J Clin Neurol.
2015 Jan;11(1):42-47. 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.1.42.
Whole-Brain Diffusion-Tensor Changes in Parkinsonian Patients with Impulse Control Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. jaes@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University-Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University-Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. brain@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2179571
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.1.42
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the changes in diffusion-tensor images associated with medication-related impulse control disorder (ICD) in Parkinson's disease (PD) patients undergoing chronic dopamine-replacement therapy.
METHODS
Nineteen PD patients, comprising 10 with ICD (PD-ICD) and 9 without ICD (PD-nonICD), and 18 age-matched healthy controls (HCs) with no cognitive or other psychiatric disorders were analyzed. All subjects underwent 3-T magnetic resonance diffusion-tensor imaging. For all PD patients, clinical data on PD duration, antiparkinsonian medication dosages, Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale and Mini-Mental State Examination were collected. Whole-brain voxel-based measures of fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) were analyzed.
RESULTS
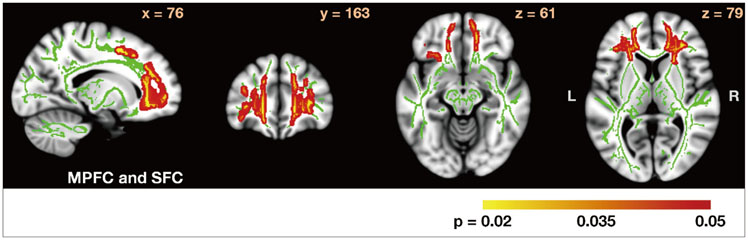
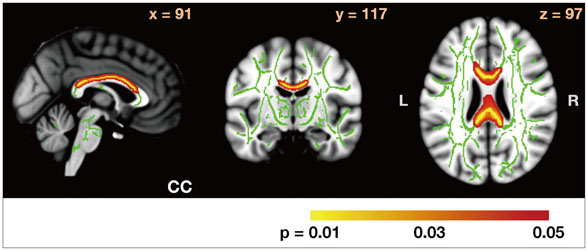
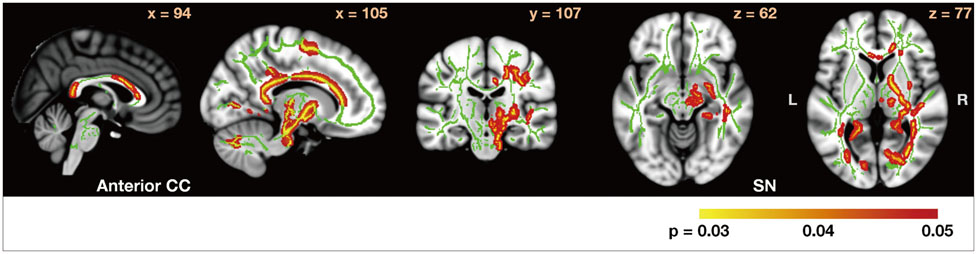
In comparison with HCs, the PD-nonICD subjects had low FA at the bilateral orbitofrontal areas. While the PD-ICD subjects exhibited no such difference, their FA was significantly elevated at the anterior corpus callosum. Analysis of FA between the two PD groups revealed that FA in the anterior corpus callosum, right internal capsule posterior limbs, right posterior cingulum, and right thalamic radiations were significantly higher (corrected p<0.05) in the PD-ICD than in the PD-nonICD patients. MD did not differ between the PD-ICD and PD-nonICD groups in any brain regions.
CONCLUSIONS
The PD-ICD patients appear to have relatively preserved white-matter integrity in the regions involved in reward-related behaviors compared to PD-nonICD patients. Further investigation is required to determine whether the difference in FA between PD-ICD and PD-nonICD patients reflects microstructural differences in the pathological progression of PD or is secondary to ICD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weintraub D, Koester J, Potenza MN, Siderowf AD, Stacy M, Voon V, et al. Impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease: a cross-sectional study of 3090 patients. Arch Neurol. 2010; 67:589–595.2. Lee JY, Kim JM, Kim JW, Cho J, Lee WY, Kim HJ, et al. Association between the dose of dopaminergic medication and the behavioral disturbances in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2010; 16:202–207.
Article3. Cilia R, Siri C, Marotta G, Isaias IU, De Gaspari D, Canesi M, et al. Functional abnormalities underlying pathological gambling in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2008; 65:1604–1611.
Article4. Joutsa J, Martikainen K, Niemelä S, Johansson J, Forsback S, Rinne JO, et al. Increased medial orbitofrontal [18F]fluorodopa uptake in Parkinsonian impulse control disorders. Mov Disord. 2012; 27:778–782.
Article5. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage. 2006; 31:1487–1505.
Article6. Lawrence AD, Evans AH, Lees AJ. Compulsive use of dopamine replacement therapy in Parkinson's disease: reward systems gone awry? Lancet Neurol. 2003; 2:595–604.
Article7. Ouchi Y, Yoshikawa E, Okada H, Futatsubashi M, Sekine Y, Iyo M, et al. Alterations in binding site density of dopamine transporter in the striatum, orbitofrontal cortex, and amygdala in early Parkinson's disease: compartment analysis for beta-CFT binding with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1999; 45:601–610.
Article8. Reuter J, Raedler T, Rose M, Hand I, Gläscher J, Büchel C. Pathological gambling is linked to reduced activation of the mesolimbic reward system. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 8:147–148.
Article9. Thiel A, Hilker R, Kessler J, Habedank B, Herholz K, Heiss WD. Activation of basal ganglia loops in idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a PET study. J Neural Transm. 2003; 110:1289–1301.
Article10. Tzschentke TM. The medial prefrontal cortex as a part of the brain reward system. Amino Acids. 2000; 19:211–219.
Article11. Moeller FG, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Kramer LA, Dougherty DM, Santos RM, et al. Reduced anterior corpus callosum white matter integrity is related to increased impulsivity and reduced discriminability in cocaine-dependent subjects: diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005; 30:610–617.
Article12. Grant JE, Brewer JA, Potenza MN. The neurobiology of substance and behavioral addictions. CNS Spectr. 2006; 11:924–930.
Article13. Yoo SY, Jang JH, Shin YW, Kim DJ, Park HJ, Moon WJ, et al. White matter abnormalities in drug-naïve patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a diffusion tensor study before and after citalopram treatment. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2007; 116:211–219.
Article14. Li F, Huang X, Yang Y, Li B, Wu Q, Zhang T, et al. Microstructural brain abnormalities in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: diffusion-tensor MR imaging study at 3.0 T. Radiology. 2011; 260:216–223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reversible Psychosis Caused by Disconnection of the Limbic System: Clinical Reasoning Using Diffusion Tensor Tractography
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Exploring the Motor Networks and Clinical Applications
- Analysis of Diffuse Axonal Injury Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
- Principle and Experiments in Diffusion Tensor Imaging
- Diffusion Tensor Tractography of a Gliomatosis Cerebri: A Case Report