Diabetes Metab J.
2015 Dec;39(6):481-488. 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.481.
Insulin Initiation in Insulin-Naive Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients Inadequately Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Drugs in Real-World Practice: The Modality of Insulin Treatment Evaluation Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. injkim@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan. Korea.
- 3Kim Yong Ki Internal Medicine Clinic, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2174000
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.481
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The Modality of Insulin Treatment Evaluation (MOTIV) study was performed to provide real-world data concerning insulin initiation in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with inadequate glycemic control with oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs).
METHODS
This multicenter, non-interventional, prospective, observational study enrolled T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] > or =7.0%) who had been on OHAs for > or =3 months and were already decided to introduce basal insulin by their physician prior to the start of the study. All treatment decisions were at the physician's discretion to reflect real-world practice.
RESULTS
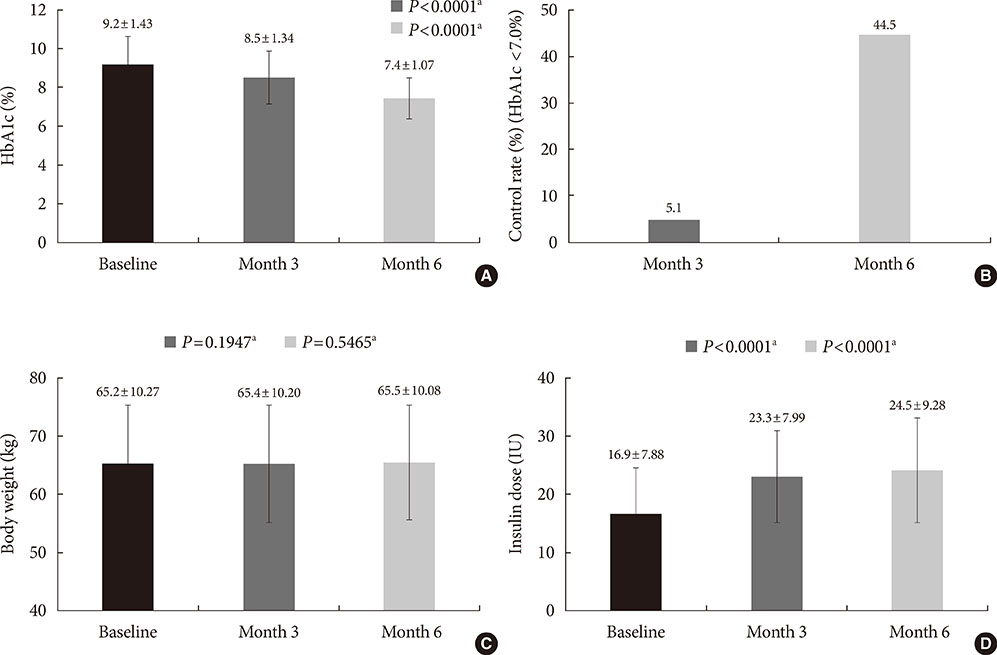
A total of 9,196 patients were enrolled, and 8,636 patients were included in the analysis (mean duration of diabetes, 8.9 years; mean HbA1c, 9.2%). Basal insulin plus one OHA was the most frequently (51.0%) used regimen. After 6 months of basal insulin treatment, HbA1c decreased to 7.4% and 44.5% of patients reached HbA1c <7%. Body weight increased from 65.2 kg to 65.5 kg, which was not significant. Meanwhile, there was significant increase in the mean daily insulin dose from 16.9 IU at baseline to 24.5 IU at month 6 (P<0.001). Overall, 17.6% of patients experienced at least one hypoglycemic event.
CONCLUSION
In a real-world setting, the initiation of basal insulin is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option in Korean patients with T2DM who are failing to meet targets with OHA therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Therapeutic Effect of Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Have Insulin Limitations
Won Sang Yoo, Do Hee Kim, Hee Jin Kim, Hyun Kyung Chung
J Korean Diabetes. 2019;20(2):117-126. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2019.20.2.117.
Reference
-
1. Jeon JY, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Kim CS, Song KH, Won JC, Lim S, Choi SH, Jang MJ, Kim Y, Oh K, Kim DJ, Cha BY. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes according to fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c. Diabetes Metab J. 2013; 37:349–357.2. Asian-Pacific Type 2 Diabetes Policy Group. Western Pacific Region of IDF: Type 2 diabetes: practical targets and treatments. cited 2015 Oct 8. Available from:http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/T2D_practical_tt.pdf.3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2014. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S14–S80.4. Jeon JY, Kim DJ, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Lim S, Choi SH, Kim CS, An JH, Kim NH, Won JC, Kim JH, Cha BY, Song KH. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Current status of glycemic control of patients with diabetes in Korea: the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:197–203.5. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999; 281:2005–2012.6. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998; 352:837–853.7. Jabbour S. Primary care physicians and insulin initiation: multiple barriers, lack of knowledge or both. Int J Clin Pract. 2008; 62:845–847.8. Riddle MC, Rosenstock J, Gerich J. Insulin Glargine 4002 Study Investigators. The treat-to-target trial: randomized addition of glargine or human NPH insulin to oral therapy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:3080–3086.9. Wahlqvist ML. Nutrition and diabetes in the Asia-Pacific region with reference to cardiovascular disease. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2001; 10:90–96.10. Tong PC, Ko GT, So WY, Chiang SC, Yang X, Kong AP, Ozaki R, Ma RC, Cockram CS, Chow CC, Chan JC. Use of anti-diabetic drugs and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: The Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008; 82:346–352.11. Tsai ST, Pathan F, Ji L, Yeung VT, Chadha M, Suastika K, Son HS, Tan KE, Benjasuratwong Y, Nguyen TK, Iqbal F. First insulinization with basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes in a real-world setting in Asia. J Diabetes. 2011; 3:208–216.12. Pan CY, Sinnassamy P, Chung KD, Kim KW. LEAD Study Investigators Group. Insulin glargine versus NPH insulin therapy in Asian type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 76:111–118.13. Kim SS, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Yoon KH, Son HY, Park SW, Sung YA, Baek HS, Ha KS. Duration of diabetes and effectiveness of insulin in the management of insulin-naive Korean patients uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: a sub-analysis of the MOdaliTy of Insulin treatment eValuation (MOTIV) registry results. Acta Diabetol. 2014; 51:655–661.14. International Diabetes Federation: Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. 2015. 10. 08. Available from: http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/IDF-Guideline-for-Type-2-Diabetes.pdf.15. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. American Diabetes Association (ADA). European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1364–1379.16. Marre M, Danchin N, Freemantle N, Balkau B, Admane K, Blonde L, Home P. Cardiovascular Risk evaluation in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D) on insulin therapy (CREDIT) study: patterns of initial prescription of insulin and associated changes in oral glucose-lowering drug (OGLD) therapy. Diabetes. 2009; 58:A126.17. Fritsche A, Schweitzer MA, Haring HU, Study G. Glimepiride combined with morning insulin glargine, bedtime neutral protamine hagedorn insulin, or bedtime insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 138:952–959.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Hypoglycemia due to Insulin Antibody after Insulin Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Psychological Insulin Resistance: Key Factors and Intervention
- Unusually Elevated Serum Insulin Level in a Diabetic Patient during Recombinant Insulin Therapy
- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Using Motivational Interviewing to Overcome Psychological Insulin Resistance