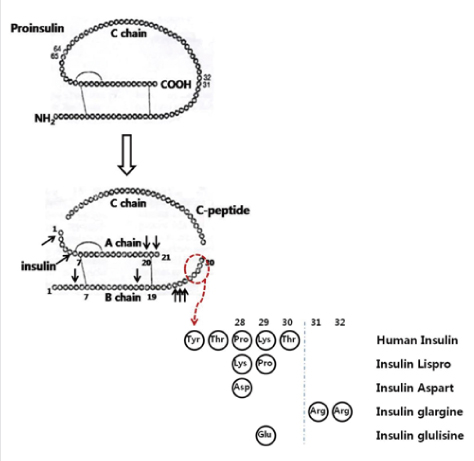
Lab Med Online.
2013 Jan;3(1):56-59. 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.56.
Unusually Elevated Serum Insulin Level in a Diabetic Patient during Recombinant Insulin Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Hanmaem Blood Center, Gwacheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ymyun@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 1845398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.56
Abstract
- Herein, we report a case of unusually elevated serum insulin level as a result of increased anti-insulin antibody (IA)-bound insulin after continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy. Detecting free insulin (unbound IAs) levels after polyethylene glycol pre-treatment could be useful to assess functional insulin levels in diabetic patients receiving insulin therapy. The E170 insulin assay can estimate total insulin (bound IAs and free insulin) levels, but it does not measure the levels of exogenous insulin analogues.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim S, Yun YM, Hur M, Moon HW, Kim JQ. The effects of anti-insulin antibodies and cross-reactivity with human recombinant insulin analogues in the E170 insulin immunometric assay. Korean J Lab Med. 2011. 31:22–29.
Article2. Sapin R. Insulin assays: previously known and new analytical features. Clin Lab. 2003. 49:113–121.3. Sapin R. Anti-insulin antibodies in insulin immunometric assays: a still possible pitfall. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1997. 35:365–367.
Article4. Owen WE, Roberts WL. Cross-reactivity of three recombinant insulin analogs with five commercial insulin immunoassays. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:257–259.
Article5. Cao Y, Smith WC, Bowsher RR. A sensitive chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for the bioanalysis of carboxyl-terminal B-chain analogues of human insulin. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2001. 26:53–61.
Article6. Radermecker RP, Renard E, Scheen AJ. Circulating insulin antibodies: influence of continuous subcutaneous or intraperitoneal insulin infusion, and impact on glucose control. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009. 25:491–501.
Article7. Jeandidier N, Boivin S, Sapin R, Rosart-Ortega F, Uring-Lambert B, Réville P, et al. Immunogenicity of intraperitoneal insulin infusion using programmable implantable devices. Diabetologia. 1995. 38:577–584.
Article8. Fineberg SE, Kawabata TT, Finco-Kent D, Fountaine RJ, Finch GL, Krasner AS. Immunological responses to exogenous insulin. Endocr Rev. 2007. 28:625–652.
Article9. Sapin R. The interference of insulin antibodies in insulin immunometric assays. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002. 40:705–708.
Article10. Arnqvist H, Olsson PO, von Schenck H. Free and total insulin as determined after precipitation with polyethylene glycol: analytical characteristics and effects of sample handling and storage. Clin Chem. 1987. 33:93–96.
Article11. Hanning I, Home PD, Alberti KG. Measurement of free insulin concentrations: the influence of the timing of extraction of insulin antibodies. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:831–835.
Article12. Hara K, Tobe K, Uchigata Y, Nakazono M, Yasuda K, Terauchi Y, et al. Antibody-mediated insulin resistance treated by cessation of insulin administration. Intern Med. 2000. 39:143–145.
Article13. Koyama R, Nakanishi K, Kato M, Yamashita S, Kuwahara H, Katori H. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia due to insulin antibodies against therapeutic human insulin: treatment with double filtration plasmapheresis and prednisolone. Am J Med Sci. 2005. 329:259–264.
Article14. Kim MR, Sheeler LR, Mansharamani N, Haug MT, Faiman C, Gupta MK. Insulin antibodies and hypoglycemia in diabetic patients. Can a quantitative analysis of antibody binding predict the risk of hypoglycemia? Endocrine. 1997. 6:285–291.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Spontaneous Hypoglycemia due to Insulin Antibody after Insulin Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Serum Insulin, Proinsulin and Proinsulin/Insulin Ratio in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: As an Index of beta-Cell Function or Insulin Resistance
- Improvement of Insulin Secretoruy Capacity According to Insulin Therapy in Non-Insulin Depentent Diabetes Mellitus
- Serum insulin, proinsulin, and proinsulin/insulin ratio in type 2 diabetic patients