J Vet Sci.
2015 Jun;16(2):151-156. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.2.151.
Involvement of the Ca2+ signaling pathway in osteoprotegerin inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and maturation
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China. liuzongping@yzu.edu.cn
- 2Jiangsu Co-innovation Center for Prevention and Control of Important Animal Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China.
- 3Department of Bioscience, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, China.
- KMID: 2164523
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.2.151
Abstract
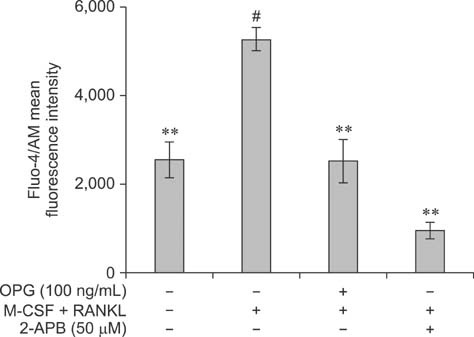
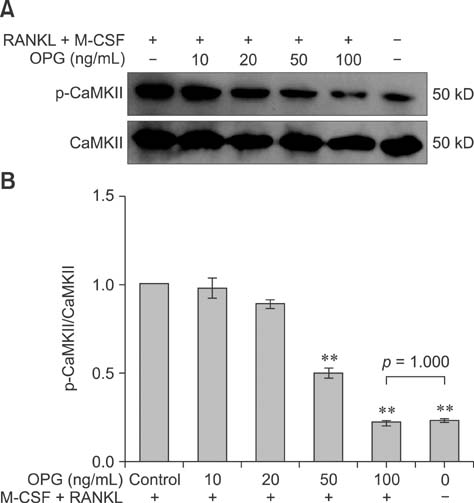
- The purpose of this study was to determine whether the Ca2+ signaling pathway is involved in the ability of osteoprotegerin (OPG) to inhibit osteoclast differentiation and maturation. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) + receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL) to stimulate osteoclastogenesis and then treated with different concentrations of OPG, an inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation. The intracellular Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i and phosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in the different treatment groups were measured by flow cytometry and Western blotting, respectively. The results confirmed that M-CSF + RANKL significantly increased [Ca2+]i and CaMKII phosphorylation in osteoclasts (p < 0.01), and that these effects were subsequently decreased by OPG treatment. Exposure to specific inhibitors of the Ca2+ signaling pathway revealed that these changes varied between the different OPG treatment groups. Findings from the present study indicated that the Ca2+ signaling pathway is involved in both the regulation of osteoclastogenesis as well as inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and activation by OPG.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Calcium/*metabolism
*Calcium Signaling
*Cell Differentiation/drug effects
Cell Line
Cell Survival/drug effects
Gene Expression Regulation/drug effects
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor/metabolism
Mice
Osteoclasts/*cytology/*drug effects/*metabolism
Osteoprotegerin/*pharmacology
RANK Ligand/metabolism
Calcium
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Osteoprotegerin
RANK Ligand
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ang ES, Zhang P, Steer JH, Tan JW, Yip K, Zheng MH, Joyce DA, Xu J. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase activity is required for efficient induction of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Cell Physiol. 2007; 212:787–795.
Article2. Blair HC, Robinson LJ, Zaidi M. Osteoclast signalling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 328:728–738.
Article3. Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003; 423:337–342.
Article4. Chang EJ, Ha J, Huang H, Kim HJ, Woo JH, Lee Y, Lee ZH, Kim JH, Kim HH. The JNK-dependent CaMK pathway restrains the reversion of committed cells during osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2008; 121:2555–2564.
Article5. Di Capite J, Ng SW, Parekh AB. Decoding of cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations through the spatial signature drives gene expression. Curr Biol. 2009; 19:853–858.
Article6. Feng X. Regulatory roles and molecular signaling of TNF family members in osteoclasts. Gene. 2005; 350:1–13.
Article7. Fu YX, Gu JH, Zhang YR, Tong XS, Zhao HY, Yuan Y, Liu XZ, Bian JC, Liu ZP. Osteoprotegerin influences the bone resorption activity of osteoclasts. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 31:1411–1417.
Article8. Hofbauer LC, Kühne CA, Viereck V. The OPG/RANKL/RANK system in metabolic bone diseases. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2004; 4:268–275.9. Hwang SY, Putney JW Jr. Calcium signaling in osteoclasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011; 1813:979–983.
Article10. Jansen ID, Vermeer JA, Bloemen V, Stap J, Everts V. Osteoclast fusion and fission. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012; 90:515–522.
Article11. Joseph SK, Hajnóczky G. IP3 receptors in cell survival and apoptosis: Ca2+ release and beyond. Apoptosis. 2007; 12:951–968.
Article12. Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E. AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997; 9:240–246.
Article13. Kim MS, Yang YM, Son A, Tian YS, Lee SI, Kang SW, Muallem S, Shin DM. RANKL-mediated reactive oxygen species pathway that induces long lasting Ca2+ oscillations essential for osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:6913–6921.
Article14. Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, Taniguchi T, Takayanagi H, Takai T. Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature. 2004; 428:758–763.
Article15. Mentaverri R, Kamel S, Brazier M. Involvement of capacitive calcium entry and calcium store refilling in osteoclastic survival and bone resorption process. Cell calcium. 2003; 34:169–175.
Article16. Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P. Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2003; 4:552–565.
Article17. Penzes P, Cahill ME, Jones KA, Srivastava DP. Convergent CaMK and RacGEF signals control dendritic structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2008; 18:405–413.
Article18. Seales EC, Micoli KJ, McDonald JM. Calmodulin is a critical regulator of osteoclastic differentiation, function, and survival. J Cell Biochem. 2006; 97:45–55.
Article19. Silver IA, Murrills RJ, Etherington DJ. Microelectrode studies on the acid microenvironment beneath adherent macrophages and osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1988; 175:266–276.
Article20. Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R, Boyle WJ. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997; 89:309–319.
Article21. Soderling TR, Chang B, Brickey D. Cellular signaling through multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:3719–3722.
Article22. Soderling TR, Stull JT. Structure and regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Chem Rev. 2001; 101:2341–2352.
Article23. Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H, Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Kodama T, Taniguchi T. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002; 3:889–901.
Article24. Teitelbaum SL. Bone remodeling and the osteoclast. J Bone Miner Res. 1993; 8:Suppl 2. S523–S525.
Article25. Yao CH, Zhang P, Zhang L. Differential protein and mRNA expression of CaMKs during osteoclastogenesis and its functional implications. Biochem Cell Biol. 2012; 90:532–539.
Article26. Zaidi M, Shankar VS, Bax CMR, Bax BE, Bevis PJR, Pazianas M, Alam ASM, Moonga BS, Huang CLH. Linkage of extracellular and intracellular control of cytosolic Ca2+ in rat osteoclasts in the presence of thapsigargin. J Bone Miner Res. 1993; 8:961–967.
Article27. Zhang L, McKenna MA, Said-Al-Naief N, Wu X, Feng X, McDonald JM. Osteoclastogenesis: the role of calcium and calmodulin. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2005; 15:1–13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Signaling Pathways in Osteoclast Differentiation
- Anti-Müllerian Hormone Negatively Regulates Osteoclast Differentiation by Suppressing the Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand Pathway
- Effects of Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate on Osteoclast Differentiation in RANKL-induced Osteoclastogenesis
- High extracellular Ca2+ alone stimulates osteoclast formation but inhibits in the presence of other osteoclastogenic factors
- Expression of Osteoprotegerin and Osteoclast Differentiation Factor in Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblast Cells