Immune Netw.
2013 Oct;13(5):218-221. 10.4110/in.2013.13.5.218.
B Cells Promote Th1- Skewed NKT Cell Response by CD1d-TCR Interaction
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul 136-701, Korea. sehopark@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1493617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2013.13.5.218
Abstract
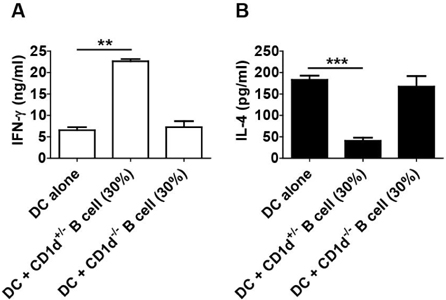
- CD1d expressing dendritic cells (DCs) are good glyco-lipid antigen presenting cells for NKT cells. However, resting B cells are very weak stimulators for NKT cells. Although alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer) loaded B cells can activate NKT cells, it is not well defined whether B cells interfere NKT cell stimulating activity of DCs. Unexpectedly, we found in this study that B cells can promote Th1-skewed NKT cell response, which means a increased level of IFN-gamma by NKT cells, concomitant with a decreased level of IL-4, in the circumstance of co-culture of DCs and B Cells. Remarkably, the response promoted by B cells was dependent on CD1d expression of B cells.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bendelac A, Rivera MN, Park SH, Roark JH. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997; 15:535–562.
Article2. De Libero G, Mori L. Recognition of lipid antigens by T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005; 5:485–496.
Article3. Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007; 25:297–336.
Article4. Shin Y, Hong C, Lee H, Shin JH, Hong S, Park SH. NKT cell-dependent regulation of secondary antigen-specific, conventional CD4+ T cell immune responses. J Immunol. 2010; 184:5589–5594.
Article5. Hong C, Lee H, Oh M, Kang CY, Hong S, Park SH. CD4+ T cells in the absence of the CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are critical and sufficient for NKT cell-dependent tumor rejection. J Immunol. 2006; 177:6747–6757.
Article6. Hong C, Lee H, Park YK, Shin J, Jung S, Kim H, Hong S, Park SH. Regulation of secondary antigen-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses by natural killer T cells. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:4301–4308.
Article7. Fujii S, Shimizu K, Kronenberg M, Steinman RM. Prolonged IFN-gamma-producing NKT response induced with alpha-galactosylceramide-loaded DCs. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3:867–874.
Article8. Bezbradica JS, Stanic AK, Matsuki N, Bour-Jordan H, Bluestone JA, Thomas JW, Unutmaz D, Van Kaer L, Joyce S. Distinct roles of dendritic cells and B cells in Va14Ja18 natural T cell activation in vivo. J Immunol. 2005; 174:4696–4705.
Article9. Leadbetter EA, Brigl M, Illarionov P, Cohen N, Luteran MC, Pillai S, Besra GS, Brenner MB. NK T cells provide lipid antigen-specific cognate help for B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008; 105:8339–8344.
Article10. Barral P, Eckl-Dorna J, Harwood NE, De Santo C, Salio M, Illarionov P, Besra GS, Cerundolo V, Batista FD. B cell receptor-mediated uptake of CD1d-restricted antigen augments antibody responses by recruiting invariant NKT cell help in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008; 105:8345–8350.
Article11. King IL, Fortier A, Tighe M, Dibble J, Watts GF, Veerapen N, Haberman AM, Besra GS, Mohrs M, Brenner MB, Leadbetter EA. Invariant natural killer T cells direct B cell responses to cognate lipid antigen in an IL-21-dependent manner. Nat Immunol. 2011; 13:44–50.
Article12. Chung Y, Kim BS, Kim YJ, Ko HJ, Ko SY, Kim DH, Kang CY. CD1d-restricted T cells license B cells to generate long-lasting cytotoxic antitumor immunity in vivo. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:6843–6850.
Article13. Kim YJ, Ko HJ, Kim YS, Kim DH, Kang S, Kim JM, Chung Y, Kang CY. alpha-Galactosylceramide-loaded, antigen-expressing B cells prime a wide spectrum of antitumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 2008; 122:2774–2783.
Article14. Diaz-de-Durana Y, Mantchev GT, Bram RJ, Franco A. TACI-BLyS signaling via B-cell-dendritic cell cooperation is required for naive CD8+ T-cell priming in vivo. Blood. 2006; 107:594–601.
Article15. Bialecki E, Paget C, Fontaine J, Capron M, Trottein F, Faveeuw C. Role of marginal zone B lymphocytes in invariant NKT cell activation. J Immunol. 2009; 182:6105–6113.
Article16. Chuang YH, Wang TC, Jen HY, Yu AL, Chiang BL. alpha-Galactosylceramide-induced airway eosinophilia is mediated through the activation of NKT cells. J Immunol. 2011; 186:4687–4692.
Article17. Hachem P, Lisbonne M, Michel ML, Diem S, Roongapinun S, Lefort J, Marchal G, Herbelin A, Askenase PW, Dy M, Leite-de-Moraes MC. Alpha-galactosylceramide-induced iNKT cells suppress experimental allergic asthma in sensitized mice: role of IFN-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 2005; 35:2793–2802.
Article18. Matsuda H, Suda T, Sato J, Nagata T, Koide Y, Chida K, Nakamura H. alpha-Galactosylceramide, a ligand of natural killer T cells, inhibits allergic airway inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005; 33:22–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Natural killer T cell and pathophysiology of asthma
- The presence of CD8+ invariant NKT cells in mice
- T Cell Receptor Rearrangement in NKT Cells Differentiated from Cord Blood CD34+ Cells
- Comparison of Invariant NKT Cells with Conventional T Cells by Using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
- The requirement of natural killer T-cells in tolerogenic APCs-mediated suppression of collagen-induced arthritis