Immune Netw.
2009 Feb;9(1):20-26. 10.4110/in.2009.9.1.20.
Increase of Plasma IL-12/p40 Ratio Induced by the Combined Therapy of DNA Vaccine and Lamivudine Correlates with Sustained Viremia Control in CHB Carriers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Molecular and Life Sciences, Pohang University of Science & Technology, Pohang, Korea. ycsung@postech.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute, Genexine Co. Ltd., Pohang, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2167993
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2009.9.1.20
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: We previously reported that IFN-gamma producing T cell responses induced by the combined therapy of DNA vaccine and lamivudine for one year are important for the induction of sustained virological response (SVR). However, IFN-gamma production is not sufficient to predict sustained viremia control in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) carriers treated.
METHODS
Twelve CHB carriers were intramuscularly immunized 12 times at a 4-week interval with 8 mg of HBV DNA vaccine during the standard lamivudine treatment (100 mg/daily/1 year). The level of cytokines during and after the combined therapy in plasma of all 12 CHB carriers treated was determined by each ELISA kit. Six out of 12 CHB carriers revisited the clinic, and their HBV DNA levels were examined.
RESULTS
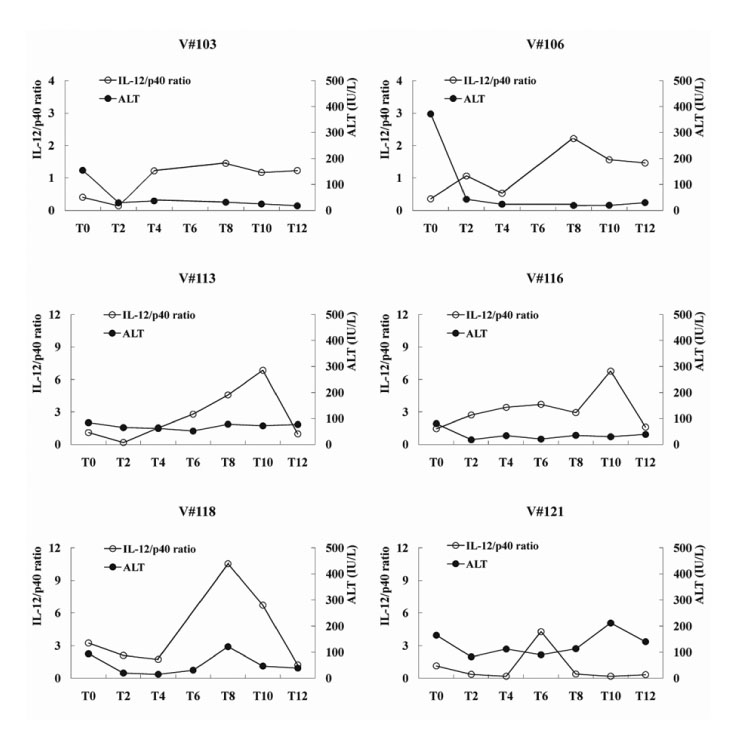
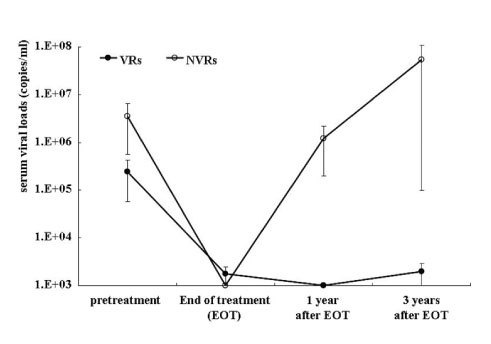
The combined therapy increased plasma IL-12 and IL-12/p40 ratio during the treatment (baseline vs. peak level: 41.8+/-8.3 vs. 163.1+/-29.2 pg/ml; p<0.01 and 0.96+/-0.25 vs. 3.58+/-0.86; p<0.01, espectively), and the peak level of plasma IL-12 and IL-12/p40 ratio was evoked at 6 to 10 months during the combined therapy. In particular, CHB carriers with SVR had two and three-fold higher level of the peak plasma IL-12 and plasma IL-12/p40 ratio than non-virological responders (NVRs), respectively (218.0+/-41.4 vs. 108.1+/-28.6 pg/ml; p=0.09 and 5.35+/-1.38 vs. 1.80+/-0.29; p<0.05, respectively), while p40 level was consistent during the combined therapy. In addition, there was no significant temporal correlation between the peak IL-12/p40 ratio and the elevation of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in this study, contrast to IFN-alpha therapy which induced peak IL-12 level following ALT flares.
CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that the combined therapy induces the increase of plasma IL-12 and IL-12/p40 ratio, which are associated with long-term SVR in CHB carriers.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lok AS, Heathcote EJ, Hoofnagle JH. Management of hepatitis B: 2000--summary of a workshop. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120:1828–1853.
Article2. de Jongh FE, Janssen HL, de Man RA, Hop WC, Schalm SW, van Blankenstein M. Survival and prognostic indicators in hepatitis B surface antigen-positive cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1992. 103:1630–1635.
Article3. Yang SH, Lee CG, Park SH, Im SJ, Kim YM, Son JM, Wang JS, Yoon SK, Song MK, Ambrozaitis A, Kharchenko N, Yun YD, Kim CM, Kim CY, Lee SH, Kim BM, Kim WB, Sung YC. Correlation of antiviral T-cell responses with suppression of viral rebound in chronic hepatitis B carriers: a proof-of-concept study. Gene Ther. 2006. 13:1110–1117.
Article4. Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, Wu PC, Dent JC, Barber J, Stephenson SL, Gray DF. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:61–68.
Article5. Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Cytokine-mediated control of viral infections. Virology. 2000. 273:221–227.
Article6. Chisari FV, Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995. 13:29–60.
Article7. Guidotti LG, McClary H, Loudis JM, Chisari FV. Nitric oxide inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in the livers of transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 2000. 191:1247–1252.
Article8. Heise T, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Characterization of nuclear RNases that cleave hepatitis B virus RNA near the La protein binding site. J Virol. 2001. 75:6874–6883.
Article9. Rossol S, Marinos G, Carucci P, Singer MV, Williams R, Naoumov NV. Interleukin-12 induction of Th1 cytokines is important for viral clearance in chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:3025–3033.
Article10. Cavanaugh VJ, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Interleukin-12 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1997. 71:3236–3243.
Article11. Carreño V, Zeuzem S, Hopf U, Marcellin P, Cooksley WG, Fevery J, Diago M, Reddy R, Peters M, Rittweger K, Rakhit A, Pardo M. A phase I/II study of recombinant human interleukin-12 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2000. 32:317–324.
Article12. Guidotti LG, Ishikawa T, Hobbs MV, Matzke B, Schreiber R, Chisari FV. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity. 1996. 4:25–36.
Article13. Barouch DH, Truitt DM, Letvin NL. Expression kinetics of the interleukin-2/immunoglobulin (IL-2/Ig) plasmid cytokine adjuvant. Vaccine. 2004. 22:3092–3097.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy of Lamivudine and Alpha-interferon Combination Treatment in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Effect and Safety of 12 Week Lamivudine Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Lamivudine therapy for chronic hepatitis B: efficacy, predictive factors for response and relapse rate after treatment
- The Effect of Long-erm Lamivudine Therapy for Chronic Liver Disease due to Hepatitis B Virus
- Co-Immunization of Plasmid DNA Encoding IL-12 and IL-18 with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Vaccine against Progressive Tuberculosis