Immune Netw.
2010 Dec;10(6):247-249. 10.4110/in.2010.10.6.247.
Presence of Foxp3-expressing CD19(+)CD5(+) B Cells in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Human CD19(+)CD5(+)Foxp3(+) Regulatory B Cell (Breg)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Animal Biotechnology, College of Animal Bioscience & Technology, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- 2Department of Immunology, College of Medicine, Konkuk University, Chungju 380-701, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Paediatrics, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon 301-721, Korea. admyth@naver.com
- 4Department of Paediatrics, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 305-764, Korea.
- KMID: 2150681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2010.10.6.247
Abstract
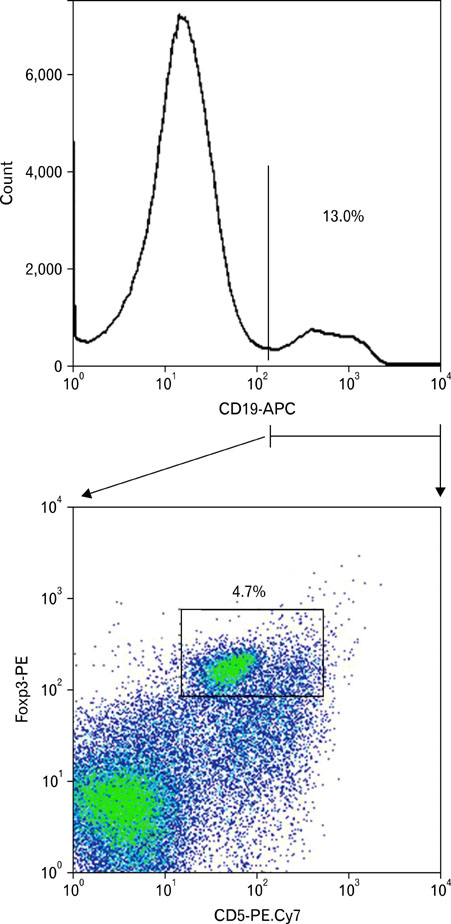
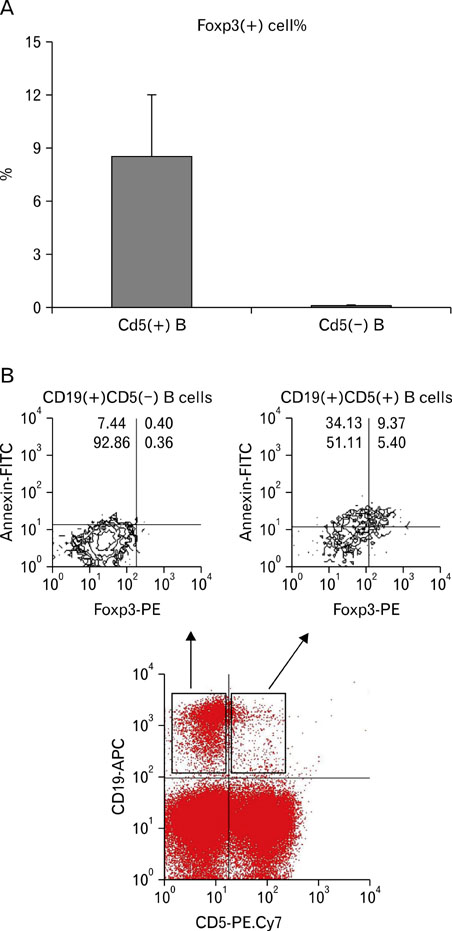
- Foxp3 is a transcript factor for regulatory T cell development. Interestingly, Foxp3-expressing cells were identified in B cells, especially in CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells, while those were not examined in CD19(+)CD5(-) B cells. Foxp3-expressing CD5(+) B cells in this study were identified in human PBMCs and were found to consist of 8.5+/-3.5% of CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells. CD19(+)CD5(+)Foxp3(+) B cells showed spontaneous apoptosis. Rare CD19(+)CD5(+) Foxp3(+) regulatory B cell (Breg) population was unveiled in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and suggested as possible regulatory B cells (Breg) as regulatory T cells (Treg). The immunologic and the clinical relevant of Breg needs to be further investigated.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mizoguchi A, Bhan AK. A case for regulatory B cells. J Immunol. 2006. 176:705–710.
Article2. Gieni RS, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. Ly1- (CD5-) B cells produce interleukin (IL)-10. Cell Immunol. 1997. 175:164–170.3. Lee JH, Noh J, Noh G, Kim HS, Mun SH, Choi WS, Cho S, Lee S. Allergen-specific B cell subset responses in cow's milk allergy of late eczematous reactions in atopic dermatitis. Cell Immunol. 2010. 262:44–51.
Article4. Noh J, Lee JH, Noh G, Bang SY, Kim HS, Choi WS, Cho S, Lee SS. Characterisation of allergen-specific responses of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells (Br1) in Cow Milk Allergy. Cell Immunol. 2010. 264:143–149.
Article5. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003. 299:1057–1061.
Article6. Amu S, Saunders SP, Kronenberg M, Mangan NE, Atzberger A, Fallon PG. Regulatory B cells prevent and reverse allergic airway inflammation via FoxP3-positive T regulatory cells in a murine model. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:1114–1124.
Article7. Lee JH, Noh J, Noh G, Choi WS, Cho S, Lee SS. Allergen-specific TGF-β-producing CD19(+)CD5(+) Regulatory B-Cell (Br3) Responses in Human Late Eczematous Allergic Reactions to Cow's Milk. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. in press.8. Douglas RS, Woo EY, Capocasale RJ, Tarshis AD, Nowell PC, Moore JS. Altered response to and production of TGF-beta by B cells from autoimmune NZB mice. Cell Immunol. 1997. 179:126–137.
Article9. Weiner HL. Oral tolerance: immune mechanisms and the generation of Th3-type TGF-beta-secreting regulatory cells. Microbes Infect. 2001. 3:947–954.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IL-10 is Predominantly Produced by CD19(low)CD5(+) Regulatory B Cell Subpopulation: Characterisation of CD19 (high) and CD19(low) Subpopulations of CD5(+) B cells
- Increased CD5 + B Cells in Neonatal Infections
- Change of Peripheral Blood CD5+ B Lymphocytes in Early Neonatal Period
- Peripheral Generation of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells
- The frequency of CD5 B lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with myasthenia gravis