J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Aug;19(4):541-546. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.4.541.
Detection of YMDD Motif Mutants by Oligonucleotide Chips in Lamivudine-Untreated Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. mcho@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology, Pusan National University College of Natural Science, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2157683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.4.541
Abstract
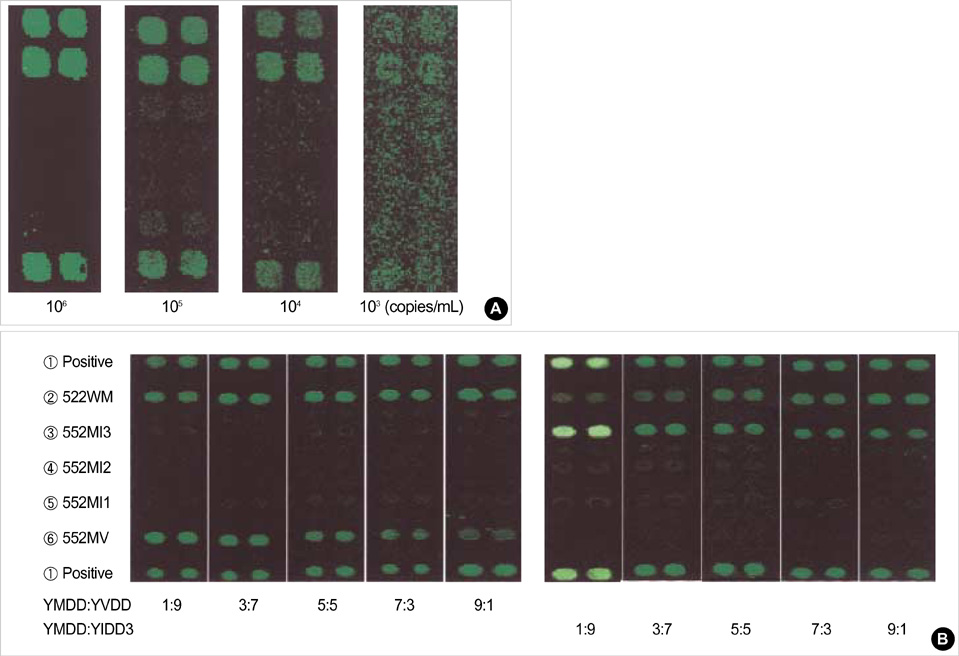
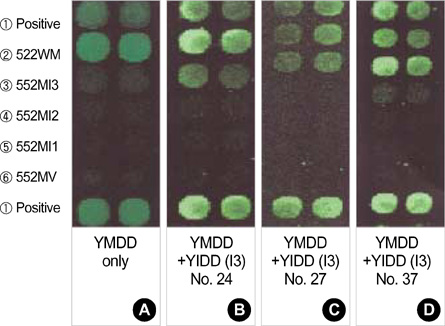
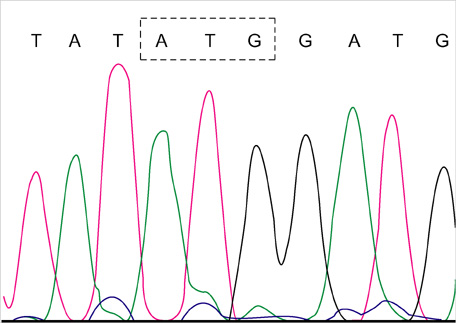
- Lamivudine, a nucleoside analogue, has been used widely as an effective antiviral agent for the treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. However, the YMDD motif mutation of HBV polymerase resistant to lamivudine occurs very frequently after long term therapy. We developed an oligonucleotide chip for the detection of YMDD motif mutants resistant to lamivudine and investigated the prevalence of the mutants in patients with chronic HBV infection who had not been treated by lamivudine before. Forty patients who had not been treated with lamivudine were included in this study. Serum samples were tested by the oligonucleotide chips designed for detection of wild-type YMDD motif, M552V and M552I. Samples were confirmed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and direct sequencing. M552I mutants were detected by the oligonucleotide chips in 7.5% (3/40) of chronic HBV infected patients (2 chronic hepatitis and 1 cirrhosis). The results were in accordance with those of RFLP. YMDD motif mutants occur as natural genome variabilities in patients with chronic HBV infection who had not been treated with lamivudine before. Oligonucleotide chip technology is a reliable and useful diagnostic tool for the detection of mutants resistant to antiviral therapy in chronic HBV infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
*Amino Acid Motifs
Chronic Disease
Female
Hepatitis B/*drug therapy
Hepatitis B virus/*genetics
Humans
Lamivudine/*therapeutic use
Male
Middle Aged
Mutation
*Oligonucleotide Array Sequence Analysis
Polymorphism, Restriction Fragment Length
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors/*therapeutic use
Sensitivity and Specificity
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Variation (Genetics)
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liaw YF, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, Chien RN, Dent J, Roman L, Edmundson S, Lai CL. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. Effects of extended lamivudine therapy in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2000. 119:172–180.
Article2. Leung NW, Lai CL, Chang TT, Guan R, Lee CM, Ng KY, Lim SG, Wu PC, Dent JC, Edmundson S, Condreay LD, Chien RN. On behalf of the Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. Extended lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion rates: results after 3 years of therapy. Hepatology. 2001. 33:1527–1532.
Article3. Lau DT, Khokhar MF, Doo E, Ghany MG, Herion D, Park Y, Kleiner DE, Schmid P, Condreay LD, Gauthier J, Kuhns MC, Liang TJ, Hoofnagle JH. Long-term therapy of chronic hepatitis B with lamivudine. Hepatology. 2000. 32:828–834.4. Chayama K, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi M, Tsubota A, Hashimoto M, Miyano Y, Koike H, Kobayashi M, Koida I, Arase Y, Saitoh S, Murashima N, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Emergence and takeover of YMDD motif mutant hepatitis B virus during long-term lamivudine therapy and re-takeover by wild type after cessation of therapy. Hepatology. 1998. 27:1711–1716.
Article5. Paik YH, Chung HY, Ryu WS, Lee KS, Lee JS, Kim JH, Lee CK, Chon CY, Moon YM, Han KH. Emergence of YMDD motif mutant of hepatitis B virus during short-term lamivudine therapy in South Korea. J Hepatol. 2001. 35:92–98.
Article6. Perrillo R, Rakela J, Dienstag J, Levy G, Martin P, Wright T, Caldwell S, Schiff E, Gish R, Villeneuve JP, Farr G, Anschuetz G, Crowther L, Brown N. Lamivudine Transplant Group. Multicenter study of lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1999. 29:1581–1586.
Article7. Liaw YF, Chien RN, Yeh CT, Tsai SL, Chu CM. Acute exacerbation and hepatitis B virus clearance after emergence of YMDD motif mutation during lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 1999. 30:567–572.
Article8. Nafa S, Ahmed S, Tavan D, Pichoud C, Berby F, Stuyver L, Johnson M, Merle P, Abidi H, Trepo C, Zoulim F. Early detection of viral resistance by determination of hepatitis B virus polymerase mutations in patients treated by lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2000. 32:1078–1088.
Article9. Mikhailovich V, Lapa S, Gryadunov D, Sobolev A, Strizhkov B, Chernyh N, Skotnikova O, Irtuganova O, Moroz A, Litvinov V, Vladimirskii M, Perelman M, Chernousova L, Erokhin V, Zasedatelev A, Mirzabekov A. Identification of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by hybridization, PCR, and lipase detection reaction on oligonucleotide microchips. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:2531–2540.10. Zoulim F. Detection of hepatitis B virus resistance to antivirals. J Clin Virol. 2001. 21:243–253.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pattern of Mutations in Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase Gene during Lamivudine Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- The Comparison of Restriction Fragment Mass Polymorphism Method with Sequecing Method for the Detection of HBV YMDD Mutants
- Detection of HBV YMDD Mutation by Sequencing Method
- Natural YMDD Motif Mutations of HBV Polymerase in the Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Patients
- Emergence of YMDD Motif Mutant Hepatitis B Virus during Short-erm Lamivudine Therapy