Electrolyte Blood Press.
2012 Dec;10(1):31-34. 10.5049/EBP.2012.10.1.31.
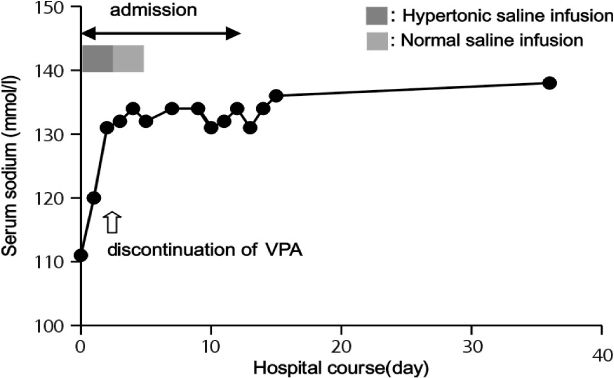
A Case of Syndrome of Inappropriate Scretion of Anti-Diuretic Hormone Associated with Sodium Valproate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. kidwon@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2168392
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2012.10.1.31
Abstract
- We report a rare case of the concurrent manifestation of central diabetes insipidus (CDI) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). A 56 year-old man was diagnosed as a type 2 DM on the basis of hyperglycemia with polyuria and polydipsia at a local clinic two months ago and started an oral hypoglycemic medication, but resulted in no symptomatic improvement at all. Upon admission to the university hospital, the patient's initial fasting blood sugar level was 140 mg/dL, and he showed polydipsic and polyuric conditions more than 8 L urine/day. Despite the hyperglycemia controlled with metformin and diet, his symptoms persisted. Further investigations including water deprivation test confirmed the coexisting CDI of unknown origin, and the patient's symptoms including an intense thirst were markedly improved by desmopressin nasal spray (10 microg/day). The possibility of a common origin of CDI and type 2 DM is raised in a review of the few relevant adult cases in the literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baylis PH. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003. 35:1495–1499.
Article2. Hoorn EJ, Lindemans J, Zietse R. Development of severe hyponatraemia in hospitalized patients: treatment-related risk factors and inadequate management. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006. 21:70–76.
Article3. Chan TY. Drug-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Causes, diagnosis and management. Drugs Aging. 1997. 11:27–44.4. Genton P, Gelisse P. Levy RH, Mattson RH, Meldrum BS, Perucca E, editors. Valproic acid. Adverse effects. Antiepileptic drugs. 2002. 5th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins;838–851.5. Zaccara G, Franciotta D, Perucca E. Idiosyncratic adverse reactions to antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 2007. 48:1223–1244.
Article6. Branten AJ, Wetzels JF, Weber AM, Koene RA. Hyponatremia due to sodium valproate. Ann Neurol. 1998. 43:265–267.
Article7. Bartter FC, Schwartz WB. The syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1967. 42:790–806.
Article8. Keranen T, Sivenius J. Side effects of carbamazepine, valproate and clonazepam during long-term treatment of epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1983. 97:69–80.9. Branten AJ, et al. Hyponatremia due to sodium valproate. Ann Neurol. 1998. 43:265–267.
Article10. Miyaoka T, et al. Contribution of sodium valproate to the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2001. 16:59–61.
Article11. Herment N, et al. Hyponatremia induced by sodium valproate. A case report. Therapie. 2006. 61:544–547.12. Bavbek N, et al. Hyponatremia associated with sodium valproate in a 22-year-old male. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008. 23:410.13. Beers E, et al. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) or hyponatraemia associated with valproic Acid: four case reports from the Netherlands and a case/non-case analysis of vigibase. Drug Saf. 2010. 33:47–55.
Article14. Corda C, et al. Hyponatremia under sodium valproate: search a drug interaction. Therapie. 1991. 46:169.15. Kim DK, KW Joo. Hyponatremia in patients with neurologic disorders. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2009. 7:51–57.
Article16. Spigset O, Hedenmalm K. Hyponatraemia and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) induced by psychotropic drugs. Drug Saf. 1995. 12:209–225.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Post-operative SIADH(syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone): A case report
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone after Lung Transplantation
- Case of Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion in a Patient with Esophageal Cancer
- Severe Hyponatremia with Mental Change after Ingestion of Picosulfate Sodium/Magnesium Citrate for Bowel Preparation
- SIADH Associated with Guillain-Barre Syndrome