Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):180-189. 10.4143/crt.2014.321.
The Prognostic Role of Mitotic Index in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients after Curative Hepatectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckpark@skku.edu
- KMID: 2152274
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.321
Abstract
- PURPOSE
High proliferation rate is a hallmark of cancer. The mitotic index is a useful and simple method for analysis of cell proliferation. However, the practical utility of mitotic index as a predictor of prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been determined. Therefore, we examined mitotic index as a prognostic marker in HCC patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
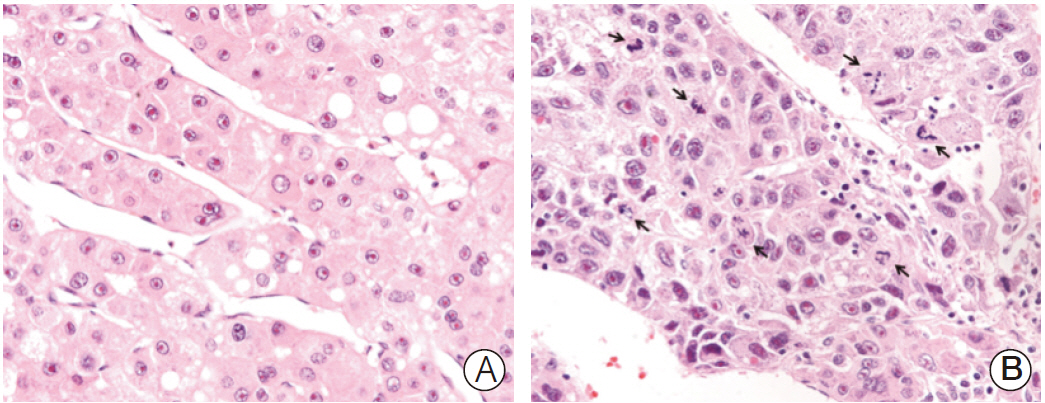
We counted the number of mitotic cells in 10 high-power fields of the tumor area on hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides representing 282 surgically resected HCCs. The highest number of mitotic cells was defined as the mitotic index.
RESULTS
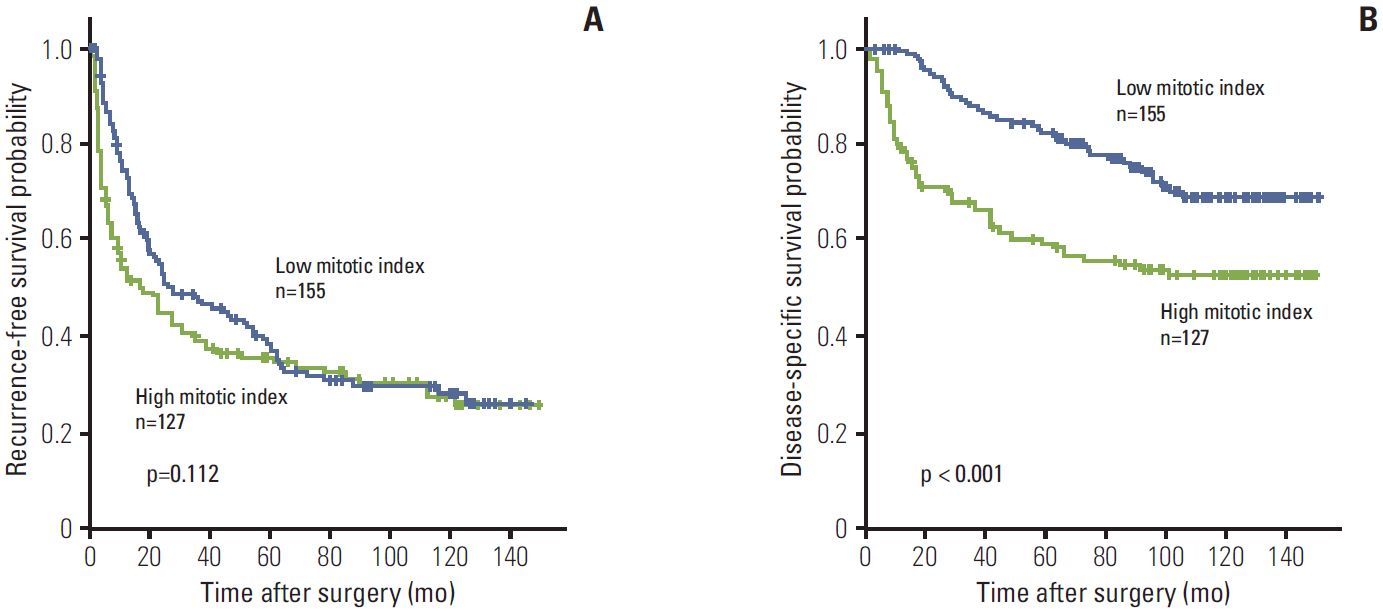
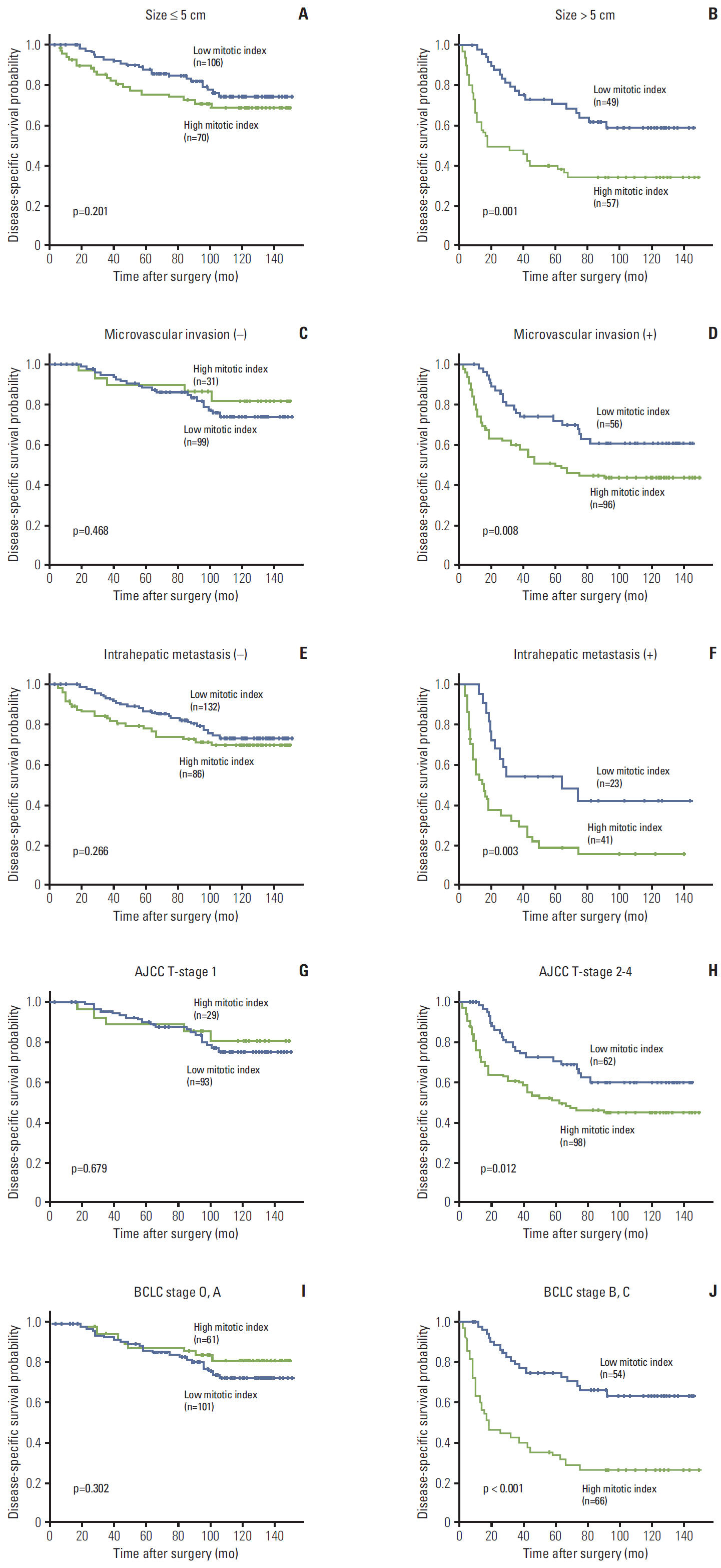
High mitotic index was observed in 127 of 282 HCCs. High mitotic index showed significant association with younger age, larger tumor size, higher Edmondson grade, microvascular invasion, major portal vein invasion, intrahepatic metastasis, higher American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) T-stage, higher Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage, higher alpha-fetoprotein level, hepatitis B virus etiology, and liver cirrhosis. Patients with high mitotic index had shorter disease-specific survival (DSS) (p < 0.001) and tended to have shorter recurrence-free survival (p=0.112). In subgroup analysis among patients with a larger tumor size, microvascular invasion, intrahepatic metastasis, higher AJCC T-stage, and higher BLCL stage, high mitotic index showed unfavorable influences on DSS (p=0.001, p=0.008, p=0.003, p=0.012, and p < 0.001, respectively). In addition, high mitotic index was an independent predictor of shorter DSS (p=0.004).
CONCLUSION
High mitotic index may be a novel predictor of DSS in patients with HCC and may have utility as an auxiliary prognostic factor in HCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, et al. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer. 1985; 56:918–28.
Article2. Llovet JM, Schwartz M, Mazzaferro V. Resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2005; 25:181–200.
Article3. Poon RT. Prevention of recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a daunting challenge. Hepatology. 2011; 54:757–9.
Article4. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000; 100:57–70.
Article5. Ouchi K, Sugawara T, Ono H, Fujiya T, Kamiyama Y, Kakugawa Y, et al. Mitotic index is the best predictive factor for survival of patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Surg. 2000; 17:42–8.
Article6. Tannapfel A, Geissler F, Kockerling F, Katalinic A, Hauss J, Wittekind C. Apoptosis and proliferation in relation to histopathological variables and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pathol. 1999; 187:439–45.
Article7. Romani AA, Crafa P, Desenzani S, Graiani G, Lagrasta C, Sianesi M, et al. The expression of HSP27 is associated with poor clinical outcome in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:232.
Article8. Bloom HJ, Richardson WW. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer: a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957; 11:359–77.9. Vang R, Shih Ie M, Kurman RJ. Ovarian low-grade and high-grade serous carcinoma: pathogenesis, clinicopathologic and molecular biologic features, and diagnostic problems. Adv Anat Pathol. 2009; 16:267–82.10. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A 3rd. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. Chicago, IL: Springer;2010. p. 191–5.11. Haratake J, Takeda S, Kasai T, Nakano S, Tokui N. Predictable factors for estimating prognosis of patients after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1993; 72:1178–83.
Article12. Nanashima A, Tanaka K, Yamaguchi H, Shibasaki S, Morino S, Yoshinaga M, et al. Fibrosis and inflammatory activity in noncancerous tissue and mitotic index of cancer tissue in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship to clinicopathological factors and prognosis after hepatic resection. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:1517–22.13. Edmondson HA, Steiner PE. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954; 7:462–503.14. Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. General rules for the clinical and pathological study of primary liver cancer. 2nd ed. Tokyo: Kanehara;2003.15. Shimada M, Hamatsu T, Yamashita Y, Rikimaru T, Taguchi K, Utsunomiya T, et al. Characteristics of multicentric hepatocellular carcinomas: comparison with intrahepatic metastasis. World J Surg. 2001; 25:991–5.
Article16. Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003; 38:200–7.
Article17. Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999; 19:329–38.
Article18. Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Kobayashi M, Peix J, Chiang DY, Camargo A, et al. Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1995–2004.
Article19. Baak JP. Mitosis counting in tumors. Hum Pathol. 1990; 21:683–5.
Article20. Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bioinformatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:7252–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two-Stage Hepatectomy for Bilateral Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombi
- Prognostic Factors and Clinicopathologic Features after Resection of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma (< or =2 cm)
- Impact of prognostic nutritional index on the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a curative resection
- Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status Score in Patients Who Underwent Hepatic Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Fibrosis-4 index, a predictor for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after curative hepatectomy even in hepatitis B virus dominant populations