Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2021 Nov;25(4):456-461. 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.456.
Impact of prognostic nutritional index on the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a curative resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Dankook University Hospital, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- KMID: 2523048
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.456
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
The purpose of this retrospective study was to determine the association between prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a curative resection.
Methods
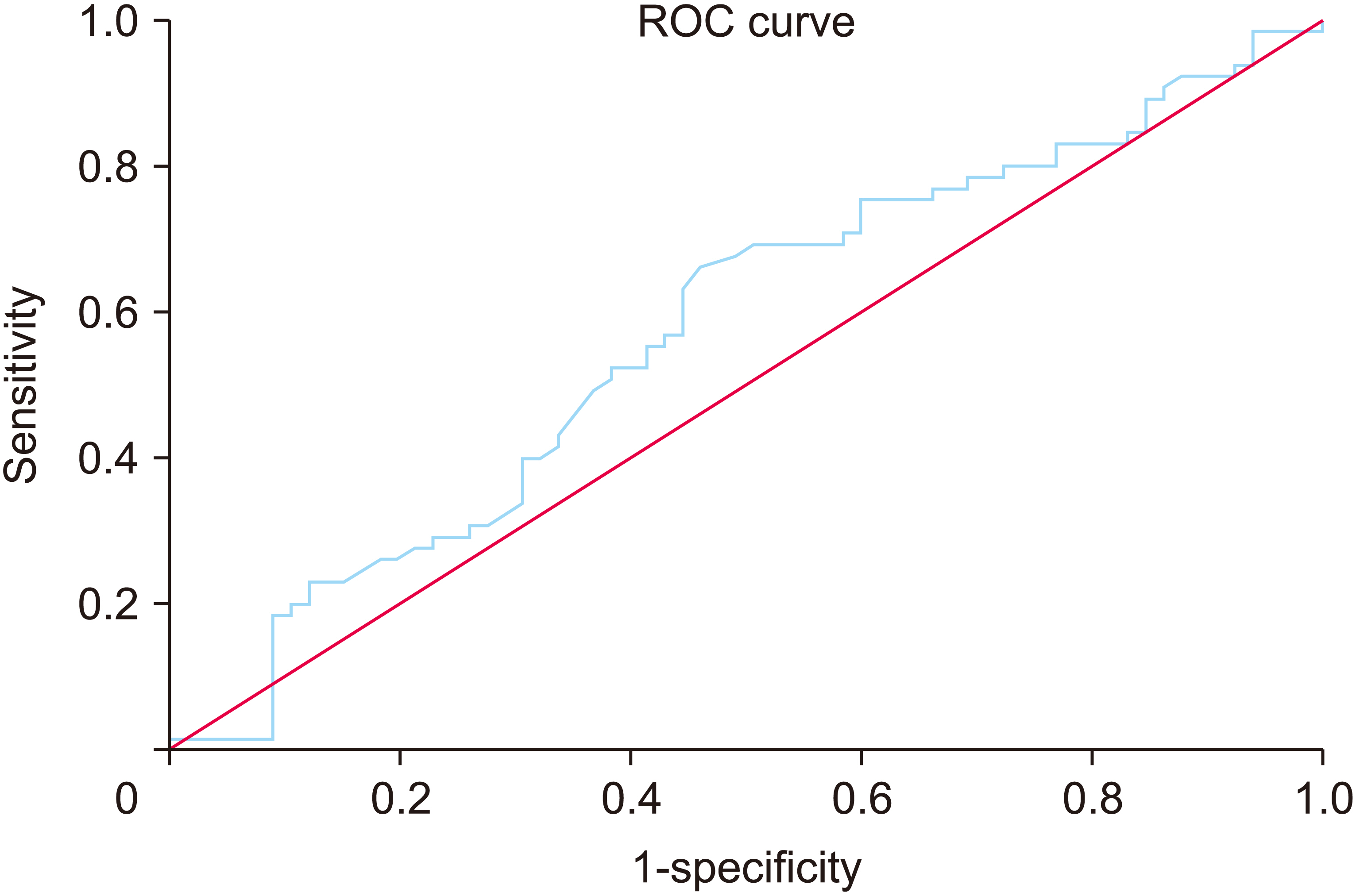
Between 2007 to 2019, 130 patients who underwent curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma were enrolled. PNI was calculated. Its cutoff value was identified through receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. According to PNI, patients were divided into two groups. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify independent risk factors for recurrence.
Results
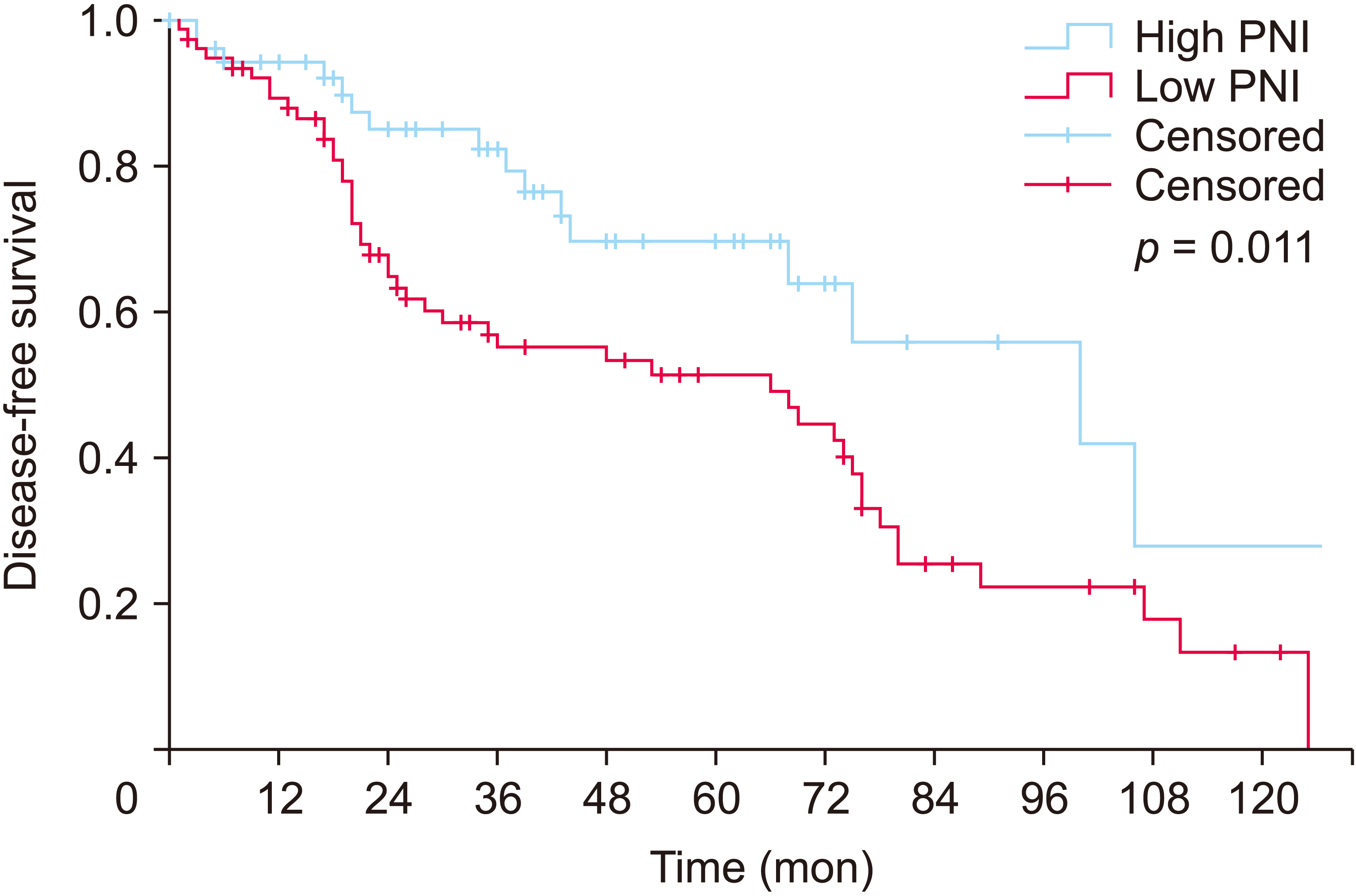
The cutoff value of PNI was 52. In univariate analysis, alcoholic liver cirrhosis (p = 0.041), protein induced by vitamin K antagonist-II ≥ 200 (p = 0.012), indocyanine green retention test (ICG R15) >10% (p = 0.001), estimated blood loss ≥ 800 mL (p = 0.037), tumor size (p = 0.001), microvascular invasion (p = 0.023), T-stage (p = 0.001), and PNI < 52 (p = 0.001) were significant factors affecting the recurrence. In multivariate analysis, alcoholic liver cirrhosis (p = 0.046), ICG R15 >10% (p = 0.025), T-stage (p = 0.003), and PNI < 52 (p = 0.046) were independent prognostic factors for disease-free survival.
Conclusions
PNI, a nutritional and immunologic factor, is an independent prognostic factor that can predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients undergoing a curative resection.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. 2015; Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.29210. PMID: 25220842.
Article2. European Association For The Study Of The Liver; European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. 2012; EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:908–943. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001. PMID: 22424438.3. Muscari F, Foppa B, Carrere N, Kamar N, Peron JM, Suc B. 2011; Resection of a transplantable single-nodule hepatocellular carcinoma in Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis: factors affecting survival and recurrence. World J Surg. 35:1055–1062. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-011-1000-3. PMID: 21360309.
Article4. Naito S, Imamura H, Tukada A, Matsuyama Y, Yoshimoto J, Sugo H, et al. 2014; Postoperative recurrence pattern and prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, with particular reference to the hepatitis viral infection status. Liver Int. 34:802–813. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12447. PMID: 24350618.
Article5. Lim KC, Chow PK, Allen JC, Chia GS, Lim M, Cheow PC, et al. 2011; Microvascular invasion is a better predictor of tumor recurrence and overall survival following surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. 254:108–113. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31821ad884. PMID: 21527845.
Article6. Zhu WJ, Huang CY, Li C, Peng W, Wen TF, Yan LN, et al. 2013; Risk factors for early recurrence of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma meeting milan criteria after curative resection. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7101–7106. DOI: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.12.7101. PMID: 24460258.
Article7. Park SK, Jung YK, Chung DH, Kim KK, Park YH, Lee JN, et al. 2013; Factors influencing hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis after hepatectomy: a single-center experience. Korean J Intern Med. 28:428–438. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.4.428. PMID: 23864801. PMCID: PMC3712151.
Article8. Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. 2010; Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025. PMID: 20303878. PMCID: PMC2866629.
Article9. Onodera T, Goseki N, Kosaki G. 1984; [Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients]. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 85:1001–1005. Japanese. PMID: 6438478.10. Mohri Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Hiro J, Uchida K, Kusunoki M. 2013; Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative outcome in colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 37:2688–2692. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-013-2156-9. PMID: 23884382.
Article11. Hong YM, Cho M, Yoon KT, Chu CW, Yang KH, Park YM, et al. 2017; Risk factors of early recurrence after curative hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:1010428317720863. DOI: 10.1177/1010428317720863. PMID: 29034775.
Article12. Gabrielson A, Wu Y, Wang H, Jiang J, Kallakury B, Gatalica Z, et al. 2016; Intratumoral CD3 and CD8 T-cell densities associated with relapse-free survival in HCC. Cancer Immunol Res. 4:419–430. DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0110. PMID: 26968206. PMCID: PMC5303359.
Article13. Wu SJ, Lin YX, Ye H, Li FY, Xiong XZ, Cheng NS. 2016; Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index predict survival outcomes of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients after curative hepatectomy. J Surg Oncol. 114:202–210. DOI: 10.1002/jso.24297. PMID: 27199001.
Article14. Liu Y, Wang ZX, Cao Y, Zhang G, Chen WB, Jiang CP. 2016; Preoperative inflammation-based markers predict early and late recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 15:266–274. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(16)60094-2. PMID: 27298102.
Article15. Goh BK, Kam JH, Lee SY, Chan CY, Allen JC, Jeyaraj P, et al. 2016; Significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutrition index as preoperative predictors of early mortality after liver resection for huge (≥10 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 113:621–627. DOI: 10.1002/jso.24197. PMID: 26861568.16. Ni XC, Yi Y, Fu YP, He HW, Cai XY, Wang JX, et al. 2015; Prognostic value of the modified Glasgow Prognostic Score in patients undergoing radical surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e1486. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001486. PMID: 26356714. PMCID: PMC4616649.
Article17. Schütte K, Tippelt B, Schulz C, Röhl FW, Feneberg A, Seidensticker R, et al. 2015; Malnutrition is a prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clin Nutr. 34:1122–1127. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.11.007. PMID: 25434576.
Article18. Huang TH, Hsieh CC, Kuo LM, Chang CC, Chen CH, Chi CC, et al. 2019; Malnutrition associated with an increased risk of postoperative complications following hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 21:1150–1155. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.01.003. PMID: 30765200.
Article19. Man Z, Pang Q, Zhou L, Wang Y, Hu X, Yang S, et al. 2018; Prognostic significance of preoperative prognostic nutritional index in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford). 20:888–895. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.03.019. PMID: 29853431.
Article20. Wang Z, Wang J, Wang P. 2018; The prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS One. 13:e0202987. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202987. PMID: 30312295. PMCID: PMC6185720.
Article21. Ji F, Liang Y, Fu S, Chen D, Cai X, Li S, et al. 2017; Prognostic value of combined preoperative prognostic nutritional index and body mass index in HCC after hepatectomy. HPB (Oxford). 19:695–705. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.04.008. PMID: 28479010.
Article22. Hatanaka T, Kakizaki S, Uehara D, Nagashima T, Ueno T, Namikawa M, et al. 2019; Impact of the prognostic nutritional index on the survival of Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib: a multicenter retrospective study. Intern Med. 58:1835–1844. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1594-18. PMID: 30918170. PMCID: PMC6663544.
Article23. Zhang X, Li C, Wen T, Peng W, Yan L, Yang J. 2017; Postoperative prognostic nutritional index predicts survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within milan criteria and hypersplenism. J Gastrointest Surg. 21:1626–1634. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-017-3414-1. PMID: 28523484.
Article24. Kim HJ, Kim CY, Park EK, Hur YH, Koh YS, Kim HJ, et al. 2015; Volumetric analysis and indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min as predictors of post-hepatectomy liver failure. HPB (Oxford). 17:159–167. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12295. PMID: 24964188. PMCID: PMC4299390.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Long Term Survival in Patient with Early Intrahepatic Recurrence and Extrahepatic Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Predictive Factors of Recurrence in Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Prognosis after intrahepatic recurrence in the patients who underwent curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Two Cases of Early Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection Which Showed Different Outcomes
- Patterns of Recurrence after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiological Type