Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):398-402. 10.4143/crt.2014.254.
SEC31A-ALK Fusion Gene in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Tumor Microenvironment Global Core Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ylachoi@skku.edu
- 4Laboratory of Cancer Genomics and Molecular Pathology, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences & Technology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Oncology Research Unit, Pfizer Worldwide Research and Development, San Diego, CA, USA.
- 7Enzymatics, Boulder, CO, USA.
- 8Department of Thoracic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhingookkim@gmail.com
- 9Department of Pathology, Baylor University Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX, USA.
- 10Department of Human Genetics, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
- KMID: 2152299
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.254
Abstract
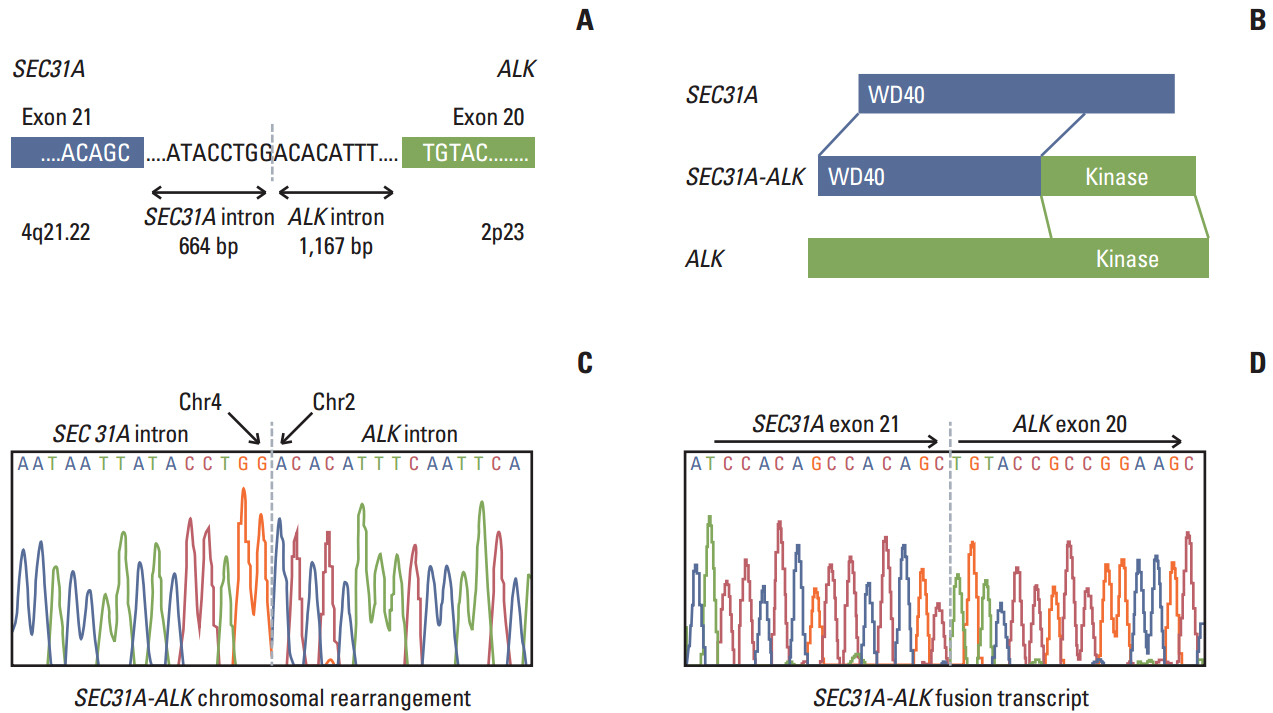
- Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion is a common mechanism underlying pathogenesis of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) where these rearrangements represent important diagnostic and therapeutic targets. In this study, we found a new ALK fusion gene, SEC31A-ALK, in lung carcinoma from a 53-year-old Korean man. The conjoined region in the fusion transcript was generated by the fusion of SEC31A exon 21 and ALK exon 20 by genomic rearrangement, which contributed to generation of an intact, in-frame open reading frame. SEC31A-ALK encodes a predicted fusion protein of 1,438 amino acids comprising the WD40 domain of SEC31A at the N-terminus and ALK kinase domain at the C-terminus. Fluorescence in situ hybridization studies suggested that SEC31A-ALK was generated by an unbalanced genomic rearrangement associated with loss of the 3'-end of SEC31A. This is the first report of SEC31A-ALK fusion transcript in clinical NSCLC, which could be a novel diagnostic and therapeutic target for patients with NSCLC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ardini E, Magnaghi P, Orsini P, Galvani A, Menichincheri M. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in specific tumours, and development of small molecule inhibitors for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2010; 299:81–94.
Article2. Webb TR, Slavish J, George RE, Look AT, Xue L, Jiang Q, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in cancer pathogenesis and small-molecule inhibitor development for therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009; 9:331–56.
Article3. Drexler HG, Gignac SM, von Wasielewski R, Werner M, Dirks WG. Pathobiology of NPM-ALK and variant fusion genes in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and other lymphomas. Leukemia. 2000; 14:1533–59.
Article4. Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007; 448:561–6.
Article5. Hong M, Kim RN, Song JY, Choi SJ, Oh E, Lira ME, et al. HIP1-ALK, a novel fusion protein identified in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:419–22.
Article6. Choi YL, Lira ME, Hong M, Kim RN, Choi SJ, Song JY, et al. A novel fusion of TPR and ALK in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:563–6.
Article7. Van Roosbroeck K, Cools J, Dierickx D, Thomas J, Vandenberghe P, Stul M, et al. ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas with cryptic SEC31A-ALK and NPM1-ALK fusions. Haematologica. 2010; 95:509–13.
Article8. Bedwell C, Rowe D, Moulton D, Jones G, Bown N, Bacon CM. Cytogenetically complex SEC31A-ALK fusions are recurrent in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas. Haematologica. 2011; 96:343–6.
Article9. Panagopoulos I, Nilsson T, Domanski HA, Isaksson M, Lindblom P, Mertens F, et al. Fusion of the SEC31L1 and ALK genes in an inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Int J Cancer. 2006; 118:1181–6.
Article10. Lira ME, Kim TM, Huang D, Deng S, Koh Y, Jang B, et al. Multiplexed gene expression and fusion transcript analysis to detect ALK fusions in lung cancer. J Mol Diagn. 2013; 15:51–61.
Article11. Mathew P, Sanger WG, Weisenburger DD, Valentine V, Pickering D, et al. Detection of the t(2;5)(p23;q35) and NPM-ALK fusion in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma by two-color fluorescence in situ hybridization. Blood. 1997; 89:1678–85.12. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1693–703.13. Ou SH, Bartlett CH, Mino-Kenudson M, Cui J, Iafrate AJ. Crizotinib for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: a success story to usher in the second decade of molecular targeted therapy in oncology. Oncologist. 2012; 17:1351–75.
Article14. Tang BL, Zhang T, Low DY, Wong ET, Horstmann H, Hong W. Mammalian homologues of yeast sec31p: an ubiquitously expressed form is localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit sites and is essential for ER-Golgi transport. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:13597–604.15. Shugrue CA, Kolen ER, Peters H, Czernik A, Kaiser C, Matovcik L, et al. Identification of the putative mammalian orthologue of Sec31P, a component of the COPII coat. J Cell Sci. 1999; 112(Pt 24):4547–56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Korean Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Simultaneously Diagnosed Lung Adenocarcinoma and Endobronchial Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor with Two Distinct Types of ALK Translocation
- Bilateral Ovarian Metastases from ALK Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-expressing Lung Adenocarcinoma with Combined Neuroendocrine Component or Neuroendocrine Transformation: Implications for Neuroendocrine Transformation and Response to ALK-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- A case of concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration against a mutated EGFR background in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma