Antinociceptive Effects of Intraperitoneal and Intrathecal Vitamin E in the Rat Formalin Test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. ane84@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2278164
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.238
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Vitamin E is widely known to be one of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavengers and a drug that can easily be obtained, and it has been shown to attenuate the pain responses induced by various causes in animal pain models. Thus, this experiment was conducted to assess the antinociceptive effects of vitamin E by comparing intraperitoneal and intrathecal injections in rats subjected to the formalin test.
METHODS
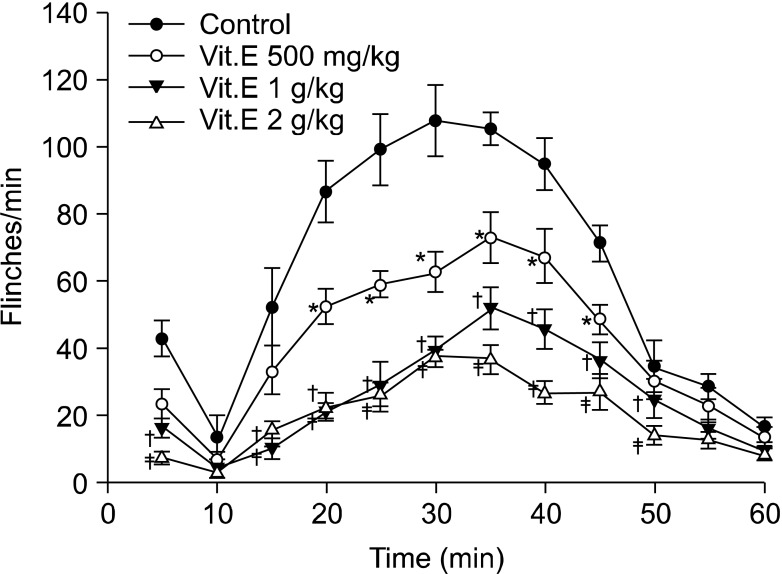
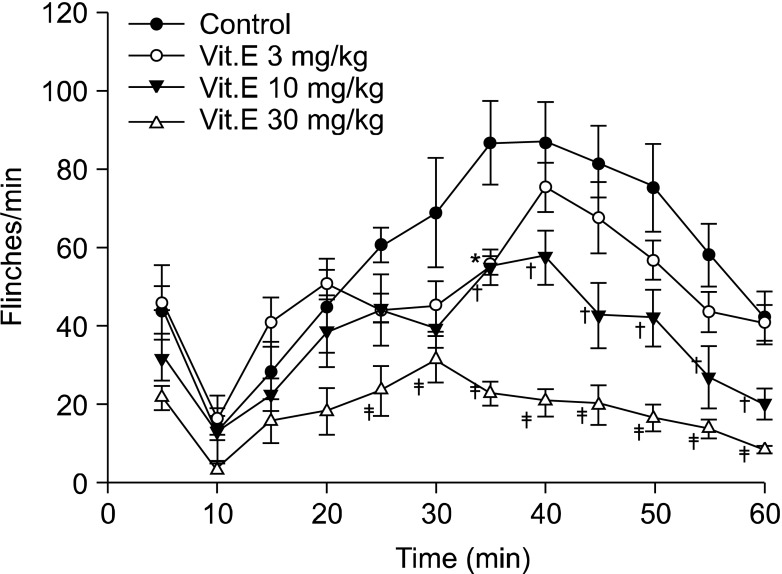
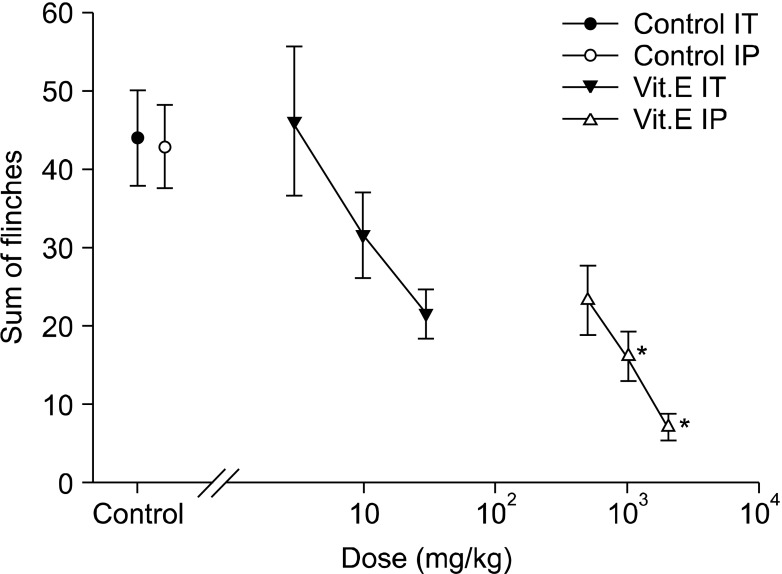
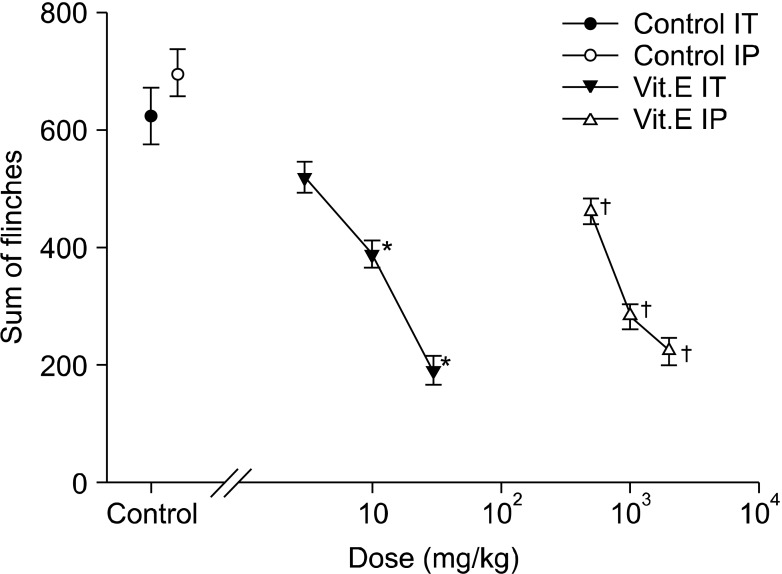
After the intraperitoneal and intrathecal injections of vitamin E were carried out, respectively (IP: 500 mg/kg, 1 g/kg, and 2 g/kg, IT: 3 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 30 mg/kg), the formalin test was perfumed. As soon as 5% formalin was injected into left hind paw, the number of flinches induced by pain was measured at 5-minute intervals for 1 hour.
RESULTS
Formalin injected into the left hind paw induced biphasic nociceptive behavior in all animals. Intraperitoneal injection of vitamin E diminished the nociceptive behavior in a dose-dependent manner during the early and late phase. Intrathecal vitamin E diminished nociceptive behavior dose dependently during the late phase but showed no significant difference in the early phase.
CONCLUSIONS
Vitamin E attenuated acute nociception when it was injected systemically, while both systemic and intrathecal injection produced analgesia in a rat model of formalin-induced hyperalgesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Effects of Pre-emptive Administration of Ketamine and norBNI on Pain Behavior, c-Fos, and Prodynorphin Protein Expression in the Rat Spinal Cord after Formalin-induced Pain Is Modulated by the DREAM Protein
Idris Long, Rapeah Suppian, Zalina Ismail
Korean J Pain. 2013;26(3):255-264. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.255.Vitamin E, an Antioxidant, as a Possible Therapeutic Agent for Treating Pain
Young Hoon Jeon
Korean J Pain. 2013;26(3):314-315. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.314.Evaluation of Pain and Its Effect on Quality of Life and Functioning in Men with Spinal Cord Injury
Marzieh Hassanijirdehi, Mohammad Khak, Sohrab Afshari-Mirak, Kourosh Holakouie-Naieni, Soheil Saadat, Taher Taheri, Vafa Rahimi-Movaghar
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(2):129-136. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.2.129.
Reference
-
1. Wang ZQ, Porreca F, Cuzzocrea S, Galen K, Lightfoot R, Masini E, et al. A newly identified role for superoxide in inflammatory pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004; 309:869–878. PMID: 14988418.
Article2. Yoon MH, Bae HB, Choi JI. Antinociceptive interactions between intrathecal gabapentin and MK801 or NBQX in rat formalin test. J Korean Med Sci. 2005; 20:307–312. PMID: 15832006.
Article3. Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G, Chung K, Coggeshall RE, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2004; 111:116–124. PMID: 15327815.
Article4. Balazs L, Leon M. Evidence of an oxidative challenge in the Alzheimer's brain. Neurochem Res. 1994; 19:1131–1137. PMID: 7824065.
Article5. Olanow CW. An introduction to the free radical hypothesis in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1992; 32 Suppl:S2–S9. PMID: 1510376.
Article6. Park ES, Gao X, Chung JM, Chung K. Levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species increase in rat neuropathic spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 391:108–111. PMID: 16183198.
Article7. Hong BH, Ko YK, Lee YJ, Han K, Kim Y, Lee W. Antinociceptive effects of vitamin E in formalin-induced nociceptive response in rats. Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 6:59–62.
Article8. Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Chopra K. Tocotrienol ameliorates behavioral and biochemical alterations in the rat model of alcoholic neuropathy. Pain. 2009; 145:129–135. PMID: 19541419.
Article9. Kuhad A, Chopra K. Tocotrienol attenuates oxidative-nitrosative stress and inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology. 2009; 57:456–462. PMID: 19555701.
Article10. Kim HK, Kim JH, Gao X, Zhou JL, Lee I, Chung K, et al. Analgesic effect of vitamin E is mediated by reducing central sensitization in neuropathic pain. Pain. 2006; 122:53–62. PMID: 16524661.
Article11. Hacimuftuoglu A, Handy CR, Goettl VM, Lin CG, Dane S, Stephens RL Jr. Antioxidants attenuate multiple phases of formalin-induced nociceptive response in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2006; 173:211–216. PMID: 16919817.
Article12. Rosland JH, Tjølsen A, Maehle B, Hole K. The formalin test in mice: effect of formalin concentration. Pain. 1990; 42:235–242. PMID: 2247320.
Article13. Coderre TJ, Vaccarino AL, Melzack R. Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection. Brain Res. 1990; 535:155–158. PMID: 2292020.
Article14. Tjølsen A, Berge OG, Hunskaar S, Rosland JH, Hole K. The formalin test: an evaluation of the method. Pain. 1992; 51:5–17. PMID: 1454405.
Article15. Nishiyama T. Interaction between intrathecal morphine and glutamate receptor antagonists in formalin test. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 395:203–210. PMID: 10812050.
Article16. Cuesta MC, Arcaya JL, Cano G, Sanchez L, Maixner W, Suarez-Roca H. Opposite modulation of capsaicin-evoked substance P release by glutamate receptors. Neurochem Int. 1999; 35:471–478. PMID: 10524715.
Article17. Lee KY, Chung K, Chung JM. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in long-term potentiation in the spinal cord dorsal horn. J Neurophysiol. 2010; 103:382–391. PMID: 19906875.
Article18. Reynolds IJ, Hastings TG. Glutamate induces the production of reactive oxygen species in cultured forebrain neurons following NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci. 1995; 15:3318–3327. PMID: 7751912.
Article19. Gao X, Kim HK, Chung JM, Chung K. Enhancement of NMDA receptor phosphorylation of the spinal dorsal horn and nucleus gracilis neurons in neuropathic rats. Pain. 2005; 116:62–72. PMID: 15936881.
Article20. Zou X, Lin Q, Willis WD. Enhanced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor 1 subunits in spinal cord dorsal horn and spinothalamic tract neurons after intradermal injection of capsaicin in rats. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:6989–6997. PMID: 10995844.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antinociceptive drug interaction between intrathecal vitamin E and gabapentin in the rat formalin test
- Antinociceptive effects of vitamin E in formalin-induced nociceptive response in rats
- Vitamin E Potentiates the Anti-nociceptive Effects by Intraperitoneal Administration of Lidocaine in Rats
- Effects of Intrathecal Flecainide for Pain Behavior in Formalin Test and Hemodynamics in Rat
- Antinociceptive effects of intrathecal cimifugin treatment: a preliminary rat study based on formalin test