Intest Res.
2014 Jan;12(1):66-69. 10.5217/ir.2014.12.1.66.
Refractory Duodenal Crohn's Disease Successfully Treated with Infliximab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. pys1109@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2174340
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.1.66
Abstract
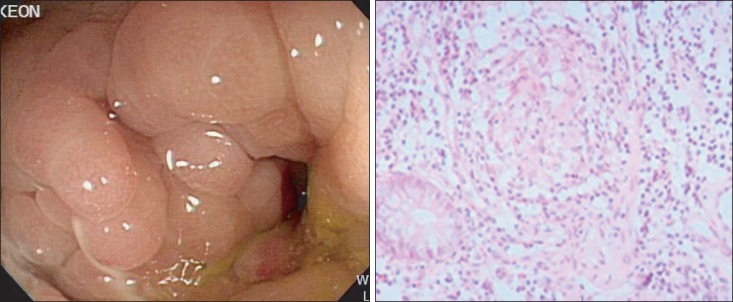
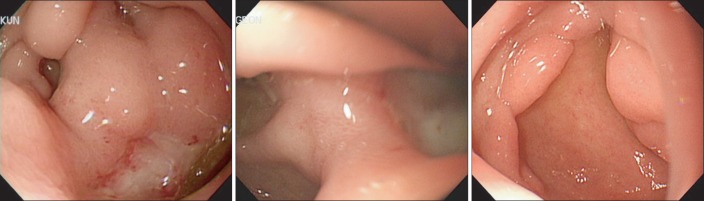
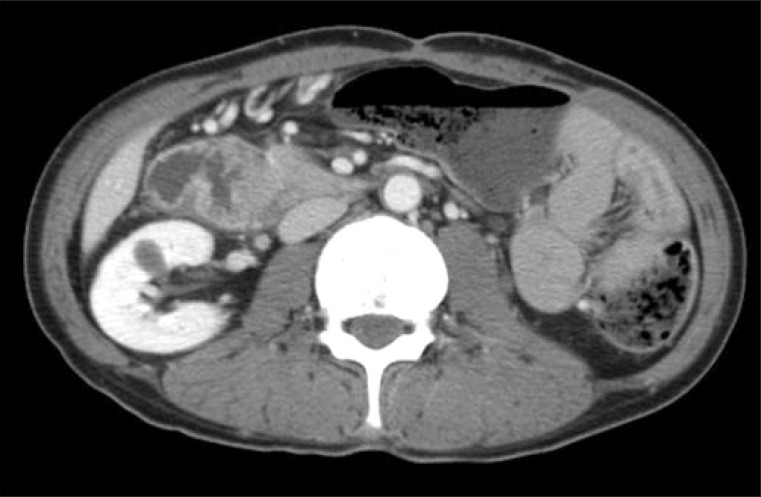
- Crohn's disease (CD) may involve any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. Approximately >90% of cases occur in the small bowel and colon. Upper gastrointestinal involvement, especially duodenal manifestation, is relatively rare. Therefore, adequate medical treatment for duodenal CD has not yet been established. We report a case of CD with duodenal involvement. A 46-year-old man with Crohn's ileocolitis presented to our hospital with right upper quadrant pain. An endoscopy showed a deep excavated ulcer with deformity at the duodenal bulb, and he was initially treated with azathioprine (1 mg/kg), Pentasa (3.0 g/day), and a proton pump inhibitor for 1 year. However, the deep ulcer did not heal. Therefore, infliximab infusion therapy was initiated, and the duodenal lesion completely resolved on follow-up esophagogastroduodenoscopy. We report a case of duodenal CD that completely resolved following infliximab infusion, with a review of the literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Targan SR, Hanauer SB, van Deventer SJ, et al. Crohn's Disease cA2 Study Group. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:1029–1035. PMID: 9321530.
Article2. Kimmins MH, Billingham RP. Duodenal Crohn's disease. Tech Coloproctol. 2001; 5:9–12. PMID: 11793253.
Article3. Tursi A. Duodenal Crohn's disease successfully treated with adalimumab. Endoscopy. 2011; 43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E22. PMID: 21271523.
Article4. Dignass A, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, et al. The second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn's disease: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2010; 4:28–62. PMID: 21122489.
Article5. Gschwantler M, Kogelbauer G, Klose W, Bibus B, Tscholakoff D, Weiss W. The pancreas as a site of granulomatous inflammation in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:1246–1249. PMID: 7698591.
Article6. Moribata K, Kato J, Iimura S, et al. Mucosal healing of esophageal involvement of Crohn's disease with granulocyte/monocyte adsorption. J Clin Apher. 2011; 26:225–227. PMID: 21786316.
Article7. Nugent FW, Richmond M, Park SK. Crohn's disease of the duodenum. Gut. 1977; 18:115–120. PMID: 856671.8. Ando T, Nobata K, Watanabe O, et al. Abnormalities in the upper gastrointestinal tract in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammopharmacology. 2007; 15:101–104. PMID: 17464554.
Article9. Alcantara M, Rodriguez R, Potenciano JL, Carrobles JL, Munoz C, Gomez R. Endoscopic and bioptic findings in the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients with Crohn's disease. Endoscopy. 1993; 25:282–286. PMID: 8330547.
Article10. Nugent FW, Roy MA. Duodenal Crohn's disease: an analysis of 89 cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989; 84:249–254. PMID: 2919581.11. Knapp AB, Mirsky FJ, Dillon EH, Korelitz BI. Successful infliximab therapy for a duodenal stricture caused by Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005; 11:1123–1125. PMID: 16306777.
Article12. Gonzalez M, Collaud S, Gervaz P, Frossard JL, Morel P. Surgical treatment of duodenal stenosis in Crohn's disease. Ann Chir. 2006; 131:636–638. PMID: 16836971.13. Odashima M, Otaka M, Jin M, et al. Successful treatment of refractory duodenal Crohn's disease with infliximab. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:31–32. PMID: 17171444.
Article14. Present DH, Rutgeerts P, Targan S, et al. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:1398–1405. PMID: 10228190.
Article15. Ferrante M, D'Haens G, Dewit O, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in refractory pouchitis and Crohn's disease-related complications of the pouch: a Belgian case series. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010; 16:243–249. PMID: 19637335.
Article16. Pajares JA, Hernandez L, Menchen P, Menchen L. Duodenopancreatic fistula complicating upper gastrointestinal Crohn's disease: successful treatment with infliximab. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:1863–1864. PMID: 19436276.
Article17. Kawachiya T, Hara J, Hirata N, Mashimo M, Arakawa T. Successful treatment of duodenal Crohn disease with infliximab: report of 3 cases. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2010; 107:1933–1940. PMID: 21139362.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Infliximab in the Treatment of Refractory Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Complication
- Factors Affecting Surgical Treatment With Infliximab Therapy in Perianal Fistula With Crohn Disease
- A Case of Infliximab-induced Psoriasis in Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- A Pityrosporum Fungal Infection Following Infliximab Therapy in a Crohn's Disease Patient
- Recent Trends of Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease