Clin Endosc.
2014 Jan;47(1):94-100.
Comparison between Midazolam Used Alone and in Combination with Propofol for Sedation during Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mhkim@amc.seoul.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an uncomfortable procedure that requires adequate sedation for its successful conduction. We investigated the efficacy and safety of the combined use of intravenous midazolam and propofol for sedation during ERCP.
METHODS
A retrospective review of patient records from a single tertiary care hospital was performed. Ninety-four patients undergoing ERCP received one of the two medication regimens, which was administered by a nurse under the supervision of a gastroenterologist. Patients in the midazolam (M) group (n=44) received only intravenous midazolam, which was titrated to achieve deep sedation. Patients in the midazolam pulse propofol (MP) group (n=50) initially received an intravenous combination of midazolam and propofol, and then propofol was titrated to achieve deep sedation.
RESULTS
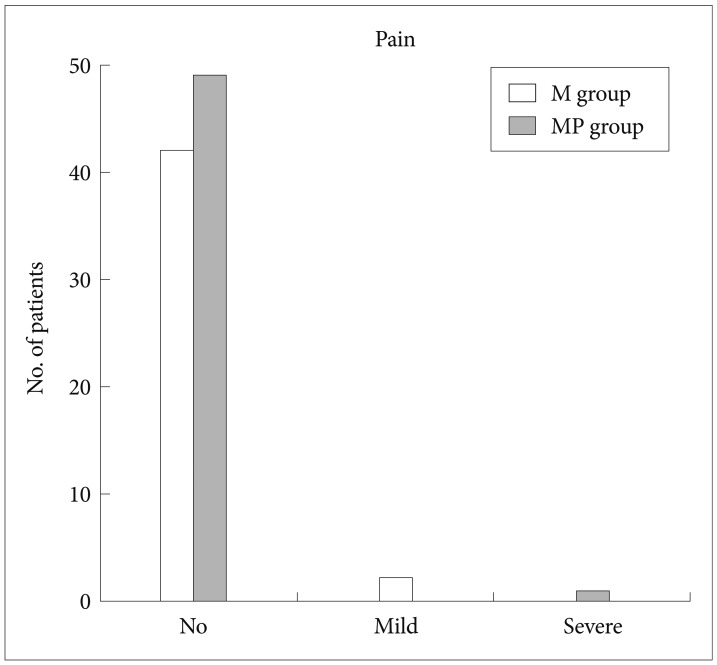
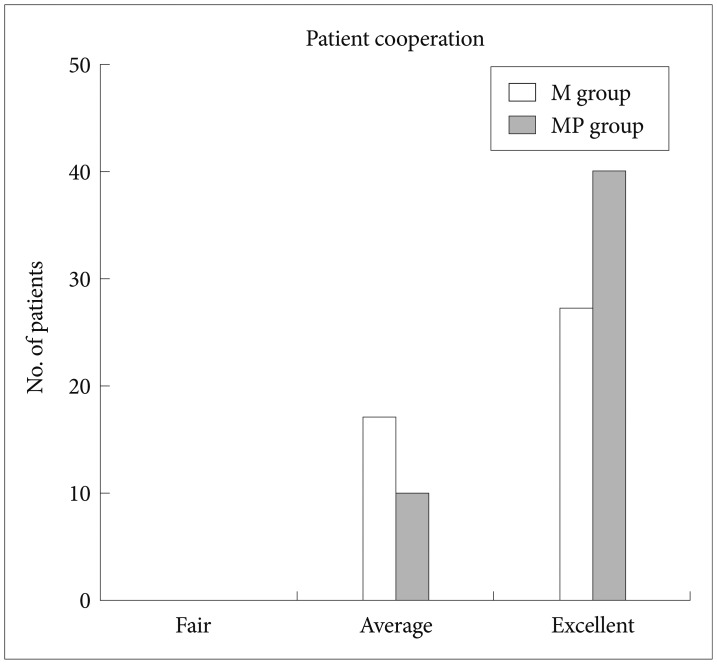
The time to the initial sedation was shorter in the MP group than in the M group (1.13 minutes vs. 1.84 minutes, respectively; p<0.001). The recovery time was faster in the MP group than in the M group (p=0.031). There were no significant differences between the two groups with respect to frequency of adverse events, pain experienced by the patient, patient discomfort, degree of amnesia, and gag reflex. Patient cooperation, rated by the endoscopist as excellent, was greater in the MP group than in the M group (p=0.046).
CONCLUSIONS
The combined use of intravenous midazolam and propofol for sedation during ERCP is more effective than midazolam alone. There is no difference in the safety of the procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garewal D, Waikar P. Propofol sedation for ERCP procedures: a dilemna? Observations from an anesthesia perspective. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012; 2012:639190. PMID: 22272061.
Article2. Walser A, Zenchoff G, Fryer RI. Quinazolines and 1,4-benzodiazepines. 75. 7-Hydroxyaminobenzodiazepines and derivatives. J Med Chem. 1976; 19:1378–1381. PMID: 1003422.
Article3. Garewal D, Powell S, Milan SJ, Nordmeyer J, Waikar P. Sedative techniques for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 6:CD007274. PMID: 22696368.
Article4. Sear JW, Uppington J, Kay NH. Haematological and biochemical changes during anaesthesia with propofol ('Diprivan'). Postgrad Med J. 1985; 61(Suppl 3):165–168. PMID: 3877288.5. Heuss LT, Schnieper P, Drewe J, Pflimlin E, Beglinger C. Conscious sedation with propofol in elderly patients: a prospective evaluation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 17:1493–1501. PMID: 12823151.
Article6. Riphaus A, Stergiou N, Wehrmann T. Sedation with propofol for routine ERCP in high-risk octogenarians: a randomized, controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1957–1963. PMID: 16128939.
Article7. Paspatis GA, Charoniti I, Manolaraki M, et al. Synergistic sedation with oral midazolam as a premedication and intravenous propofol versus intravenous propofol alone in upper gastrointestinal endoscopies in children: a prospective, randomized study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006; 43:195–199. PMID: 16877984.8. Paspatis GA, Manolaraki M, Xirouchakis G, Papanikolaou N, Chlouverakis G, Gritzali A. Synergistic sedation with midazolam and propofol versus midazolam and pethidine in colonoscopies: a prospective, randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:1963–1967. PMID: 12190161.
Article9. Paspatis GA, Manolaraki MM, Vardas E, Theodoropoulou A, Chlouverakis G. Deep sedation for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: intravenous propofol alone versus intravenous propofol with oral midazolam premedication. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:308–313. PMID: 18058653.
Article10. Reimann FM, Samson U, Derad I, Fuchs M, Schiefer B, Stange EF. Synergistic sedation with low-dose midazolam and propofol for colonoscopies. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:239–244. PMID: 10718390.
Article11. Seifert H, Schmitt TH, Gültekin T, Caspary WF, Wehrmann T. Sedation with propofol plus midazolam versus propofol alone for interventional endoscopic procedures: a prospective, randomized study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 14:1207–1214. PMID: 10971238.
Article12. VanNatta ME, Rex DK. Propofol alone titrated to deep sedation versus propofol in combination with opioids and/or benzodiazepines and titrated to moderate sedation for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2209–2217. PMID: 17032185.
Article13. Rex DK, Deenadayalu VP, Eid E, et al. Endoscopist-directed administration of propofol: a worldwide safety experience. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:1229–1237. PMID: 19549528.
Article14. Schilling D, Rosenbaum A, Schweizer S, Richter H, Rumstadt B. Sedation with propofol for interventional endoscopy by trained nurses in high-risk octogenarians: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:295–298. PMID: 19340730.
Article15. Sieg A. Propofol sedation in outpatient colonoscopy by trained practice nurses supervised by the gastroenterologist: a prospective evaluation of over 3000 cases. Z Gastroenterol. 2007; 45:697–701. PMID: 17701858.
Article16. Rex DK, Heuss LT, Walker JA, Qi R. Trained registered nurses/endoscopy teams can administer propofol safely for endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:1384–1391. PMID: 16285939.
Article17. Heuss LT, Schnieper P, Drewe J, Pflimlin E, Beglinger C. Risk stratification and safe administration of propofol by registered nurses supervised by the gastroenterologist: a prospective observational study of more than 2000 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:664–671. PMID: 12709694.
Article18. Bauerle K, Greim CA, Schroth M, Geisselbrecht M, Köbler A, Roewer N. Prediction of depth of sedation and anaesthesia by the Narcotrend EEG monitor. Br J Anaesth. 2004; 92:841–845. PMID: 15064250.19. Marshall SI, Chung F. Discharge criteria and complications after ambulatory surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:508–517. PMID: 10071996.
Article20. Vargo JJ, Zuccaro G Jr, Dumot JA, et al. Gastroenterologist-administered propofol versus meperidine and midazolam for advanced upper endoscopy: a prospective, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:8–16. PMID: 12105827.
Article21. Kongkam P, Rerknimitr R, Punyathavorn S, et al. Propofol infusion versus intermittent meperidine and midazolam injection for conscious sedation in ERCP. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2008; 17:291–297. PMID: 18836622.22. Searle NR, Sahab P. Propofol in patients with cardiac disease. Can J Anaesth. 1993; 40:730–747. PMID: 8403158.
Article23. Wehrmann T, Kokabpick S, Lembcke B, Caspary WF, Seifert H. Efficacy and safety of intravenous propofol sedation during routine ERCP: a prospective, controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49:677–683. PMID: 10343208.
Article24. Veselis RA, Reinsel RA, Feshchenko VA, Wroński M. The comparative amnestic effects of midazolam, propofol, thiopental, and fentanyl at equisedative concentrations. Anesthesiology. 1997; 87:749–764. PMID: 9357875.
Article25. Vargo JJ, Zuccaro G Jr, Dumot JA, Conwell DL, Morrow JB, Shay SS. Automated graphic assessment of respiratory activity is superior to pulse oximetry and visual assessment for the detection of early respiratory depression during therapeutic upper endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:826–831. PMID: 12024135.
Article26. Fanti L, Agostoni M, Casati A, et al. Target-controlled propofol infusion during monitored anesthesia in patients undergoing ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:361–366. PMID: 15332024.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Monitored Anesthesia Care for Sedation during Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
- Comparison of Midazolam Alone versus Midazolam Plus Propofol during Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Appropriate Sedation for Safe Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
- Conscious Sedation During Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Midazolam vs Propofol
- Sedation Regimens for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy