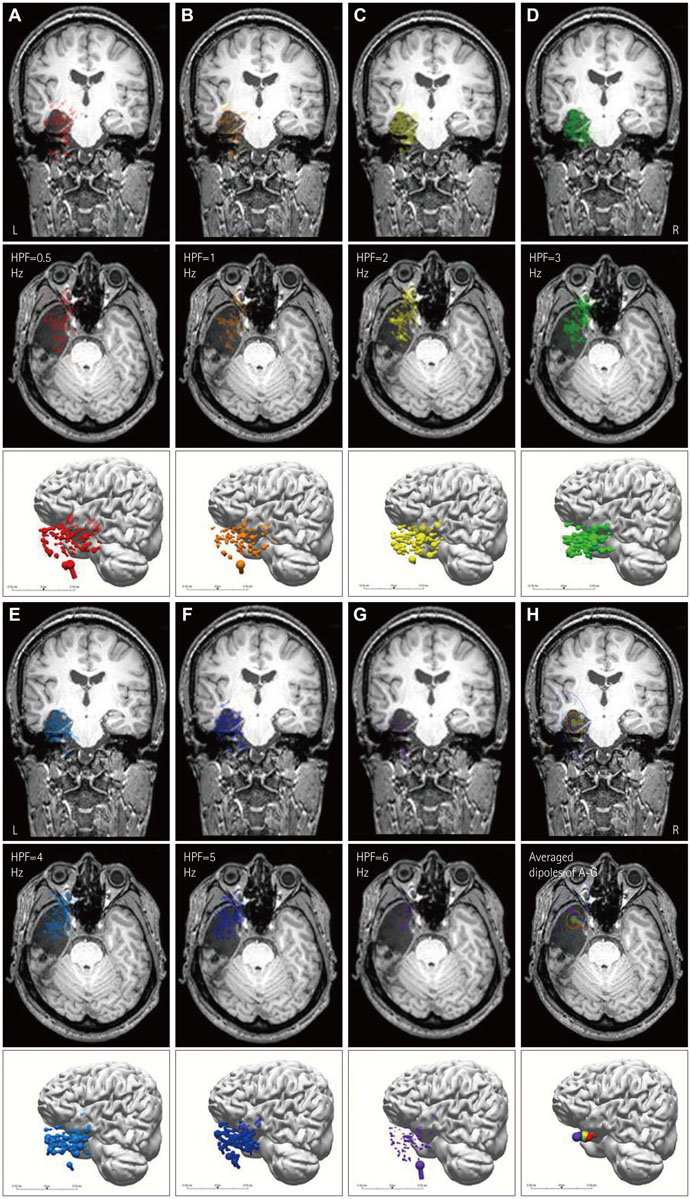
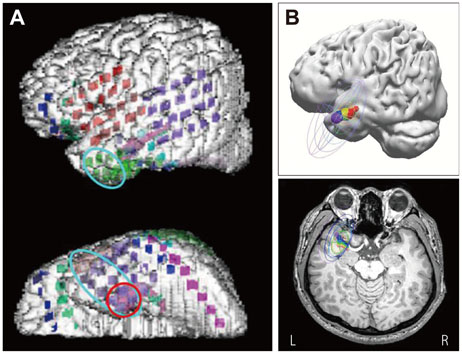
ESI and MEG source imaging (MSI) results were well concordant with the results of presurgical evaluations (in 96.3% and 100% cases for ESI and MSI, respectively) at the lobar level. However, there were no spikes in the MEG recordings of three patients. The ESI results were well concordant with MSI results in 90.0% of cases. Compared to ECoG, the ESI results tended to be localized deeper than the cortex, whereas the MSI results were generally localized on the cortical surface. ESI was well concordant with ECoG in 8 of 9 (88.9%) cases, and MSI was also well concordant with ECoG in 4 of 5 (80.0%) cases. The EEG single dipoles in one patient with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy were tightly clustered with the averaged dipole when a 3 Hz high-pass filter was used.
CONCLUSIONS
The ESI results were well concordant with the results of the presurgical evaluation, MSI, and ECoG. The ESI analysis was found to be useful for localizing the seizure focus and is recommended for the presurgical evaluation of intractable epilepsy patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diekmann V, Becker W, Jürgens R, Grözinger B, Kleiser B, Richter HP, et al. Localisation of epileptic foci with electric, magnetic and combined electromagnetic models. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998; 106:297–313.
Article2. Ding L, Worrell GA, Lagerlund TD, He B. Ictal source analysis: localization and imaging of causal interactions in humans. Neuroimage. 2007; 34:575–586.
Article3. Brodbeck V, Spinelli L, Lascano AM, Pollo C, Schaller K, Vargas MI, et al. Electrical source imaging for presurgical focus localization in epilepsy patients with normal MRI. Epilepsia. 2010; 51:583–591.
Article4. Brodbeck V, Spinelli L, Lascano AM, Wissmeier M, Vargas MI, Vulliemoz S, et al. Electroencephalographic source imaging: a prospective study of 152 operated epileptic patients. Brain. 2011; 134(Pt 10):2887–2897.
Article5. Lantz G, Grave de Peralta R, Spinelli L, Seeck M, Michel CM. Epileptic source localization with high density EEG: how many electrodes are needed? Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:63–69.
Article6. Michel CM, Lantz G, Spinelli L, De Peralta RG, Landis T, Seeck M. 128-channel EEG source imaging in epilepsy: clinical yield and localization precision. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2004; 21:71–83.
Article7. Sperli F, Spinelli L, Seeck M, Kurian M, Michel CM, Lantz G. EEG source imaging in pediatric epilepsy surgery: a new perspective in presurgical workup. Epilepsia. 2006; 47:981–990.
Article8. Wang G, Worrell G, Yang L, Wilke C, He B. Interictal spike analysis of high-density EEG in patients with partial epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011; 122:1098–1105.
Article9. Wennberg R, Cheyne D. EEG source imaging of anterior temporal lobe spikes: validity and reliability. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014; 125:886–902.
Article10. Yamazaki M, Terrill M, Fujimoto A, Yamamoto T, Tucker DM. Integrating dense array EEG in the presurgical evaluation of temporal lobe epilepsy. ISRN Neurol. 2012; 2012:924081.
Article11. Plummer C, Harvey AS, Cook M. EEG source localization in focal epilepsy: where are we now? Epilepsia. 2008; 49:201–218.
Article12. Zumsteg D, Friedman A, Wennberg RA, Wieser HG. Source localization of mesial temporal interictal epileptiform discharges: correlation with intracranial foramen ovale electrode recordings. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 116:2810–2818.
Article13. Ebersole JS, Hawes-Ebersole S. Clinical application of dipole models in the localization of epileptiform activity. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 24:120–129.
Article14. Gavaret M, Trébuchon A, Bartolomei F, Marquis P, McGonigal A, Wendling F, et al. Source localization of scalp-EEG interictal spikes in posterior cortex epilepsies investigated by HR-EEG and SEEG. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:276–289.
Article15. Huppertz HJ, Hoegg S, Sick C, Lücking CH, Zentner J, Schulze-Bonhage A, et al. Cortical current density reconstruction of interictal epileptiform activity in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001; 112:1761–1772.
Article16. He B, Musha T, Okamoto Y, Homma S, Nakajima Y, Sato T. Electric dipole tracing in the brain by means of the boundary element method and its accuracy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1987; 34:406–414.
Article17. Herrendorf G, Steinhoff BJ, Kolle R, Baudewig J, Waberski TD, Buchner H, et al. Dipole-source analysis in a realistic head model in patients with focal epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000; 41:71–80.
Article18. Roth BJ, Ko D, von Albertini-Carletti IR, Scaffidi D, Sato S. Dipole localization in patients with epilepsy using the realistically shaped head model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997; 102:159–166.
Article19. Gavaret M, Badier JM, Marquis P, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P. Electric source imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2004; 21:267–282.
Article20. Merlet I, Gotman J. Reliability of dipole models of epileptic spikes. Clin Neurophysiol. 1999; 110:1013–1028.
Article21. Plummer C, Litewka L, Farish S, Harvey AS, Cook MJ. Clinical utility of current-generation dipole modelling of scalp EEG. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 118:2344–2361.
Article22. Gavaret M, Badier JM, Marquis P, McGonigal A, Bartolomei F, Regis J, et al. Electric source imaging in frontal lobe epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2006; 23:358–370.
Article23. Lantz G, Holub M, Ryding E, Rosén I. Simultaneous intracranial and extracranial recording of interictal epileptiform activity in patients with drug resistant partial epilepsy: patterns of conduction and results from dipole reconstructions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1996; 99:69–78.
Article24. Jin K, Nakasato N, Shamoto H, Kanno A, Itoyama Y, Tominaga T. Neuromagnetic localization of spike sources in perilesional, contralateral mirror, and ipsilateral remote areas in patients with cavernoma. Epilepsia. 2007; 48:2160–2166.
Article25. Knowlton RC, Laxer KD, Aminoff MJ, Roberts TP, Wong ST, Rowley HA. Magnetoencephalography in partial epilepsy: clinical yield and localization accuracy. Ann Neurol. 1997; 42:622–631.
Article26. Nakasato N, Levesque MF, Barth DS, Baumgartner C, Rogers RL, Sutherling WW. Comparisons of MEG, EEG, and ECoG source localization in neocortical partial epilepsy in humans. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1994; 91:171–178.
Article27. Stefan H. Clinical applications of MEG in epilepsy. Brain Topogr. 1993; 5:425–427.
Article28. Scherg M, Bast T, Berg P. Multiple source analysis of interictal spikes: goals, requirements, and clinical value. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1999; 16:214–224.
Article29. Ebersole JS, Ebersole SM. Combining MEG and EEG source modeling in epilepsy evaluations. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2010; 27:360–371.
Article30. Fuchs M, Wagner M, Kastner J. Confidence limits of dipole source reconstruction results. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004; 115:1442–1451.
Article31. Rose S, Ebersole JS. Advances in spike localization with EEG dipole modeling. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2009; 40:281–287.
Article32. Ebersole JS. EEG dipole modeling in complex partial epilepsy. Brain Topogr. 1991; 4:113–123.
Article33. Rampp S, Stefan H. On the opposition of EEG and MEG. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 118:1658–1659.
Article