Hanyang Med Rev.
2012 May;32(2):77-82. 10.7599/hmr.2012.32.2.77.
Tailored Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, ASsessment Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS) Group, Korea. ktj1562@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168200
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2012.32.2.77
Abstract
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic rheumatic disease of the axial skeleton (spine and sacroiliac joints). Only nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha inhibitors have currently been shown as effective for the treatment of signs and symptoms of active AS with predominant axial involvement. In contrast to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) play only a minor role in the management of AS and only in cases with peripheral joint involvement. Herein, this review describes the pharmacological and nonpharmacological management of AS, based on recent international recommendations for the management of AS by the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis (ASAS) group. Despite the overall demonstrated efficacy of currently available treatments for AS, up to 40% of treated patients do not achieve an acceptable clinical improvement during therapy. Therefore, this article also reviews the evidence regarding the potential role for new agents targeting B-cells, T-cells, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-12/23 in patients with AS.
MeSH Terms
-
Antirheumatic Agents
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
B-Lymphocytes
Biological Agents
Disease Management
Humans
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Joints
Rheumatic Diseases
Skeleton
Spondylitis, Ankylosing
T-Lymphocytes
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Antirheumatic Agents
Biological Agents
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
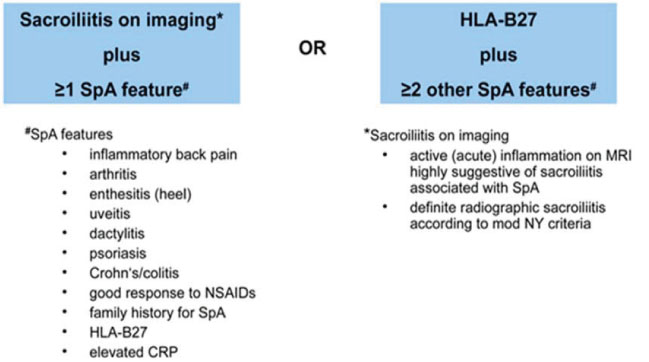
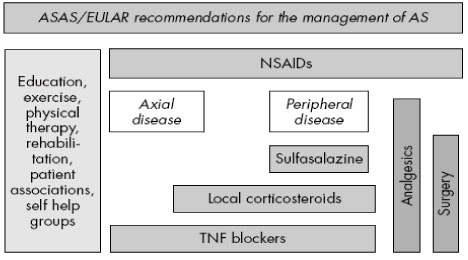
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arnett FC. Seronegative spondylarthropathies. Bull Rheum Dis. 1987. 37:1–12.
Article2. Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey M, James DC, Sturrock RD. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973. 1:904–907.
Article3. Khan MA. HLA-B27 and its subtypes in world populations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1995. 7:263–269.
Article4. Khan MA. Spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1994. 6:351–353.
Article5. Kim TJ, Kim TH. Clinical spectrum of ankylosing spondylitis in Korea. Joint Bone Spine. 2010. 77:235–240.
Article6. Khan MA. Medical and surgical treatment of seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1990. 2:592–599.
Article7. Braun J, de Keyser F, Brandt J, Mielants H, Sieper J, Veys E. New treatment options in spondyloarthropathies: increasing evidence for significant efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13:245–249.
Article8. Braun J, van den Berg R, Baraliakos X, Boehm H, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes-Estevez E, et al. 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:896–904.
Article9. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. 27:361–368.
Article10. Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. 68:777–783.
Article11. Poddubnyy D, Haibel H, Listing J, Marker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, Braun J, et al. Baseline radiographic damage, elevated acute phase reactants and cigarette smoking status predict radiographic progression in the spine in early axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. 64:1388–1398.12. Sieper J. Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, editors. Management of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology. 2008. 4th ed. Edinburgh: Mosby-Elsevier;1143–1164.13. Van Tubergen A, Boonen A, Landewe R, Rutten-Van Molken M, Van Der Heijde D, Hidding A, et al. Cost effectiveness of combined spa-exercise therapy in ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. 47:459–467.
Article14. Wanders A, Heijde D, Landewe R, Behier JM, Calin A, Olivieri I, et al. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs reduce radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:1756–1765.
Article15. Chen J. Is methotrexate effective for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis? Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007. 3:490–491.
Article16. Haibel H, Brandt HC, Song IH, Brandt A, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, et al. No efficacy of subcutaneous methotrexate in active ankylosing spondylitis: a 16-week open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. 66:419–421.
Article17. Chen J, Liu C, Lin J. Methotrexate for ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. CD004524.18. Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Braun J, Sieper J. Six months open label trial of leflunomide in active ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:124–126.19. van Denderen JC, van der Paardt M, Nurmohamed MT, de Ryck YM, Dijkmans BA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE. Double blind, randomised, placebo controlled study of leflunomide in the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1761–1764.
Article20. Goh L, Samanta A. A systematic MEDLINE analysis of therapeutic approaches in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2009. 29:1123–1135.
Article21. Zochling J, van der Heijde D, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes E, Davis JC Jr, Dijkmans B, et al. ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:442–452.
Article22. Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Burmester GR, Sieper J, et al. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2007. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. 66:Suppl 3. iii2–iii22.
Article23. Reddy AR, Backhouse OC. Does etanercept induce uveitis? Br J Ophthalmol. 2003. 87:925.
Article24. Elewaut D, Matucci-Cerinic M. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and extra-articular manifestations in everyday rheumatology practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009. 48:1029–1035.
Article25. Braun J, Kalden JR. Biologics in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009. 27:S164–S167.
Article26. van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Einstein S, Ory P, Vosse D, Ni L, et al. Radiographic progression of ankylosing spondylitis after up to two years of treatment with etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:1324–1331.
Article27. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Godolias G, Bohm H. Therapy of ankylosing spondylitis--a review. Part I: Conventional medical treatment and surgical therapy. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005. 34:97–108.
Article28. Calin A, Elswood J. The outcome of 138 total hip replacements and 12 revisions in ankylosing spondylitis: high success rate after a mean followup of 7.5 years. J Rheumatol. 1989. 16:955–958.
Article29. Gill JB, Levin A, Burd T, Longley M. Corrective osteotomies in spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90:2509–2520.
Article30. Cho WJ, Kang CN, Park YS, Kim HJ, Cho JL. Surgical correction of fixed kyphosis. Asian Spine J. 2007. 1:12–18.
Article31. Song IH, Heldmann F, Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Appel H, Braun J, et al. Different response to rituximab in tumor necrosis factor blocker-naive patients with active ankylosing spondylitis and in patients in whom tumor necrosis factor blockers have failed: a twenty-four-week clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. 62:1290–1297.
Article32. Song IH, Heldmann F, Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Weiss A, Braun J, et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with abatacept: an open-label, 24-week pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:1108–1110.
Article33. Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Sieper J. Open label trial of anakinra in active ankylosing spondylitis over 24 weeks. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:296–298.
Article34. Song IH, Poddubnyy D. New treatment targets in ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011. 23:346–351.
Article35. Cohen JD, Ferreira R, Jorgensen C. Ankylosing spondylitis refractory to tumor necrosis factor blockade responds to tocilizumab. J Rheumatol. 2011. 38:1527.36. Henes JC, Horger M, Guenaydin I, Kanz L, Koetter I. Mixed response to tocilizumab for ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69:2217–2218.37. Dudler J, Aubry-Rozier B. Tocilizumab in axial spondylarthropathies: about 18 cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:Suppl 3. 128.38. Baeten D, Sieper J, Emery P, Braun J, van der Heijde D, McInnes I, et al. The anti-IL17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab (AIN457) showed good safety and efficacy in the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:Suppl 3. 127.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Treatment of Cervical Cord Injury with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Case Report
- Treatment of Cervical Cord Injury in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Orthopaedic Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis