Chonnam Med J.
2008 Aug;44(2):104-108. 10.4068/cmj.2008.44.2.104.
Effect of Intrathecal Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on Formalin-induced Pain Rat Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Medical School, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. mhyoon@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Biomedical Human Resources at Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2045758
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2008.44.2.104
Abstract
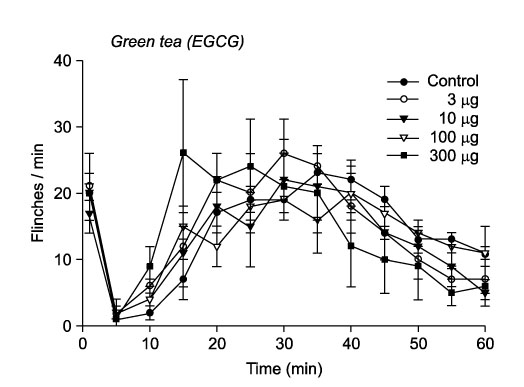
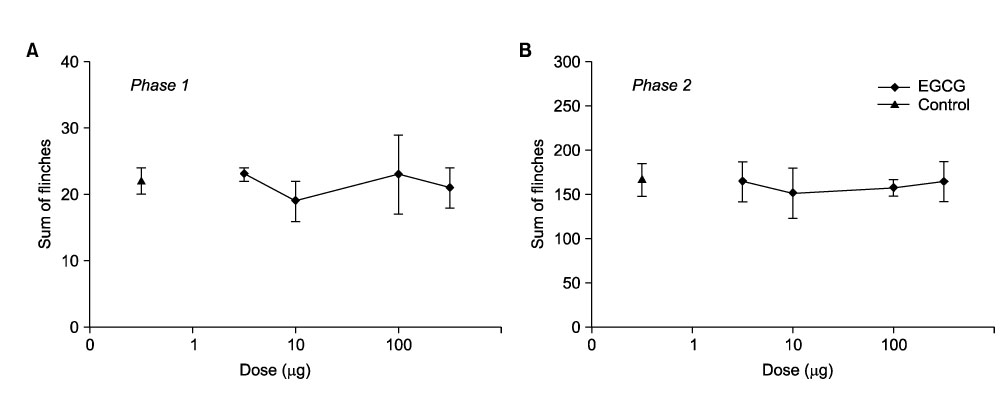
- Green tea is being widely consumed as a health beverage. Recently, green tea polyphenols have been shown to possess potent anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins; in particular, systemic green tea is shown to produce an antinociceptive effect. We examined the effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), one of green tea catechins, administered at the spinal level, on the nociception. Male Sprague-Dwaley rats were used. Nociception was induced by subcutaneous injection of formalin solution (5%, 50microliter) into the paw of the rat. For EGCG administration, intrathecal catheter was inserted into the subarachnoid space of the spine. Formalin-induced pain behavior (flinching response) was observed for 60 min and divided into the two phases, Intrathecal EGCG did not affect the flinching responses during both phase 1 and phase 2. These findings suggest that intrathecal EGCG may be ineffective against acute pain and facilitated state pain evoked by subcutaneously injected formalin.
Keyword
- Tea; Pain; Spinal cord; Rat
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sawynok J. Purines in pain management. Curr Opin CPNS Invest Drugs. 1999. 1:27–38.2. Rane K, Segerdahl M, Goiny M, Sollevi A. Intrathecal adenosine administration: a phase 1 clinical safety study in healthy volunteers, with additional evaluation of its influence on sensory thresholds and experimental pain. Anesthesiology. 1998. 89:1108–1115.3. Weisbuerger JH. Tea and health: the underlying mechanisms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999. 220:271–275.
Article4. Miura S, Watanabe J, Tamita T, Sano M, Tomita I. The inhibitory effects of tea polyphenols (flavan-3-ol derivatives) on Cu2+ mediated oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein. Biol Pharm Bull. 1994. 17:1567–1572.
Article5. Singal A, Anjaneyulu M, Chopra K. Modulatory role of green tea extract on antinociceptive effect of morphine in diabetic mice. J Med Food. 2005. 8:386–391.
Article6. Kaur S, Anurag A, Tirkey N, Chopra K. Reversal of LPS-induced central and peripheral hyperalgesia by green tea extract. Phytother Res. 2005. 19:39–43.
Article7. Ahmed S, Rahman A, Hasnain A, Lalonde M, Goldberg VM, Haqqi TM. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the IL-1betainduced activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in human chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. 33:1097–1105.
Article8. Yoon MH, Yaksh TL. The effect of intrathecal gabapentin on pain behavior and hemodynamics on the formalin test in the rat. Anesth Analg. 1999. 89:434–439.
Article9. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976. 17:1031–1036.
Article10. Malmberg AB, Yaksh TL. Cyclooxygenase inhibition and the spinal release of prostaglandin E2 and amino acids evoked by paw formalin injection: a microdialysis study in unanesthetized rats. J Neurosci. 1995. 15:2768–2776.
Article11. Singh R, Ahmed S, Islam N, Goldberg VM, Haqqi TM. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase and production of nitric oxide in human chondrocytes: suppression of nuclear factor kappaB activation by degradation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. 46:2079–2086.
Article12. Paquay JB, Haenen GR, Stender G, Wiseman SA, Tijburg LB, Bast A. Protection against nitric oxide toxicity by tea. J Agric Food Chem. 2000. 48:5768–5772.
Article13. Meller ST, Gebhart GF. Nitric oxide (NO) and nociceptive processing in the spinal cord. Pain. 1993. 52:127–136.
Article14. Lin JK, Liang YC, Lin-Shiau SY. Cancer chemoprevention by tea polyphenols through mitotic signal transduction blockade. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. 58:911–915.
Article15. Grover VS, Sharma A, Singh M. Role of nitric oxide in diabetesinduced attenuation of antinociceptive effect of morphine in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. 399:161–164.
Article16. Ahmed S, Rahman A, Hasnain A, Lalonde M, Goldberg VM, Haqqi TM. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the IL-1beta-induced activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in human chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. 33:1097–1105.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Intrathecal Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Development of Antinociceptive Tolerance to Morphine
- Antinociceptive Effects of Intraperitoneal and Intrathecal Vitamin E in the Rat Formalin Test
- Antinociceptive Effects of Intrathecal Melatonin on Formalin: and Thermal-induced Pain in Rats
- Effects of Intrathecal Flecainide for Pain Behavior in Formalin Test and Hemodynamics in Rat
- Evaluation of the Interaction between Intrathecal 5-Hydroxytryptamine and Adenosine in the Formalin Test in a Rat Model