Infect Chemother.
2010 Dec;42(6):383-390. 10.3947/ic.2010.42.6.383.
Outcome of Surgical Resection for Invasive Pulmonary Fungal Diseases in Patients with Acute Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sumichoi@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2170317
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2010.42.6.383
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
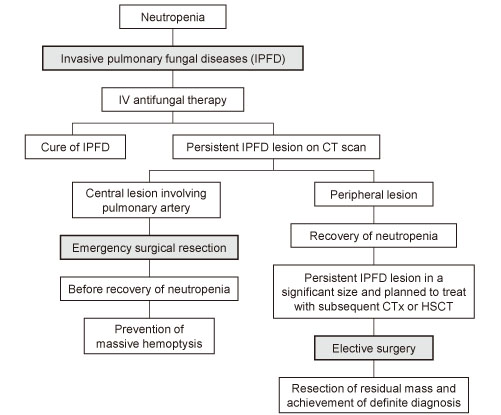
In patients with hematologic diseases, surgical resection can be recommended for definite diagnosis, curative treatment, and prevention of complications or redevelopment of invasive pulmonary fungal diseases (IPFD). The purpose of this study was to investigate the outcome of surgical resection for IPFD in patients planned to undergo subsequent chemotherapy (CTx) or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acute leukemia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of adult patients with acute leukemia who underwent surgical resection for IPFD which developed during the neutropenic period after CTx.
RESULTS
From January 2004 through August 2008, a total of 15 patients (8 males and 7 females with median age of 49 years) underwent surgical resection. All patients were treated by elective surgical resection of residual IPFD lesion before subsequent CTx or HSCT. The median diameter of the main lesion was 66 mm (range, 33-98 mm). Pericardial adhesion due to local invasion of pulmonary lesion was observed in one patient. Lobectomy was performed in 13 cases, lobectomy with wedge resection in 1 case, and segmentectomy with wedge resection in 1 case. Air leakage was complicated in 2 patients. Thirty-day mortality after surgical resection was 0%. After subsequent CTx or HSCT, IPFD redeveloped in 5 patients. However, the overall mortality was not different between the groups with or without the redevelopment of IPFD. Also, mortality attributable to IPFD was only 6% (1/15) during the overall follow-up period (median 184 days, range 58-1,251 days).
CONCLUSIONS
In patients planned to receive subsequent CTx or HSCT for acute leukemia, surgical resection combined with medical therapy for IPFD could be considered for those who have significant residual lesion. Further study will be needed to determine whether surgical resection can shorten the duration of medical treatment and improve survival outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Shattil SJ, Furie B, Silberstein LE, McGlave P, Heslop H. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 2008. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone.2. Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood. 2002. 100:4358–4366.
Article3. Martino R, Subirà M. Invasive fungal infections in hematology: new trends. Ann Hematol. 2002. 81:233–243.
Article4. Paterson DL, Singh N. Invasive aspergillosis in transplant recipients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1999. 78:123–138.
Article5. Wald A, Leisenring W, van Burik JA, Bowden RA. Epidemiology of Aspergillus infections in a large cohort of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1997. 175:1459–1466.
Article6. Baddley JW, Andes DR, Marr KA, Kontoyiannis DP, Alexander BD, Kauffman CA, Oster RA, Anaissie EJ, Walsh TJ, Schuster MG, Wingard JR, Patterson TF, Ito JI, Williams OD, Chiller T, Pappas PG. Factors associated with mortality in transplant patients with invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. 50:1559–1567.
Article7. Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verhoef G, Verschakelen J, Lagrou K, Verbeken E, Wilmer A, Verhaegen J, Boogaerts M, Van Eldere J. Galactomannan and computed tomography-based preemptive antifungal therapy in neutropenic patients at high risk for invasive fungal infection: a prospective feasibility study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 41:1242–1250.
Article8. Habicht JM, Matt P, Passweg JR, Reichenberger F, Gratwohl A, Zerkowski HR, Tamm M. Invasive pulmonary fungal infection in hematologic patients: is resection effective? Hematol J. 2001. 2:250–256.
Article9. Moreau P, Zahar JR, Milpied N, Baron O, Mahé B, Wu D, Germaud P, Despins P, Delajartre AY, Harousseau JL. Localized invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with neutropenia. Effectiveness of surgical resection. Cancer. 1993. 72:3223–3226.
Article10. Reichenberger F, Habicht J, Kaim A, Dalquen P, Bernet F, Schläpfer R, Stulz P, Perruchoud AP, Tichelli A, Gratwohl A, Tamm M. Lung resection for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients with hematologic diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:885–890.
Article11. Matt P, Bernet F, Habicht J, Gambazzi F, Gratwohl A, Zerkowski HR, Tamm M. Predicting outcome after lung resection for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with neutropenia. Chest. 2004. 126:1783–1788.
Article12. Pidhorecky I, Urschel J, Anderson T. Resection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2000. 7:312–317.
Article13. Wong K, Waters CM, Walesby RK. Surgical management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1992. 6:138–142.
Article14. Danner BC, Didilis V, Dörge H, Mikroulis D, Bougioukas G, Schöndube FA. Surgical treatment of pulmonary aspergillosis/mycosis in immunocompromised patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2008. 7:771–776.
Article15. Hughes WT, Armstrong D, Bodey GP, Bow EJ, Brown AE, Calandra T, Feld R, Pizzo PA, Rolston KV, Shenep JL, Young LS. 2002 guidelines for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis. 2002. 34:730–751.
Article16. Herbrecht R, Letscher-Bru V, Oprea C, Lioure B, Waller J, Campos F, Villard O, Liu KL, Natarajan-Amé S, Lutz P, Dufour P, Bergerat JP, Candolfi E. Aspergillus galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:1898–1906.
Article17. Maertens JA, Klont R, Masson C, Theunissen K, Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Heinen C, Crépin B, Van Eldere J, Tabouret M, Donnelly JP, Verweij PE. Optimization of the cutoff value for the Aspergillus double-sandwich enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:1329–1336.
Article18. Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verbeken E, Lagrou K, Verhaegen J, Boogaerts M, Eldere JV. Prospective clinical evaluation of lower cut-offs for galactomannan detection in adult neutropenic cancer patients and haematological stem cell transplant recipients. Br J Haematol. 2004. 126:852–860.
Article19. Yoo JH. Aspergillosis. The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases. Infectious Diseases. 2007. Seoul: Koonja;881–889.20. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, Pappas PG, Maertens J, Lortholary O, Kauffman CA, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Maschmeyer G, Bille J, Dismukes WE, Herbrecht R, Hope WW, Kibbler CC, Kullberg BJ, Marr KA, Muñoz P, Odds FC, Perfect JR, Restrepo A, Ruhnke M, Segal BH, Sobel JD, Sorrell TC, Viscoli C, Wingard JR, Zaoutis T, Bennett JE. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:1813–1821.
Article21. Yeghen T, Kibbler CC, Prentice HG, Berger LA, Wallesby RK, McWhinney PH, Lampe FC, Gillespie S. Management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in hematology patients: a review of 87 consecutive cases at a single institution. Clin Infect Dis. 2000. 31:859–868.
Article22. Caillot D, Mannone L, Cuisenier B, Couaillier JF. Role of early diagnosis and aggressive surgery in the management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001. 7:Suppl 2. 54–61.
Article23. Bernard A, Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Casasnovas O, Guy H, Favre JP. Surgical management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997. 64:1441–1447.
Article24. Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Morrison VA, Segal BH, Steinbach WJ, Stevens DA, van Burik JA, Wingard JR, Patterson TF. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:327–360.
Article25. Milito MA, Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE, Liu P, Mawlawi OR, Truong MT, Marom EM. Influence of host immunosuppression on CT findings in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Med Mycol. 2010. 48:817–823.
Article26. Brodoefel H, Vogel M, Hebart H, Einsele H, Vonthein R, Claussen C, Horger M. Long-term CT follow-up in 40 non-HIV immunocompromised patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: kinetics of CT morphology and correlation with clinical findings and outcome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 187:404–413.
Article27. Matt P, Bernet F, Habicht J, Gambazzi F, Passweg J, Gratwohl A, Tamm M, Zerkowski HR. Short- and long-term outcome after lung resection for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003. 51:221–225.
Article28. Zhang P, Song A, Wang Z, Feng S, Qiu L, Han M. Hematopoietic SCT in patients with a history of invasive fungal infection. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009. 43:533–537.
Article29. Habicht JM, Reichenberger F, Gratwohl A, Zerkowski HR, Tamm M. Surgical aspects of resection for suspected invasive pulmonary fungal infection in neutropenic patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999. 68:321–325.
Article30. Gow KW, Hayes-Jordan AA, Billups CA, Shenep JL, Hoffer FA, Davidoff AM, Rao BN, Schropp KP, Shochat SJ. Benefit of surgical resection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in pediatric patients undergoing treatment for malignancies and immunodeficiency syndromes. J Pediatr Surg. 2003. 38:1354–1360.
Article31. Caillot D, Casasnovas O, Bernard A, Couaillier JF, Durand C, Cuisenier B, Solary E, Piard F, Petrella T, Bonnin A, Couillault G, Dumas M, Guy H. Improved management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients using early thoracic computed tomographic scan and surgery. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:139–147.
Article32. Young VK, Maghur HA, Luke DA, McGovern EM. Operation for cavitating invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992. 53:621–624.
Article33. Sa YJ, Park JK, Kim YH, Nam SY, Sim SB, Lee SH. Pulmonary resection for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in hematological malignancy patients. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007. 40:617–623.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgery for Pulmonary Fungal Infections Complicating Hematological Malignancies
- Surgical Management of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Hemtologic Malignancy Patients: Report of 2 cases
- Pneumonia due to Schizophyllum commune in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Disseminated Candidiasis and Subsequent Breakthrough Pulmonary Mucormycosis after Consolidation Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- A Case of Pulmonary Embolism Caused by Aspergillus in a Child with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia