Ewha Med J.
2013 Sep;36(2):79-83. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.2.79.
Role of Sleep Center for Integrative Approach to Sleep Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leeh@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dentistry, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Otolaryngology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2171234
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.2.79
Abstract
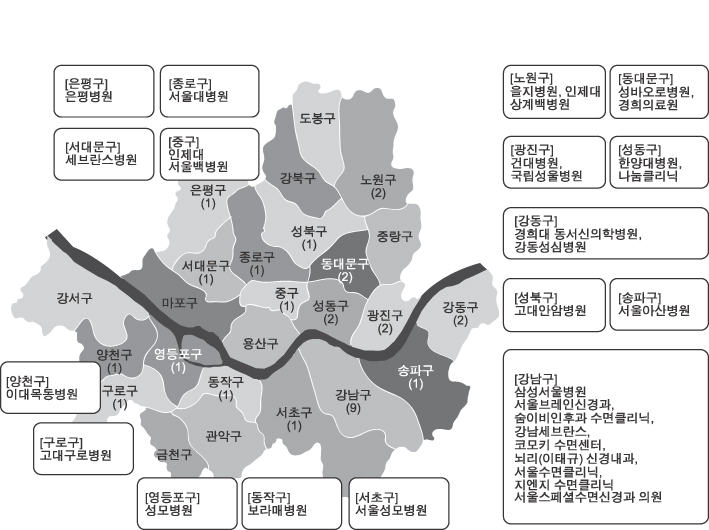
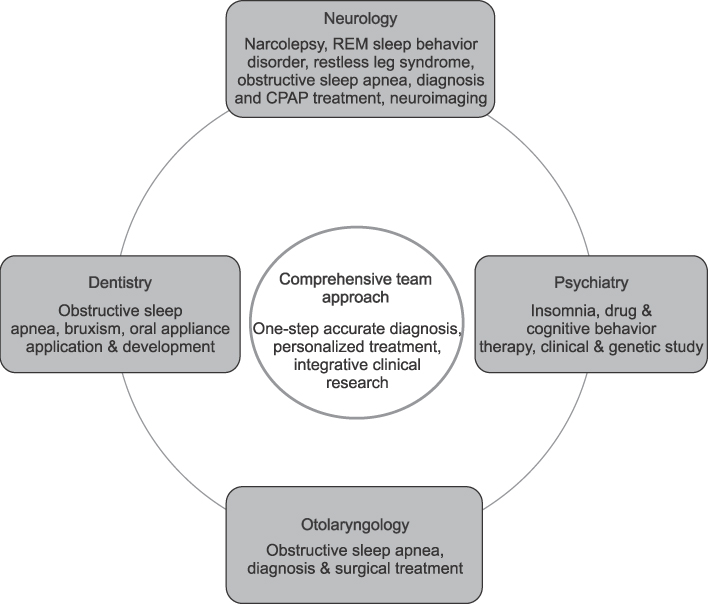
- The prevalence of sleep disorder is about 30% of the population. Common sleep disorders are insomnia, obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, restless legs syndrome, rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and parasomnia. These sleep disorders lead various medical and mental complications. However, most sleep disorders are underdiagnosed and not treated appropriately. Sleep medicine is important for treating these sleep disorders and maintaining general healthy conditions. Specialized and comprehensive treatments for sleep disorder are important in sleep medicine.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dinges DF. An overview of sleepiness and accidents. J Sleep Res. 1995; 4:Suppl 2. 4–14.2. Hong SB. Sleep disorders medicine. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:410–422.3. Shepard JW Jr, Buysse DJ, Chesson AL Jr, Dement WC, Goldberg R, Guilleminault C, et al. History of the development of sleep medicine in the United States. J Clin Sleep Med. 2005; 15:61–82.4. Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993; 328:1230–1235.5. Gastaut H, Tassinari CA, Duron B. Polygraphic study of the episodic diurnal and nocturnal (hypnic and respiratory) manifestations of the Pickwickian syndrome. Brain Res. 1966; 1:167–186.6. Kryger MH, Roth T, Dement WC. Principles and practice of sleep medicine. 5th ed. St. Louis: Elservier Sauders;2011.7. Diagnostic classification of sleep and arousal disorders. 1997 first edition. Association of Sleep Disorders Centers and the Association for the Psychophysiological Study of Sleep. Sleep. 1979; 2:1–154.8. Sullivan CE, Issa FG, Berthon-Jones M, Eves L. Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares. Lancet. 1981; 1:862–865.9. American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The international classification of sleep disorders: diagnostic and coding manual. 2nd ed. Westchester: American Academy of Sleep Medicine;2005.10. National Center on Sleep Disorders Research. National Institutes of Health sleep disorders research plan [Internet]. National Institutes of Health;2011. cited 2013 Aug 10. Available from: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/prof/sleep/201101011NationalSleepDisordersResearchPlanDHHSPublication11-7820.pdf.11. Williams J, Roth A, Vatthauer K, McCrae CS. Cognitive behavior treatment of insomnia. Chest. 2013; 143:554–565.12. Yang KI. What obstructive sleep apnea brings to us. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2013; 31:93–100.13. Huang QR, Qin Z, Zhang S, Chow CM. Clinical patterns of obstructive sleep apnea and its comorbid conditions: a data mining approach. J Clin Sleep Med. 2008; 4:543–550.14. Engleman HM, Douglas NJ. Sleep. 4: Sleepiness, cognitive function, and quality of life in obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Thorax. 2004; 59:618–622.15. Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Vicente E, Agusti AG. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: an observational study. Lancet. 2005; 365:1046–1053.16. Morgenthaler TI, Kapur VK, Brown T, Swick TJ, Alessi C, Aurora RN, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin. Sleep. 2007; 30:1705–1711.17. Nau SD, Dillon HR, Geyer JD, Carney PR, Lichstein KL. Insomnia: causes and treatments. Carney PR, Geyer JD, Berry RB. Clinical sleep disorders. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2012. p. 157–184.18. Morgenthaler T, Kramer M, Alessi C, Friedman L, Boehlecke B, Brown T, et al. Practice parameters for the psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine report. Sleep. 2006; 29:1415–1419.19. Allen RP, Picchietti D, Hening WA, Trenkwalder C, Walters AS, Montplaisi J, et al. Restless legs syndrome: diagnostic criteria, special considerations, and epidemiology. A report from the restless legs syndrome diagnosis and epidemiology workshop at the National Institutes of Health. Sleep Med. 2003; 4:101–119.20. Hong SY, Lee JH, Cho YW. Quality of life in patients with restless legs syndrome in Korea: comparison with other chronic diseases. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2010; 28:257–262.21. Rothdach AJ, Trenkwalder C, Haberstock J, Keil U, Berger K. Prevalence and risk factors of RLS in an elderly population: the MEMO study. Memory and Morbidity in Augsburg Elderly. Neurology. 2000; 54:1064–1068.22. Gorman CA, Dyck PJ, Pearson JS. Symptoms of restless legs. Arch Intern Med. 1965; 115:155–160.23. Boeve BF. Idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder in the development of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013; 12:469–482.