Korean J Perinatol.
2016 Mar;27(1):60-66. 10.14734/kjp.2016.27.1.60.
RSV Outbreak at a Single Postpartum Care Center in Gyeongsangbukdo
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. csm21@dongguk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2164270
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2016.27.1.60
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We performed an analysis of the RSV outbreak in a postpartum center in Gyeongsangbukdo to provide preliminary data for health and hygiene management of postpartum care centers.
METHODS
All of 22 newborns who were transferred to our hospital from a postpartum care center from December 2014 to January 2015 showed positive for RSV by viral culture and enrolled in the study group. To identify early symptoms in RSV infected newborn in the nursery 31 infants (1 month to 24 month of age) who were hospitalized in our hospital due to RSV infection during the same period were selected as control group and clinical symptoms were compared with the study group. A retrospective study was also performed on the newborns who were cared and not transferred to our hospital in the postpartum care center, as well as the facilities offered by the center.
RESULTS
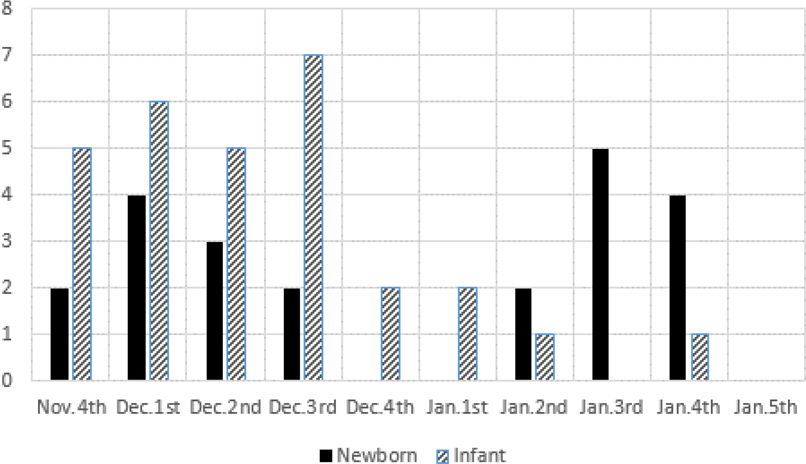
All of 22 neonatal patients who were transferred to our hospital had early symptoms of rhinorrhea and cough compared to control group. Rhinorrhea appeared 4.2±2.0 days before the admission, and cough occurred 1.0±1.1 days after rhinorrhea. The level of infection control specified by the law for general facilities relating to postpartum care centers was applied to the postpartum center, RSV infection was not controlled. Strict hand washing, individual equipment such as stethoscopes and exclusion of visitors with respiratory symptoms were done and infected neonates were segregated in separate air circulation system and cared by nurse-infant ratios from 1:1 to 1:2 depending on the needs of the individual neonates. Additional transmission was not observed after transfer to our hospital
CONCLUSION
Neonates with cough and rhinorrhea were initial symptom for RSV infection in the postpartum center and should be evaluated for RSV infection during high risk season. Current guideline or support for infection control in postpartum center should be reevaluated for RSV infection control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Development and Evaluation of an Infection Control Education Program for Postpartum Care Workers
Sung Ran Kim, Su Hyun Kim, Hee Jung Son, Nan Hyoung Cho, Kyeong Sook Cha, Hee Kyung Chun, Jong Rim Choi, Hae Kyung Hong
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2019;24(2):60-68. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2019.24.2.60.Associated Factors with Respiratory Virus Detection in Newborn with Suspected Infection
Jin-Hyeok Lee, Sun-Young Cho, Myo-Jing Kim
Perinatology. 2017;28(4):134-139. doi: 10.14734/PN.2017.28.4.134.
Reference
-
1). Ahn JG., Choi SY., Kim DS., Kim KH. A Nationwide survey on the child day care and common infectious diseases. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2012. 19:19–27.
Article2). Stensballe LG., Devasundaram JK., Simoes EA. Respiratory syncytial virus epidemics the ups and downs of a seasonal virus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:21–32.
Article3). Hall CB. Nosocomial respiratory syncytial virus infections: the “cold war” has not ended. Clin Infect Dis. 2000. 31:590–6.
Article4). Department of Health and Human Services. Infection control guidelines for postpartum care centers. Seoul: The Department;2013.5). Fair Trade Commission. Consumer report: Illness, injury occurred in postpartum care center. Fair Trade Commission 2014 Nov.6). Yoo EK. Development of wise sanhujori guideline. Seoul: National Health Report;2013. Contact No.: Jung Chack 13-32. Sponsored by the Korea Institute of Child Care and Education.7). Garcia CG., Bhore R., Soriano-Fallas A., Trost M., Chason R., Ramilo O, et al. Risk factors in children hospitalized with RSV bronchiolitis versus non-RSV bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 2010. 126:e1453–60.
Article8). Eem YJ., Bae EY., Lee JH., Jeong DC. Risk factors associated with respiratory virus detection in infants younger than 90 days of age. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2014. 21:22–8.
Article9). Hacimustagaoglu M., Celebi S., Bozdemir SE., Ozgur T., Ozcan I., Guray A, et al. RSV frequency in children below 2 years hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infections. Turkish J Pediatr. 2013. 55:130–9.10). Hall CB. Nosocomial viral respiratory infections: perennial weeds on pediatric wards. Am J Med. 1981. 70:670–6.
Article11). Nagayama Y., Tsubaki T., Nakayama S., Sawada K., Taguchi K., Tateno N, et al. Gender analysis in acute bronchiolitis due to respiratory syncytial virus. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2006. 17:29–36.
Article12). Cho JI., Choi HC., Kim JD., Cho JH. The clinical study of the lower respiratory tract infection by respiratory syncytial virus on children under 2 year of age. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. 7:193–200.
Article13). Lim IS., Shim Mj., Kim BE., Chung JY., Kim CK., Chey MJ, et al. A comparison of clinical manifestations in neonates and infants infected by respiratory syncytial virus. Korean J Pediatr. 2004. 47:949–52.14). Hall CB., Douglas RG Jr., Geiman JM. Respiratory syncytial virus infections in infants: quantitation and duration of shedding. J Pediatr. 1976. 89:11–5.
Article15). Shay DK., Holman RC., Roosevelt GE., Clarke MJ., Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis-associated mortality and estimates of respiratory syncytial virus-associated deaths among US children 1979-1997. J Infect Dis. 2001. 183:16–22.
Article16). Halasa NB., Williams JV., Wilson GJ., Walsh WF., Schaffner W., Wright PF. Medical and economic impact of a respiratory syncytial virus outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:1040–1044.
Article17). Siegel JD., Rhinehart E., Jackson M., Chiarello L. 2007 Guideline for isolation precautions: preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. Am J Infect Control. 2007. 35(10 Suppl 2):S65–164.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Outbreak at Postpartum Care Center in Busan, Korea
- Development and Validation of a Postpartum Care Mobile Application for First-time Mothers
- Effects of a Postpartum Care Program for Postpartum Women on Postpartum Activity and Postpartum Discomfort in Primiparous Women
- RSV Prevention Strategies in Korean Children: A Review of Current Approaches and Emerging Options
- Clinical Features of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Neonates: A Single Center Study