Clin Nutr Res.
2015 Jul;4(3):201-207. 10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.201.
Six-month Outcomes of Mobile Phone Application-based Self-management in a Patient with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dietetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. youngyun.cho@samsung.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea.
- KMID: 2148630
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2015.4.3.201
Abstract
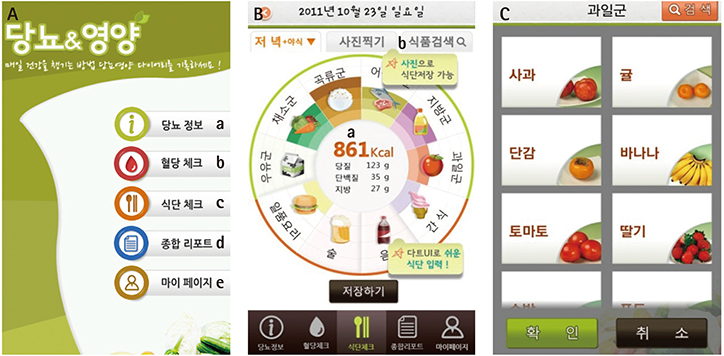
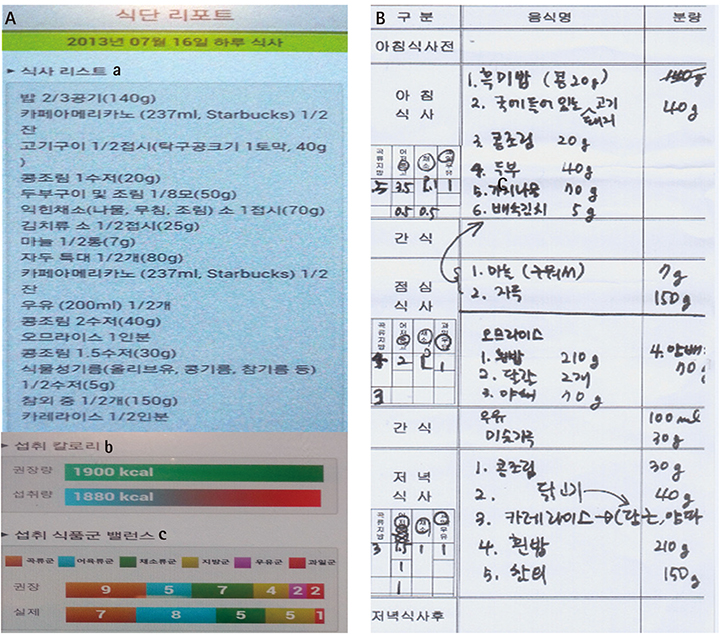
- We report the case in order to examine the effect of a mobile application program ("Diabetes & Nutrition") developed in 2011-2012 for self-management in patients with type 2 diabetes and to recommend important considerations when the mobile application program is developed. A 46-year-old man was newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2013 and had no complications. The height of the patient was 168 cm and the body weight was 75.6 kg. Nutrition education was conducted according to a medical prescription, and follow-up nutrition education was conducted after 3 and 6 months. After nutrition education, the patient was engaged in self-management using "Diabetes & Nutrition" program during 3 months. At 3 months, the body weight had decreased by 4.4 kg (from 75.6 to 71.2 kg), waist circumference by 5 cm (from 88 to 83 cm) and HbA1c level from 7.9% to 6.1%. Also at 3 months, the medication was reduced from from the dose of 850 mg to the dose of 500 mg metformin per twice a day. Since then, the patient did not continue to use the "Diabetes & Nutrition" because the level of blood glucose had stabilized, and the patient felt inconvenient and annoying to use the program. At 6 months, no significant change in the body weight and body composition was observed in comparison with those at 3 months. The present case demonstrates that the early use of "Diabetes & Nutrition" could be helpful for self-management of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Developing self-management mobile application programs in the future will require strategies of how to promote continuous use of application program and self-management of type 2 diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Diabetes Association Board of Education. Diabetes education guideline. 3rd ed. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2013.2. Norris SL, Lau J, Smith SJ, Schmid CH, Engelgau MM. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1159–1171.3. Haas L, Maryniuk M, Beck J, Cox CE, Duker P, Edwards L, Fisher EB, Hanson L, Kent D, Kolb L, McLaughlin S, Orzeck E, Piette JD, Rhinehart AS, Rothman R, Sklaroff S, Tomky D, Youssef G. 2012 Standards Revision Task Force. National standards for diabetes self-management education and support. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S144–S153.
Article4. Lee SL, Kim YL, Lee SJ, Cho YK, Choi YK, Chun CH, Chang YK. Effects of diabetes education on diabetic management in non-insulin-dependent diabetics mellitus patients. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2004; 10:300–308.5. Hieftje K, Edelman EJ, Camenga DR, Fiellin LE. Electronic media-based health interventions promoting behavior change in youth: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2013; 167:574–580.
Article6. Santoro E, Castelnuovo G, Zoppis I, Mauri G, Sicurello F. Social media and mobile applications in chronic disease prevention and management. Front Psychol. 2015; 6:567.
Article7. Kirwan M, Vandelanotte C, Fenning A, Duncan MJ. Diabetes self-management smartphone application for adults with type 1 diabetes: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2013; 15:e235.
Article8. Kim SI, Kim HS. Effectiveness of mobile and internet intervention in patients with obese type 2 diabetes. Int J Med Inform. 2008; 77:399–404.
Article9. Kim YJ, Rhee SY, Byun JK, Park SY, Hong SM, Chin SO, Chon S, Oh S, Woo JT, Kim SW, Kim YS. A smartphone application significantly improved diabetes self-care activities with high user satisfaction. Diabetes Metab J. 2015; 39:207–217.
Article10. Brooke J. SUS - a quick and dirty usability scale. 1996. cited 2009 September 30. Available from: http://www.usabilitynet.org/trump/documents/Suschapt.doc.11. Brooke J. SUS: a 'quick and dirty' usability scale. In : Jordan PW, Thomas B, Weerdmeester BA, McClelland IL, editors. Usability evaluation in industry. London: Taylor & Francis;1996. p. 189–194.12. Arsand E, Tatara N, Østengen G, Hartvigsen G. Mobile phone-based self-management tools for type 2 diabetes: the few touch application. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010; 4:328–336.
Article13. Klein S, Sheard NF, Pi-Sunyer X, Daly A, Wylie-Rosett J, Kulkarni K, Clark NG. American Diabetes Association. North American Association for the Study of Obesity. American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Weight management through lifestyle modification for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: rationale and strategies: a statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2067–2073.
Article14. Van Gaal L, Scheen A. Weight management in type 2 diabetes: current and emerging approaches to treatment. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1161–1172.
Article15. Wing RR. Look AHEAD Research Group. Long-term effects of a lifestyle intervention on weight and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: four-year results of the Look AHEAD trial. Arch Intern Med. 2010; 170:1566–1575.16. Williams KV, Kelley DE. Metabolic consequences of weight loss on glucose metabolism and insulin action in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2000; 2:121–129.
Article17. Cho Y, Lee M, Jang H, Rha M, Kim J, Park Y, Sohn C. The clinical and cost effectiveness of medical nutrition therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Nutr. 2008; 41:147–155.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and User Satisfaction of a Mobile Phone Application for Image-based Dietary Assessment
- Diabetes Management via a Mobile Application: a Case Report
- Diabetes Management according to Blood Glucose Measurement Trend
- The association of usual mobile telephone usage with blood pressure, body mass index, and hemoglobin
- HealthTWITTER Initiative: Design of a Social Networking Service Based Tailored Application for Diabetes Self-Management