Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cohort Studies in Korea: Present and Future
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jpim0911@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- KMID: 2174464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.3.213
Abstract
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is defined as a chronic and relapsing inflammatory disorder of the intestine. Intestinal inflammation in IBD has been proposed to be attributable to the interplay between microbial, genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. The incidence and prevalence rates of IBD are rapidly increasing apparently in other parts of the world, with dramatic increases especially in East Asia. Generally, cohort studies are useful for estimating the incidence, prevalence, natural course, prognosis, and risk factors of diseases. In particular, cohort studies performed in Western countries have well described the prevalence, risk factors, and natural course of IBD and investigated its genetic pathophysiology. However, the outcomes of IBD cohort studies performed in Korea are not as persuasive as those of Western studies because of the relatively low prevalence of IBD and short follow-up periods of the cohorts in Korea. Despite this critical limitation, members of the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases have demonstrated outstanding results. Some unique features of IBD patients in Korea are well demonstrated, such as thiopurine-induced leukopenia or risks of opportunistic tuberculosis infection in patients receiving tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. In this review, the present authors summarized the key points of the results of the cohort studies performed in Korea and explored future perspectives.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Dermatologic Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Hyun Yi Suh, Woo Jin Lee, Soo-Young Na
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(5):285-293. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.5.285.Fusobacterium Isolates Recovered From Colonic Biopsies of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients in Korea
Yangsoon Lee, Chang Soo Eun, A Reum Lee, Chan Hyuk Park, Dong Soo Han
Ann Lab Med. 2016;36(4):387-389. doi: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.4.387.A new opportunity for innovative inflammatory bowel disease research: the moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis in Korea (MOSAIK) cohort study
Chang Kyun Lee, Kang-Moon Lee, Dong Il Park, Sung-Ae Jung, Yoon Tae Jeen, Young Sook Park, Hyo Jong Kim
Intest Res. 2019;17(1):1-5. doi: 10.5217/ir.2019.00005.Impact of inflammatory bowel disease on daily life: an online survey by the Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases
Young Sun Kim, Sung-Ae Jung, Kang-Moon Lee, Soo Jung Park, Tae Oh Kim, Chang Hwan Choi, Hyun Gun Kim, Won Moon, Chang Mo Moon, Hye Kyoung Song, Soo-Young Na, Suk-Kyun Yang,
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):338-344. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.338.Ophthalmologic manifestations in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
Hye Jin Lee, Hyun Joo Song, Jin Ho Jeong, Heung Up Kim, Sun-Jin Boo, Soo-Young Na
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):380-387. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.380.
Reference
-
1. Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011; 474:298–306. PMID: 21677746.
Article2. Burisch J, Pedersen N, Cukovic-Cavka S, et al. Environmental factors in a population-based inception cohort of inflammatory bowel disease patients in Europe-an ECCO-EpiCom study. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:607–616. PMID: 24315795.
Article3. Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:46–54. PMID: 22001864.
Article4. Kim ES, Kim WH. Inflammatory bowel disease in Korea: epidemiological, genomic, clinical, and therapeutic characteristics. Gut Liver. 2010; 4:1–14. PMID: 20479907.
Article5. Lee KM, Lee JM. Crohn's disease in Korea: past, present, and future. Korean J Intern Med. 2014; 29:558–570. PMID: 25228829.
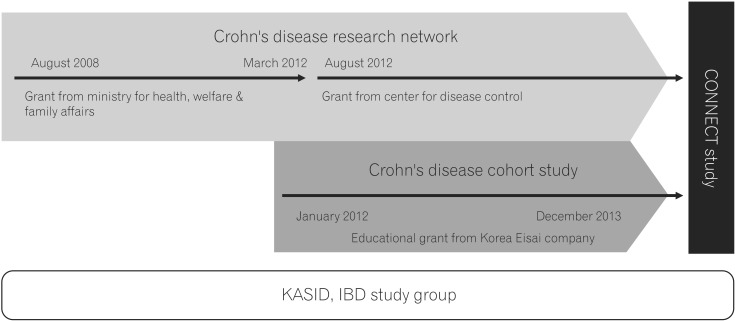
Article6. Cheon JH, Kim YS, Ye BD, et al. Crohn's Disease Clinical Network and Cohort (CONNECT) Study: the first step toward nationwide multicenter research of Crohn's disease in Korea. Intest Res. 2014; 12:173–175. PMID: 25349589.
Article7. Shin DH, Sinn DH, Kim YH, et al. Increasing incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among young men in Korea between 2003 and 2008. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:1154–1159. PMID: 20844953.
Article8. Thia KT, Loftus EV Jr, Sandborn WJ, Yang SK. An update on the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:3167–3182. PMID: 19086963.
Article9. Park SJ, Kim WH, Cheon JH. Clinical characteristics and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a comparison of Eastern and Western perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:11525–11537. PMID: 25206259.
Article10. Ali RA. The positive influences of increasing age at diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease on disease prognostication in asian perspective. Intest Res. 2015; 13:4–5. PMID: 25691837.
Article11. Kim JH, Cheon JH, Kim WH. The frequency and the course of the adverse effects of azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine treatment in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:291–297. PMID: 18516013.12. Lim SM, Nam CM, Kim YN, et al. The effect of the menstrual cycle on inflammatory bowel disease: a prospective study. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:51–57. PMID: 23423645.
Article13. Jung YS, Song CS, Kim ER, et al. Seasonal variation in months of birth and symptom flares in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:661–667. PMID: 24312706.
Article14. Yang SK, Hong WS, Min YI, et al. Incidence and prevalence of ulcerative colitis in the Songpa-Kangdong District, Seoul, Korea,1986-1997. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000; 15:1037–1042. PMID: 11059934.
Article15. Yang SK, Yun S, Kim JH, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986-2005: a KASID study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:542–549. PMID: 17941073.
Article16. Park SH, Kim YM, Yang SK, et al. Clinical features and natural history of ulcerative colitis in Korea. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:278–283. PMID: 17206722.
Article17. Park SK, Ye BD, Yang SK, et al. Clinical features and course of ulcerative colitis diagnosed in asymptomatic subjects. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:1254–1260. PMID: 24662395.
Article18. Yao T, Matsui T, Hiwatashi N. Crohn's disease in Japan: diagnostic criteria and epidemiology. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43:S85–S93. PMID: 11052483.19. Bernstein CN, Wajda A, Svenson LW, et al. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in Canada: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1559–1568. PMID: 16863561.
Article20. Park SH, Yang SK, Park SK, et al. Long-term prognosis of Crohn's disease and its temporal change between 1981 and 2012: a hospital-based cohort study from Korea. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014; 20:488–494. PMID: 24412992.
Article21. Park SK, Yang SK, Park SH, et al. Long-term prognosis of the jejunal involvement of Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013; 47:400–408. PMID: 23269310.
Article22. Ye BD, Yang SK, Cho YK, et al. Clinical features and long-term prognosis of Crohn's disease in Korea. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010; 45:1178–1185. PMID: 20560811.
Article23. Park SC, Jeen YT. Current and emerging biologics for ulcerative colitis. Gut Liver. 2015; 9:18–27. PMID: 25547087.
Article24. Seo HI, Park DI, Kim TO, et al. The effect of infliximab on patients with ulcerative colitis in Korea. Intest Res. 2014; 12:214–220. PMID: 25349595.
Article25. Chung KB, Lee EY, Im JP, Han SK, Yim JJ. Clinical characteristics and treatment responses of patients who developed tuberculosis following use of a tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor. Korean J Intern Med. 2013; 28:174–179. PMID: 23525649.
Article26. Shim TS. Diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases due to initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Intest Res. 2014; 12:12–19. PMID: 25349559.
Article27. Byun JM, Lee CK, Rhee SY, et al. Risks for opportunistic tuberculosis infection in a cohort of 873 patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving a tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50:312–320. PMID: 25581784.
Article28. Zhiqin W, Palaniappan S, Raja Ali RA. Inflammatory bowel disease-related colorectal cancer in the Asia-Pacific region: past, present, and future. Intest Res. 2014; 12:194–204. PMID: 25349593.
Article29. Kim BJ, Yang SK, Kim JS, et al. Trends of ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer in Korea: A KASID study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:667–671. PMID: 19378391.
Article30. Lee HS, Park SH, Yang SK, et al. The risk of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: a hospital-based cohort study from Korea. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50:188–196. PMID: 25515241.
Article31. Kim JH, Cheon JH, Hong SS, et al. Influences of thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and activity on thiopurine-induced leukopenia in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a retrospective cohort study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:e242–e248. PMID: 20308917.32. Yang SK, Hong M, Baek J, et al. A common missense variant in NUDT15 confers susceptibility to thiopurine-induced leukopenia. Nat Genet. 2014; 46:1017–1020. PMID: 25108385.
Article33. Park SK, Ye BD, Lee C, et al. Risk and clinical characteristics of lymphoma in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: a multicenter study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015; 49:e11–e16. PMID: 24705089.34. Liu JZ, Anderson CA. Genetic studies of Crohn's disease: past, present and future. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014; 28:373–386. PMID: 24913378.
Article35. Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:596–604. PMID: 17435756.36. Yang DH, Yang SK, Song K, et al. TNFSF15 is an independent predictor for the development of Crohn's disease-related complications in Koreans. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:1315–1326. PMID: 24835165.
Article37. Yang SK, Hong M, Zhao W, et al. Genome-wide association study of Crohn's disease in Koreans revealed three new susceptibility loci and common attributes of genetic susceptibility across ethnic populations. Gut. 2014; 63:80–87. PMID: 23850713.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Systematic Review of Recent Lipidomics Approaches Toward Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Artificial intelligence in inflammatory bowel disease: implications for clinical practice and future directions
- Optimization of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cohort Studies in Asia
- Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease: a nationwide population‑based cohort study
- Abdominal Pain over 6 Months