Immune Netw.
2013 Dec;13(6):289-294. 10.4110/in.2013.13.6.289.
Acute Phase Protein Lipocalin-2 Is Associated with Formalin-induced Nociception and Pathological Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Brain Science & Engineering Institute, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu 700-422, Korea. ksuk@knu.ac.kr
- 2School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- KMID: 2150790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2013.13.6.289
Abstract
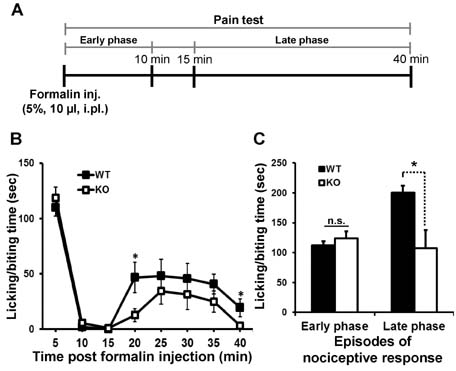
- Lipocalin-2 (LCN2) is an acute-phase protein induced by injury, infection, or other inflammatory stimuli. LCN2 binds small hydrophobic ligands and interacts with cell surface receptor to regulate diverse cellular processes. The role of LCN2 as a chemokine inducer in the central nervous system (CNS) has been previously reported. Based on the previous participation of LCN2 in neuroinflammation, we investigated the role of LCN2 in formalin-induced nociception and pathological pain. Formalin-induced nociceptive behaviors (licking/biting) and spinal microglial activation were significantly reduced in the second or late phase of the formalin test in Lcn2 knockout mice. Likewise, antibody-mediated neutralization of spinal LCN2 attenuated the mechanical hypersensitivity induced by peripheral nerve injury in mice. Taken together, our results suggest that LCN2 can be therapeutically targeted, presumably for both prevention and reversal of acute inflammatory pain as well as pathological pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. 2002; 420:846–852.
Article2. Jha MK, Jeon S, Suk K. Glia as a Link between Neuroinflammation and Neuropathic Pain. Immune Netw. 2012; 12:41–47.
Article3. Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP, Ma D. Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci Res. 2013; In press: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2013.10.004.
Article4. Campbell JN, Meyer RA. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Neuron. 2006; 52:77–92.
Article5. Scholz J, Woolf CJ. The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci. 2007; 10:1361–1368.
Article6. Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF. Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci. 2001; 24:450–455.
Article7. Jeon S, Jha MK, Ock J, Seo J, Jin M, Cho H, Lee WH, Suk K. Role of lipocalin-2-chemokine axis in the development of neuropathic pain following peripheral nerve injury. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288:24116–24127.
Article8. Ji RR, Berta T, Nedergaard M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain. 2013; In press: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.022.
Article9. Milligan ED, Watkins LR. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009; 10:23–36.
Article10. Inoue K, Tsuda M. Microglia and neuropathic pain. Glia. 2009; 57:1469–1479.
Article11. Gao YJ, Ji RR. Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 126:56–68.
Article12. Raghavendra V, Tanga F, Rutkowski MD, DeLeo JA. Anti-hyperalgesic and morphine-sparing actions of propentofylline following peripheral nerve injury in rats: mechanistic implications of spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines. Pain. 2003; 104:655–664.
Article13. Woolf CJ. Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain. 2011; 152:S2–S15.
Article14. Cowland JB, Borregaard N. Molecular characterization and pattern of tissue expression of the gene for neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin from humans. Genomics. 1997; 45:17–23.
Article15. Hraba-Renevey S, Turler H, Kress M, Salomon C, Weil R. SV40-induced expression of mouse gene 24p3 involves a post-transcriptional mechanism. Oncogene. 1989; 4:601–608.16. Flower DR. The lipocalin protein family: structure and function. Biochem J. 1996; 318(Pt 1):1–14.
Article17. Nilsen-Hamilton M, Liu Q, Ryon J, Bendickson L, Lepont P, Chang Q. Tissue involution and the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003; 995:94–108.
Article18. Poh KW, Yeo JF, Stohler CS, Ong WY. Comprehensive gene expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex links immune activation and neutrophil infiltration to antinociception. J Neurosci. 2012; 32:35–45.
Article19. Mucha M, Skrzypiec AE, Schiavon E, Attwood BK, Kucerova E, Pawlak R. Lipocalin-2 controls neuronal excitability and anxiety by regulating dendritic spine formation and maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:18436–18441.
Article20. Lee S, Lee J, Kim S, Park JY, Lee WH, Mori K, Kim SH, Kim IK, Suk K. A dual role of lipocalin 2 in the apoptosis and deramification of activated microglia. J Immunol. 2007; 179:3231–3241.
Article21. Lee S, Park JY, Leem WH, Kim H, Park HC, Mori K, Suk K. Lipocalin-2 is an autocrine mediator of reactive astrocytosis. J Neurosci. 2009; 29:234–249.
Article22. Lee S, Lee WH, Lee MS, Mori K, Suk K. Regulation by lipocalin-2 of neuronal cell death, migration, and morphology. J Neurosci Res. 2012; 90:540–550.
Article23. Lee S, Kim JH, Seo JW, Han HS, Lee WH, Mori K, Nakao K, Barasch J, Suk K. Lipocalin-2 Is a chemokine inducer in the central nervous system: role of chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) in lipocalin-2-induced cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:43855–43870.24. Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ, Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S, Aderem A. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature. 2004; 432:917–921.
Article25. Nairz M, Theurl I, Schroll A, Theurl M, Fritsche G, Lindner E, Seifert M, Crouch ML, Hantke K, Akira S, Fang FC, Weiss G. Absence of functional Hfe protects mice from invasive Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection via induction of lipocalin-2. Blood. 2009; 114:3642–3651.
Article26. Hylden JL, Wilcox GL. Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980; 67:313–316.
Article27. Decosterd I, Woolf CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. 2000; 87:149–158.
Article28. Tegeder I, Costigan M, Griffin RS, Abele A, Belfer I, Schmidt H, Ehnert C, Nejim J, Marian C, Scholz J, Wu T, Allchorne A, Diatchenko L, Binshtok AM, Goldman D, Adolph J, Sama S, Atlas SJ, Carlezon WA, Parsegian A, Lotsch J, Fillingim RB, Maixner W, Geisslinger G, Max MB, Woolf CJ. GTP cyclohydrolase and tetrahydrobiopterin regulate pain sensitivity and persistence. Nat Med. 2006; 12:1269–1277.
Article29. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994; 53:55–63.
Article30. Dixon WJ. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980; 20:441–462.
Article31. Hunskaar S, Hole K. The formalin test in mice: dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain. 1987; 30:103–114.
Article32. Latremoliere A, Woolf CJ. Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J Pain. 2009; 10:895–926.
Article33. Woolf CJ, Salter MW. Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science. 2000; 288:1765–1769.
Article34. Austin PJ, Moalem-Taylor G. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. J Neuroimmunol. 2010; 229:26–50.
Article35. Hashioka S, Miyaoka T, Wake R, Furuya M, Horiguchi J. Glia: an important target for anti-inflammatory and antidepressant activity. Curr Drug Targets. 2013; 14:1322–1328.
Article36. Skaper SD, Giusti P, Facci L. Microglia and mast cells: two tracks on the road to neuroinflammation. FASEB J. 2012; 26:3103–3117.
Article37. Vega-Avelaira D, Ballesteros JJ, Lopez-Garcia JA. Inflammation-induced hyperalgesia and spinal microglia reactivity in neonatal rats. Eur J Pain. 2013; 17:1180–1188.
Article38. Nowak L, Zurowski D, Dobrogowski J, Wordliczek J, Thor PJ. Pentoxifylline modifies central and peripheral vagal mechanism in acute and chronic pain models. Folia Med Cracov. 2012; 52:83–95.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antinociceptive Effect of Intraperitoneally Administered 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide on Formalin Induced Nociception in Rats
- Antinociceptive Effects of Intraperitoneal and Intrathecal Vitamin E in the Rat Formalin Test
- Antinociceptive Effects of Intrathecal Melatonin on Formalin: and Thermal-induced Pain in Rats
- The Antinociceptive Effect of Intrathecal Anticholinesterase on the Formalin Test in Rats
- Effect of Intrathecal Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on Formalin-induced Pain Rat Model