J Breast Cancer.
2014 Dec;17(4):314-322. 10.4048/jbc.2014.17.4.314.
Anticancer Activity of Cobra Venom Polypeptide, Cytotoxin-II, against Human Breast Adenocarcinoma Cell Line (MCF-7) via the Induction of Apoptosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Toxicology, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences School of Pharmacy, Tehran, Iran. k.najafabady@sbmu.ac.ir
- 2Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute, Karaj, Iran.
- 4Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences School of Pharmacy, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 2176121
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2014.17.4.314
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Breast cancer is a significant health problem worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all cancer diagnoses in women. Current strategies for breast cancer treatment are not fully effective, and there is substantial interest in the identification of novel anticancer agents especially from natural products including toxins. Cytotoxins are polypeptides found in the venom of cobras and have various physiological effects. In the present study, the anticancer potential of cytotoxin-II against the human breast adenocarcinoma cell line (MCF-7) was investigated.
METHODS
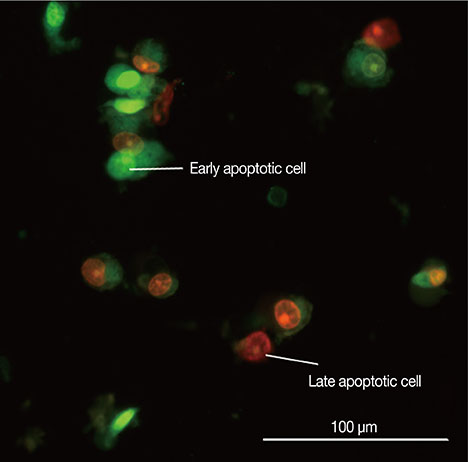
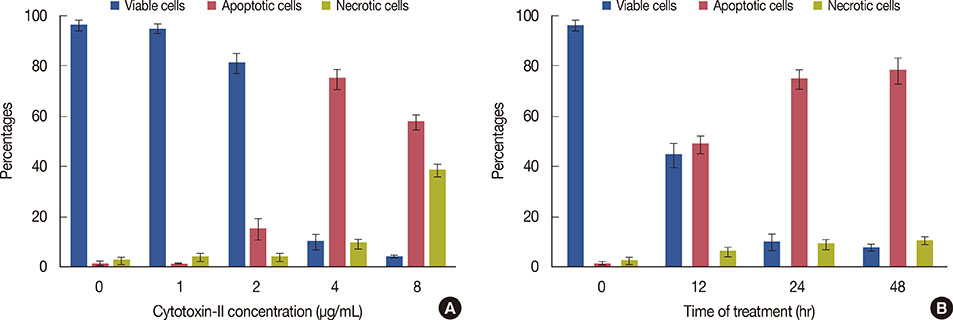
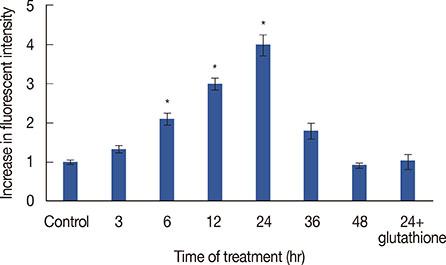
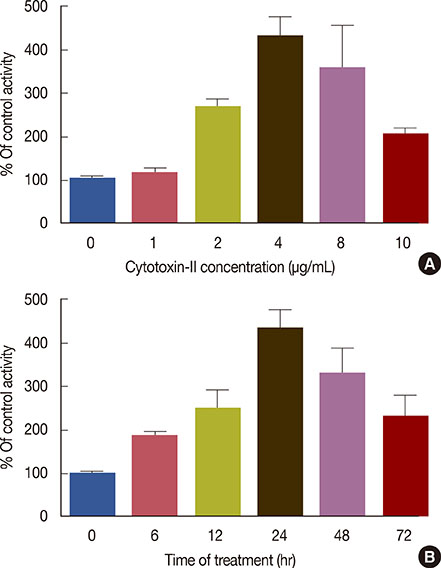
The cytotoxic effects of cytotoxin-II were determined by morphological analysis and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. The mode and mechanism of cell death were investigated via acridine orange/ethidium bromide (AO/EtBr) double staining, flow cytometric analysis of cell death, detection of mitochondrial membrane potential, measurement of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), annexin V/propidium iodide staining, and caspase-9 activity assays.
RESULTS
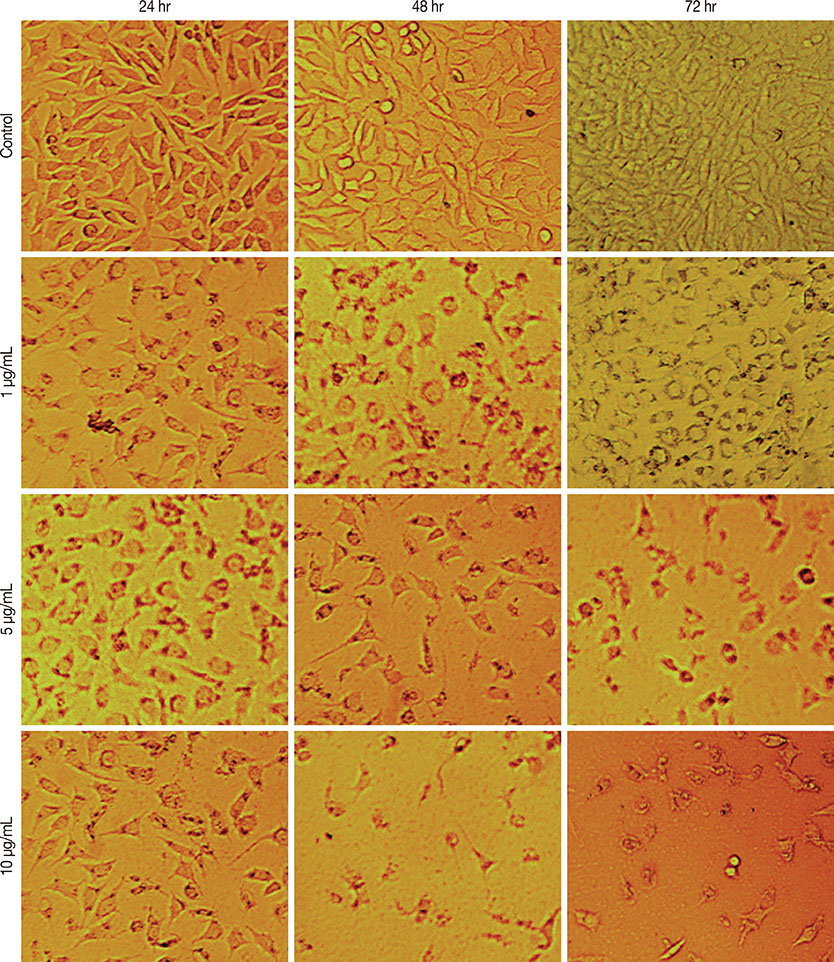
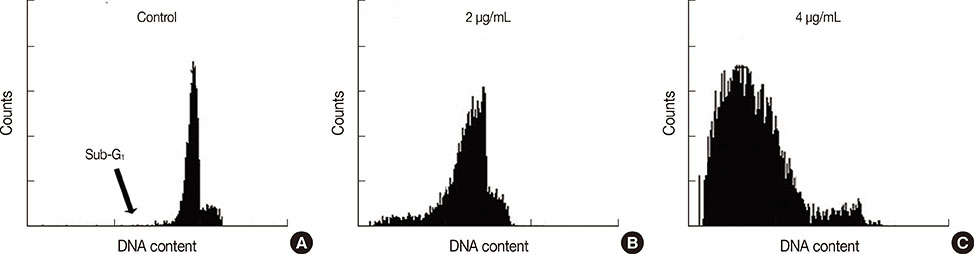
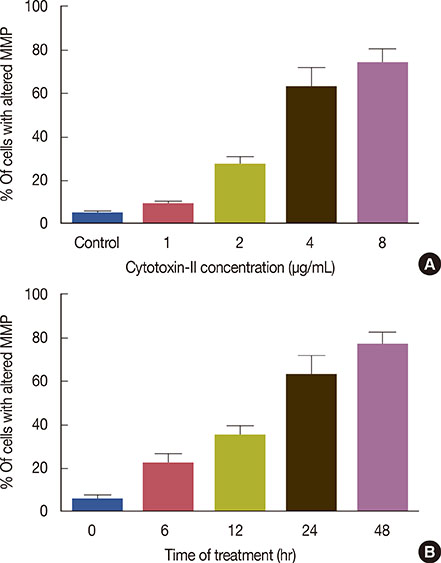
The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of cytotoxin-II in MCF-7 cells was 4.18+/-1.23 microg/mL, while the value for cisplatin was approximately 28.02+/-1.87 microg/mL. Morphological analysis and AO/EtBr double staining showed typical manifestations of apoptotic cell death (in doses lower than 8 microg/mL). Dose- and time-dependent ROS generation, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, caspase-9 activation, and cell cycle arrest were observed in their respective tests.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, cytotoxin-II has potent anticancer effects in the MCF-7 cell line, which are induced via the intrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Based on these findings, cytotoxin-II is a suitable choice for breast cancer treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma*
Antineoplastic Agents
Apoptosis*
Biological Products
Breast Neoplasms
Breast*
Caspase 9
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Cell Death
Cell Line*
Cisplatin
Cobra Venoms*
Cytotoxins
Diagnosis
Elapidae
Female
Humans
MCF-7 Cells
Membrane Potential, Mitochondrial
Peptides
Reactive Oxygen Species
Snakes
Venoms
Antineoplastic Agents
Biological Products
Caspase 9
Cisplatin
Cobra Venoms
Cytotoxins
Peptides
Reactive Oxygen Species
Venoms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Patel NM, Nozaki S, Shortle NH, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Newton TR, Rice S, et al. Paclitaxel sensitivity of breast cancer cells with constitutively active NF-kappaB is enhanced by IkappaBalpha super-repressor and parthenolide. Oncogene. 2000; 19:4159–4169.
Article3. Bruckheimer EM, Kyprianou N. Apoptosis in prostate carcinogenesis: a growth regulator and a therapeutic target. Cell Tissue Res. 2000; 301:153–162.4. Sun SY, Hail N Jr, Lotan R. Apoptosis as a novel target for cancer chemoprevention. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004; 96:662–672.
Article5. Yang XH, Sladek TL, Liu X, Butler BR, Froelich CJ, Thor AD. Reconstitution of caspase 3 sensitizes MCF-7 breast cancer cells to doxorubicin- and etoposide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:348–354.6. Calmette A, Saenz A, Costil L. Effects du venin de cobra sur les greffes cancereuses et sur le cancer spontane (adeno-carcinome) de la souris. C R Acad Sci. 1933; 197:205–210.7. D'Suze G, Rosales A, Salazar V, Sevcik C. Apoptogenic peptides from Tityus discrepans scorpion venom acting against the SKBR3 breast cancer cell line. Toxicon. 2010; 56:1497–1505.8. Deshane J, Garner CC, Sontheimer H. Chlorotoxin inhibits glioma cell invasion via matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:4135–4144.
Article9. Gupta SD, Gomes A, Debnath A, Saha A, Gomes A. Apoptosis induction in human leukemic cells by a novel protein Bengalin, isolated from Indian black scorpion venom: through mitochondrial pathway and inhibition of heat shock proteins. Chem Biol Interact. 2010; 183:293–303.
Article10. Feofanov AV, Sharonov GV, Dubinnyi MA, Astapova MV, Kudelina IA, Dubovskii PV, et al. Comparative study of structure and activity of cytotoxins from venom of the cobras Naja oxiana, Naja kaouthia, and Naja haje. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2004; 69:1148–1157.
Article11. Konshina AG, Dubovskii PV, Efremov RG. Structure and dynamics of cardiotoxins. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012; 13:570–584.
Article12. Su SH, Su SJ, Lin SR, Chang KL. Cardiotoxin-III selectively enhances activation-induced apoptosis of human CD8+ T lymphocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2003; 193:97–105.
Article13. Dementieva DV, Bocharov EV, Arseniev AS. Two forms of cytotoxin II (cardiotoxin) from Naja naja oxiana in aqueous solution: spatial structures with tightly bound water molecules. Eur J Biochem. 1999; 263:152–162.
Article14. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193:265–275.
Article15. Ho K, Yazan LS, Ismail N, Ismail M. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009; 33:155–160.
Article16. Riccardi C, Nicoletti I. Analysis of apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat Protoc. 2006; 1:1458–1461.
Article17. Libério MS, Joanitti GA, Azevedo RB, Cilli EM, Zanotta LC, Nascimento AC, et al. Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic activity of pentadactylin isolated from Leptodactylus labyrinthicus on melanoma cells. Amino Acids. 2011; 40:51–59.
Article18. Zhang L, Cui L. A cytotoxin isolated from Agkistrodon acutus snake venom induces apoptosis via Fas pathway in A549 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2007; 21:1095–1103.
Article19. Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR. Detection of apoptosis by annexin V labeling. Methods Enzymol. 2000; 322:15–18.
Article20. Park MH, Choi MS, Kwak DH, Oh KW, Yoon do Y, Han SB, et al. Anticancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-kappaB. Prostate. 2011; 71:801–812.
Article21. Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004; 116:205–219.22. Zhang L, Wei LJ. ACTX-8, a cytotoxic L-amino acid oxidase isolated from Agkistrodon acutus snake venom, induces apoptosis in Hela cervical cancer cells. Life Sci. 2007; 80:1189–1197.
Article23. Hayashi MA, Nascimento FD, Kerkis A, Oliveira V, Oliveira EB, Pereira A, et al. Cytotoxic effects of crotamine are mediated through lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Toxicon. 2008; 52:508–517.
Article24. Feofanov AV, Sharonov GV, Astapova MV, Rodionov DI, Utkin YN, Arseniev AS. Cancer cell injury by cytotoxins from cobra venom is mediated through lysosomal damage. Biochem J. 2005; 390(Pt 1):11–18.
Article25. Turk B, Stoka V. Protease signalling in cell death: caspases versus cysteine cathepsins. FEBS Lett. 2007; 581:2761–2767.
Article26. Orrenius S, Nicotera P, Zhivotovsky B. Cell death mechanisms and their implications in toxicology. Toxicol Sci. 2011; 119:3–19.
Article27. Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis. 2000; 5:415–418.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Apoptotic Effects of 6-Gingerol in Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Regulatory Role of Autophagy in Globular Adiponectin-Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Cells
- Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Two Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines by Dieckol Isolated from Ecklonia cava
- Effects of retinoic acid isomers on apoptosis and enzymatic antioxidant system in human breast cancer cells
- Imidazole Antifungal Drugs Inhibit the Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Human Breast Cancer Cells