J Bacteriol Virol.
2008 Mar;38(1):19-27. 10.4167/jbv.2008.38.1.19.
Antimicrobial Resistance and Multilocus Sequence Typing of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Deagu, Korea. dtcho@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Cardiology in Internal Medicine, Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2168515
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2008.38.1.19
Abstract
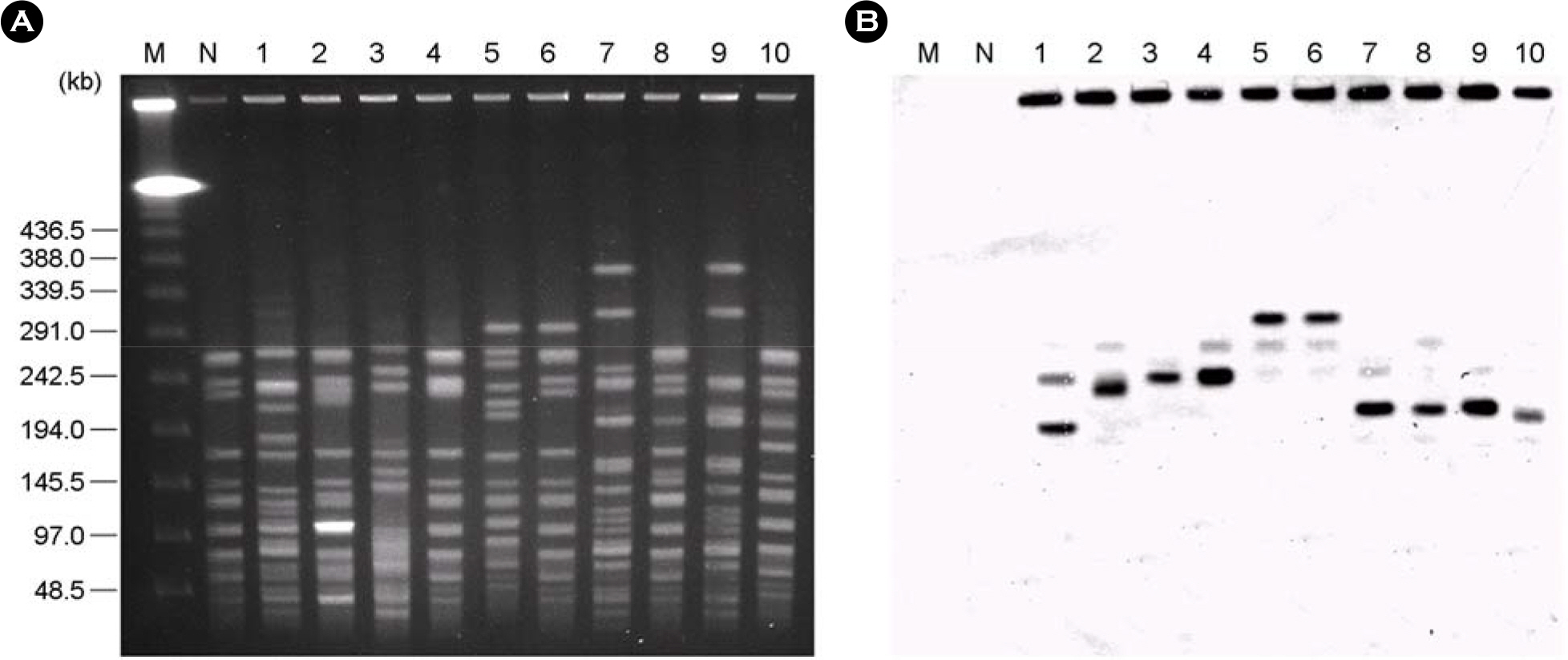
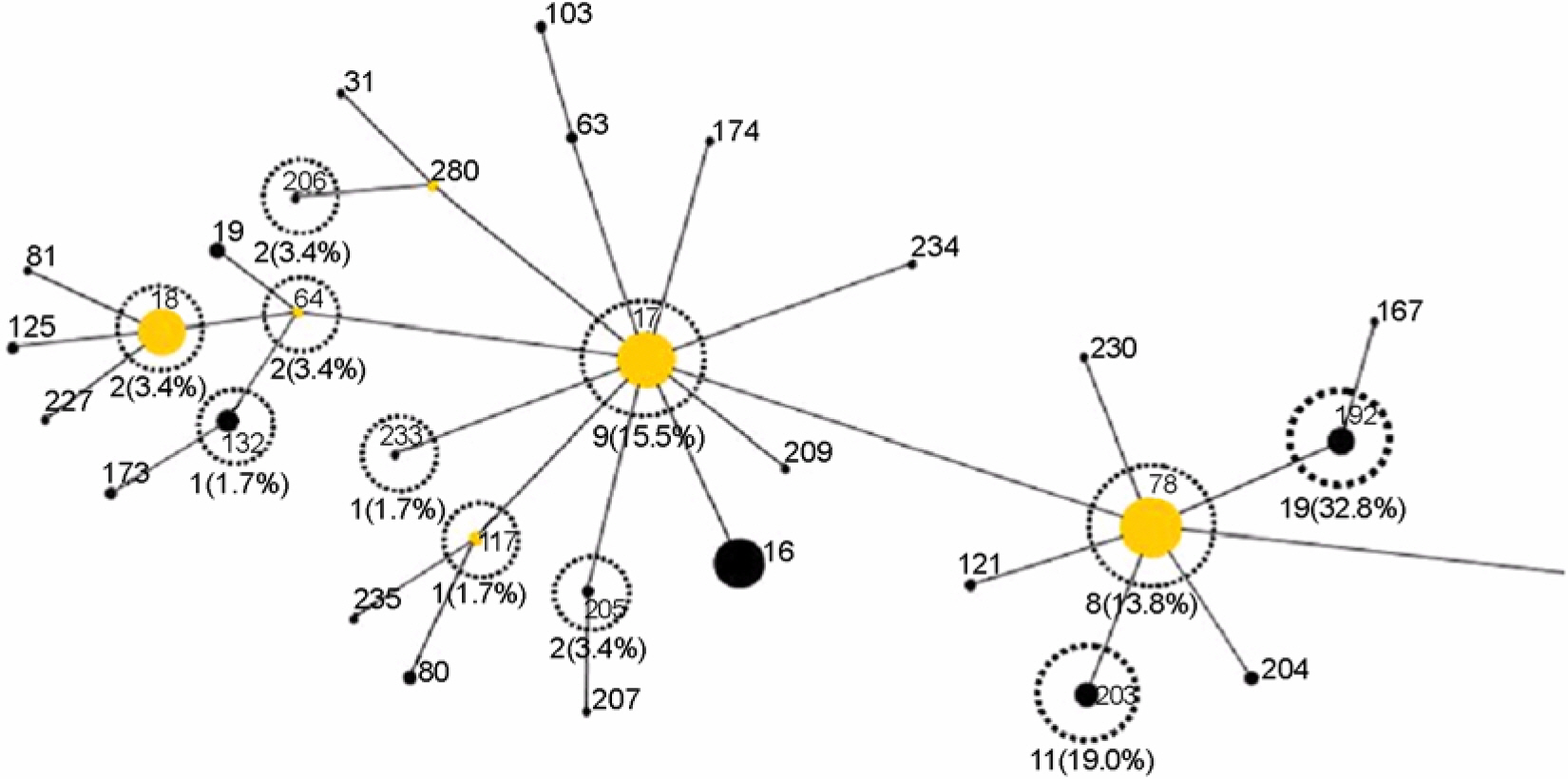
- A total of 58 vancomycin-resistant E. faecium (VREF) was isolated from 3 hospitals located in Daegu, Korea. The VREF isolates were evaluated for the antimicrobial susceptibility pattern and resistance determinants against vancomcin, aminoglycosides, and macrolides. The multilocus sequence types (MLST) were determined to characterize the clonal diversity of the VREF isolates. The VREF isolates were highly resistance to teicoplanin, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, and streptomycin, whereas quinupristin-dalfopristin and linezolid were the most susceptible drugs. All isolates carried the vanA gene. The aac6'-aph2" (n=53) and aadE (n=27) genes were detected in the high-level aminoglycoside resistant (HLAR) isolates. The aac6'-aph2" gene was located in the conjugally transferable plasmids. The ermB and ermA genes were detected in the 54 and 3 VREF isolates, respectively. The VREF isolates showed 11 different sequence types (ST). The VREF isolates belonging to ST192 was the most prevalent (n=19), but detected in one hospital, whereas the isolates belonging to ST203 (n=11) were detected in 3 hospitals. These results suggest that the VREF isolates resistant to aminoglycosides and erythromycin are originated from different clones and specific VREF clones are spread in the study hospitals.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetamides
Aminoglycosides
Ciprofloxacin
Clone Cells
Enterococcus
Enterococcus faecium
Erythromycin
Gentamicins
Korea
Linezolid
Macrolides
Multilocus Sequence Typing
Oxazolidinones
Plasmids
Streptomycin
Teicoplanin
Virginiamycin
Acetamides
Aminoglycosides
Ciprofloxacin
Erythromycin
Gentamicins
Macrolides
Oxazolidinones
Streptomycin
Teicoplanin
Virginiamycin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Antimicrobial Resistance and Multilocus Sequence Typing of Vancomycin-Resistant
Enterococcus faecium Isolated from the Chungcheong Area
Hye Hyun Cho, Ji Youn Sung, Kye Chul Kwon, Jin Sook Lim, Sun Hoe Koo
Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2011;14(2):60-66. doi: 10.5145/KJCM.2011.14.2.60.
Reference
-
References
1). 최원석, 서유빈, 조유미, 김정연, 기세윤, 정혜원, 송준 영, 정희진, 송기준, 김우주. Vancomycin 내성 장구균에 의한 세균뇨의 역학과 임상적 중요성. 감염과화학요법. 38:242–249. 2006.2). 홍기숙, 강은숙, 이미애. Vancomycin 내성 Enterococci의 빈도 조사 및 중합효소연쇄반응을 이용한 유전자형의 분석. 대한임상병리학회지. 18:372–378. 1998.3). Agerso Y, Pedersen AG, Aarestrup FM. Identification of Tn5397-like and Tn916-like transposons and diversity of the tetracycline resistance gene tet (M) in enterococci from humans, pigs and poultry. J Antimicrob Chemother. 57:832–839. 2006.4). Biavasco F, Miele A, Vignaroli C, Manso E, Lupidi R, Varaldo PE. Genotypic characterization of a nosocomial outbreak of VanA Enterococcus faecalis. Microb Drug Resist. 2:231–237. 1996.5). Camargo IL, Gilmore MS, Darini AL. Multilocus sequence typing and analysis of putative virulence factors in vancomycin-resistant and vancomycin-sensitive Enterococcus faecium isolates from Brazil. Clin Microbiol Infect. 12:1123–1130. 2006.6). Chang SC, Chen YC, Luh KT, Hsieh WC. Macrolides resistance of common bacteria isolated from Taiwan. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 23:147–154. 1995.
Article7). del Campo R, Tenorio C, Rubio C, Castillo J, Torres C, Gomez-Lus R. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in high-level streptomycin and gentamicin resistant Enterococcus spp. in Spain. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 15:221–226. 2000.8). del Campo R, Ruiz-Garbajosa P, Sanchez-Moreno MP, Baquero F, Torres C, Canton R, Coque TM. Antimicrobial resistance in recent fecal enterococci from healthy volunteers and food handlers in Spain: genes and phenotypes. Microb Drug Resist. 9:47–60. 2003.
Article9). Eom JS, Hwang IS, Hwang BY, Lee JG, Lee YJ, Cheong HJ, Park YH, Park SC, Kim WJ. Emergence of vanA Genotype Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci with Low or Moderate Levels of Teicoplanin Resistance in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 42:1785–1786. 2004.10). Gordon KA, Jones RN. Susceptibility patterns of orally administered antimicrobials among urinary tract infection pathogens from hospitalized patients in North America: comparison report to Europe and Latin America. Results from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (2000). Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 45:295–301. 2003.
Article11). Harada T, Tsuji N, Otsuki K, Murase T. Detection of the esp gene in high-level gentamicin resistant Enterococcus faecalis strains from pet animals in Japan. Vet Microbiol. 106:139–143. 2005.12). Hashimoto Y, Tanimoto K, Ozawa Y, Murata T, Ike Y. Amino acid substitutions in the VanS sensor of the VanA-type vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus strains result in high-level vancomycin resistance and low-level teicoplanin resistance. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 185:247–254. 2000.13). Homan WL, Tribe D, Poznanski S, Li M, Hogg G, Spalburg E, Van Embden JD, Willems RJ. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for Enterococcus faecium. J Clin Microbiol. 40:1963–1971. 2002.14). Kainer MA, Devasia RA, Jones TF, Simmons BP, Melton K, Chow S, Broyles J, Moore KL, Craig AS, Schaffner W. Response to emerging infection leading to outbreak of linezolid-resistant enterococci. Emerg Infect Dis. 13:1024–1030. 2007.
Article15). Klare I, Heier H, Claus H, Witte W. Environmental strains of Enterococcus faecium with inducible high-level resistance to glycopeptides. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 106:23–29. 1993.16). Ko KS, Baek JY, Lee JY, Oh WS, Peck KR, Lee N, Lee WG, Lee K, Song JH. Molecular characterization of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium isolates from Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 43:2303–2306. 2005.17). Kolar M, Pantucek R, Vagnerova I, Cekanova L, Kesselova M, Sauer P, Koukalova D, Kolar V, Ruzi kova M, Dosar J. Prevalence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in hospital and community environment. Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. 11:47–50. 2005.18). Leavis H, Top J, Shankar N, Borgen K, Bonten M, van Embden J, Willems RJ. A novel putative Enterococcal pathogenicity island linked to the esp virulence gene of Enter-ococcus faecium and associated with epidemicity. J Bacteriol. 186:672–682. 2004.19). Lee WG, Huh JY, Cho SR, Lim YA. Reduction in glycopeptide resistance in vancomycin-resistant enterococci as a result of vanA cluster rearrangements. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 48:1379–1381. 2004.20). Lim JA, Kwon AR, Kim SK, Chong Y, Lee K, Choi EC. Prevalence of resistance to macrolide, lincosamide and streptogarmin antibiotics in Gram-positive cocci isolated in a Korean hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 49:489–495. 2002.21). Murray BE. The life and times of the enterococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 3:46–65. 1990.
Article22). Murray BE. Diversity among multidrug-resistant enterococci. Emerg Infect Dis. 4:37–47. 1998.
Article23). Nichol KA, Sill M, Laing NM, Johnson JL, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG. Molecular epidemiology of urinary tract isolates of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium from North America. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 27:392–396. 2006.24). Oancea C, Klare I, Witte W, Werner G. Conjugative transfer of the virulence gene, esp, among isolates of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 54:232–235. 2004.25). Oh JY, An S, Jin JS, Lee YC, Cho DT, Lee JC. Phenotypic and genotypic differences of the vancomycin-resistant Enter-ococcus faecium isolates from humans and poultry in Korea. J Microbiol. 45:466–472. 2007.26). Poeta P, Costa D, Rodrigues J, Torres C. Antimicrobial resistance and the mechanisms implicated in faecal enterococci from healthy humans, poultry and pets in Portugal. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 27:131–137. 2006.
Article27). Rice LB, Carias L, Rudin S, Vael C, Goossens H, Konstabel C, Klare I, Nallapareddy SR, Huang W, Murray BE. A potential virulence gene, hylsEfm, predominates in Enterococcus faecium of clinical origin. J Infect Dis. 187:508–512. 2003.28). Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. p. 10.1–10.52. 2nd ed.Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory;Cold Spring Harbor NY.: 1989.29). Sanchez ML, Flint KK, Jones RN. Occurrence of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin resistance among staphylsococcal clinical isolates at a university medical center. Is false susceptibility to new macrolides and clindamycin a contemporary clinical and in vitro testing problem? Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 16:205–213. 1993.30). Shankar N, Lockatell CV, Baghdayan AS, Drachenberg C, Gilmore MS, Johnson DE. Role of Enterococcus faecalis surface protein Esp in the pathogenesis of ascending urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 69:4366–4372. 2001.31). Tunger A, Aydemir S, Uluer S, Cilli F. In vitro activity of linezolid & quinupristin/dalfopristin against Gram-positive cocci. Indian J Med Res. 120:546–552. 2004.32). Uttley AH, Collins CH, Naidoo J, George RC. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet. 1:57–58. 1998.
Article33). van den Braak N, van Belkum A, van Keulen M, Vliegenthart J, Verbrugh HA, Endtz HP. Molecular characterization of vancomycin-resistant enterococci from hospitalized patients and poultry products in the Netherlands. J Clin Microbiol. 36:1927–1932. 1998.
Article34). Willems RJ, Top J, van Santen M, Robinson DA, Coque TM, Baquero F, Grundmann H, Bonten MJ. Global spread of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium from distinct nosocomial genetic complex. Emerg Infect Dis. 11:821–828. 2005.35). Zervos MJ, Mikesell TS, Schaberg DR. Heterogeneity of plasmids determining high-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 30:78–81. 1986.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance and Multilocus Sequence Typing of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Isolated from the Chungcheong Area
- Comparison of Enterococcus faecium Bacteremic Isolates from Hematologic and Non-hematologic Patients: Differences in Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characteristics
- Comparison of Multilocus Sequence Typing Change Patterns of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium from 2015 to 2017
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus avium Isolated from the Wound of a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus
- Susceptibility of Fosfomycin against Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci