Immune Netw.
2011 Dec;11(6):406-411. 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.406.
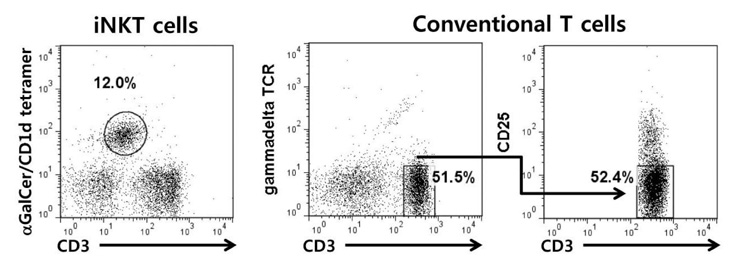
Comparison of Invariant NKT Cells with Conventional T Cells by Using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Laboratory of Immune Regulation in Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea. doohyun@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2150727
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.6.406
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Invariant Natural killer T (iNKT) cells, a distinct subset of CD1d-restricted T cells with invariant Valphabeta TCR, functionally bridge innate and adaptive immunity. While iNKT cells share features with conventional T cells in some functional aspects, they simultaneously produce large amount of Th1 and Th2 cytokines upon T-cell receptor (TCR) ligation. However, gene expression pattern in two types of cells has not been well characterized.
METHODS
we performed comparative microarray analyses of gene expression in murine iNKT cells and conventional CD4+CD25-gammadeltaTCR- T cells by using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) method.
RESULTS
Here, we describe profound differences in gene expression pattern between iNKT cells and conventional CD4+CD25-gammadeltaTCR- T cells.
CONCLUSION
Our results provide new insights into the functional competence of iNKT cells and a better understanding of their various roles during immune responses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bendelac A, Lantz O, Quimby ME, Yewdell JW, Bennink JR, Brutkiewicz RR. CD1 recognition by mouse NK1+ T lymphocytes. Science. 1995. 268:863–865.2. Chen H, Paul WE. Cultured NK1.1+ CD4+ T cells produce large amounts of IL-4 and IFN-gamma upon activation by anti-CD3 or CD1. J Immunol. 1997. 159:2240–2249.3. Mendiratta SK, Martin WD, Hong S, Boesteanu A, Joyce S, Van Kaer L. CD1d1 mutant mice are deficient in natural T cells that promptly produce IL-4. Immunity. 1997. 6:469–477.
Article4. Godfrey DI, Stankovic S, Baxter AG. Raising the NKT cell family. Nat Immunol. 2010. 11:197–206.
Article5. Kim JH, Kim HY, Kim S, Chung JH, Park WS, Chung DH. Natural killer T (NKT) cells attenuate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by producing interferon-gamma. Am J Pathol. 2005. 167:1231–1241.
Article6. Kim HY, Kim HJ, Min HS, Kim S, Park WS, Park SH, Chung DH. NKT cells promote antibody-induced joint inflammation by suppressing transforming growth factor beta1 production. J Exp Med. 2005. 201:41–47.
Article7. Oh SJ, Chung DH. Invariant NKT cells producing IL-4 or IL-10, but not IFN-gamma, inhibit the Th1 response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, whereas none of these cells inhibits the Th17 response. J Immunol. 2011. 186:6815–6821.
Article8. Hwang SJ, Kim S, Park WS, Chung DH. IL-4-secreting NKT cells prevent hypersensitivity pneumonitis by suppressing IFN-gamma-producing neutrophils. J Immunol. 2006. 177:5258–5268.
Article9. Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. 23:877–900.
Article10. Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007. 25:297–336.
Article11. Keller A, Backes C, Lenhof HP. Computation of significance scores of unweighted Gene Set Enrichment Analyses. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. 8:290.
Article12. Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. 102:15545–15550.
Article13. Taniguchi M, Seino K, Nakayama T. The NKT cell system: bridging innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:1164–1165.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Discovery of Cellular RhoA Functions by the Integrated Application of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
- B Cells Promote Th1- Skewed NKT Cell Response by CD1d-TCR Interaction
- Analysis of gene expression during odontogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp cells
- Natural killer T cell and pathophysiology of asthma
- Deficiencies of Circulating Mucosal-associated Invariant T Cells and Natural Killer T Cells in Patients with Acute Cholecystitis