Blood Res.
2014 Sep;49(3):170-176. 10.5045/br.2014.49.3.170.
Treatment of primary testicular diffuse large B cell lymphoma without prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy: a single center experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csuh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2172788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2014.49.3.170
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a rare but aggressive extranodal lymphoma, and its relapse in the central nervous system (CNS) is a major concern during treatment. Despite this, the role of intrathecal prophylaxis in primary testicular DLBCL remains controversial.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 14 patients with primary testicular DLBCL diagnosed between November 2000 and June 2012, and analyzed the CNS relapse rate in patients treated without intrathecal prophylaxis. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS
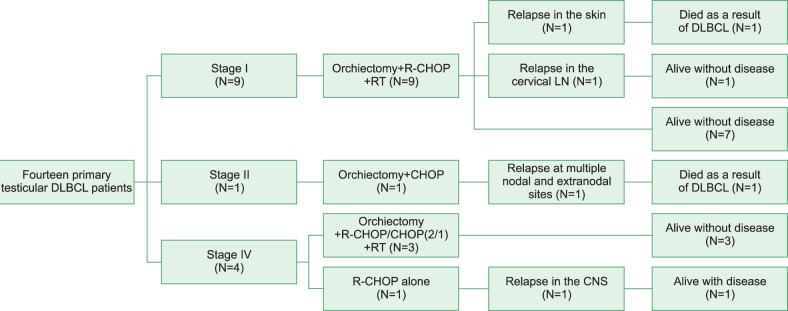
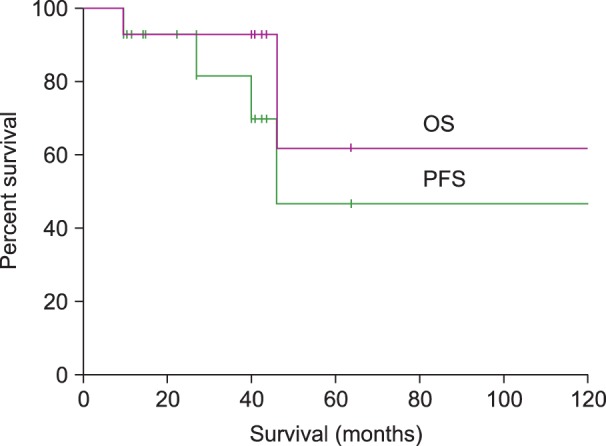
The median age at diagnosis was 57 years (range, 41-79 years). Unilateral testicular involvement was observed in 13 patients. Nine patients had stage I, 1 had stage II, and 4 had stage IV disease. The international prognostic index was low or low-intermediate risk in 12 patients and high-intermediate risk in 2 patients. Thirteen patients underwent orchiectomy. All the patients received systemic chemotherapy without intrathecal prophylaxis, and prophylactic radiotherapy was administered to the contralateral testis in 12 patients. The median follow-up period of surviving patients was 39 months (range, 10-139 months). Median overall survival was not reached and the median progression-free survival was 3.8 years. Four patients experienced relapse, but CNS relapse was observed in only one patient (7.1%) with stage IV disease, 27 months after a complete response.
CONCLUSION
Even without intrathecal prophylaxis, the rate of relapse in the CNS was lower in the Korean patients with primary testicular DLBCL compared to prior reports.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moller MB, d'Amore F, Christensen BE. The Danish Lymphoma Study Group, LYFO. Testicular lymphoma: a population-based study of incidence, clinicopathological correlations and prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 1994; 30A:1760–1764. PMID: 7880601.2. Shahab N, Doll DC. Testicular lymphoma. Semin Oncol. 1999; 26:259–269. PMID: 10375083.3. Zucca E, Roggero E, Bertoni F, Cavalli F. Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Part 1: Gastrointestinal, cutaneous and genitourinary lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 1997; 8:727–737. PMID: 9332679.
Article4. Park BB, Kim JG, Sohn SK, et al. Consideration of aggressive therapeutic strategies for primary testicular lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2007; 82:840–845. PMID: 17563078.
Article5. Sussman EB, Hajdu SI, Lieberman PH, Whitmore WF. Malignant lymphoma of the testis: a clinicopathologic study of 37 cases. J Urol. 1977; 118:1004–1007. PMID: 336911.
Article6. Lantz AG, Power N, Hutton B, Gupta R. Malignant lymphoma of the testis: a study of 12 cases. Can Urol Assoc J. 2009; 3:393–398. PMID: 19829735.
Article7. Kridel R, Dietrich PY. Prevention of CNS relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:1258–1266. PMID: 21933751.
Article8. Tomita N, Kodama F, Kanamori H, Motomura S, Ishigatsubo Y. Prophylactic intrathecal methotrexate and hydrocortisone reduces central nervous system recurrence and improves survival in aggressive non-hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer. 2002; 95:576–580. PMID: 12209750.
Article9. Vitolo U, Chiappella A, Ferreri AJ, et al. First-line treatment for primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with rituximab-CHOP, CNS prophylaxis, and contralateral testis irradiation: final results of an international phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2766–2772. PMID: 21646602.10. Zucca E, Conconi A, Mughal TI, et al. Patterns of outcome and prognostic factors in primary large-cell lymphoma of the testis in a survey by the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:20–27. PMID: 12506165.
Article11. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2008.12. Krol AD, le Cessie S, Snijder S, Kluin-Nelemans JC, Kluin PM, Noordijk EM. Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL): the impact of alternative definitions tested in the Comprehensive Cancer Centre West population-based NHL registry. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:131–139. PMID: 12488305.
Article13. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:987–994. PMID: 8141877.14. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–586. PMID: 17242396.15. Mazloom A, Fowler N, Medeiros LJ, Iyengar P, Horace P, Dabaja BS. Outcome of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the testis by era of treatment: the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010; 51:1217–1224. PMID: 20443676.
Article16. Vitolo U, Ferreri AJ, Zucca E. Primary testicular lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008; 65:183–189. PMID: 17962036.
Article17. Boehme V, Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Loeffler M, Pfreundschuh M. CNS events in elderly patients with aggressive lymphoma treated with modern chemotherapy (CHOP-14) with or without rituximab: an analysis of patients treated in the RICOVER-60 trial of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Study Group (DSHNHL). Blood. 2009; 113:3896–3902. PMID: 19144985.
Article18. Shimazu Y, Notohara K, Ueda Y. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with central nervous system relapse: prognosis and risk factors according to retrospective analysis from a single-center experience. Int J Hematol. 2009; 89:577–583. PMID: 19353238.
Article19. Villa D, Connors JM, Shenkier TN, Gascoyne RD, Sehn LH, Savage KJ. Incidence and risk factors for central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: the impact of the addition of rituximab to CHOP chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:1046–1052. PMID: 19861575.
Article20. Tai WM, Chung J, Tang PL, et al. Central nervous system (CNS) relapse in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL): pre- and post-rituximab. Ann Hematol. 2011; 90:809–818. PMID: 21229246.
Article21. Yamamoto W, Tomita N, Watanabe R, et al. Central nervous system involvement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol. 2010; 85:6–10. PMID: 20236301.
Article22. Seymour JF, Solomon B, Wolf MM, Janusczewicz EH, Wirth A, Prince HM. Primary large-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the testis: a retrospective analysis of patterns of failure and prognostic factors. Clin Lymphoma. 2001; 2:109–115. PMID: 11707851.
Article23. Turner RR, Colby TV, MacKintosh FR. Testicular lymphomas: a clinicopathologic study of 35 cases. Cancer. 1981; 48:2095–2102. PMID: 7296517.
Article24. Touroutoglou N, Dimopoulos MA, Younes A, et al. Testicular lymphoma: late relapses and poor outcome despite doxorubicin-based therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13:1361–1367. PMID: 7751880.
Article25. Blasberg RG, Patlak C, Fenstermacher JD. Intrathecal chemotherapy: brain tissue profiles after ventriculocisternal perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975; 195:73–83. PMID: 810575.26. Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM. Methotrexate: distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med. 1975; 293:161–166. PMID: 806016.
Article27. Fleischhack G, Jaehde U, Bode U. Pharmacokinetics following intraventricular administration of chemotherapy in patients with neoplastic meningitis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005; 44:1–31. PMID: 15634030.
Article28. Gundrum JD, Mathiason MA, Moore DB, Go RS. Primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a population-based study on the incidence, natural history, and survival comparison with primary nodal counterpart before and after the introduction of rituximab. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5227–5232. PMID: 19770371.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of the Cauda Equina Syndrome Associated With the Intrathecal Chemotherapy in a Patient With Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
- Two Cases of Primary Esophageal Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Therapeutic Considerations and a Literature Review
- A Case of Primary NK/T Cell Lymphoma of the Testis
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting with cholecystitis-like symptoms