Healthc Inform Res.
2014 Jul;20(3):226-230. 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.226.
HealthTWITTER Initiative: Design of a Social Networking Service Based Tailored Application for Diabetes Self-Management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul National University Biomedical Informatics (SNUBI), Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Medical Informatics and Health Technology (MIT), Department of Health Care Management, College of Social Science, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea. hjseo@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2284586
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.226
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Diabetes is a chronic disease of continuously increasing prevalence. It is a disease with risks of serious complications, thus warranting its long-term management. However, current health management and education programs for diabetes mainly consist of one-way communication, and systematic social support backup to solve diabetics' emotional problems is insufficient.
METHODS
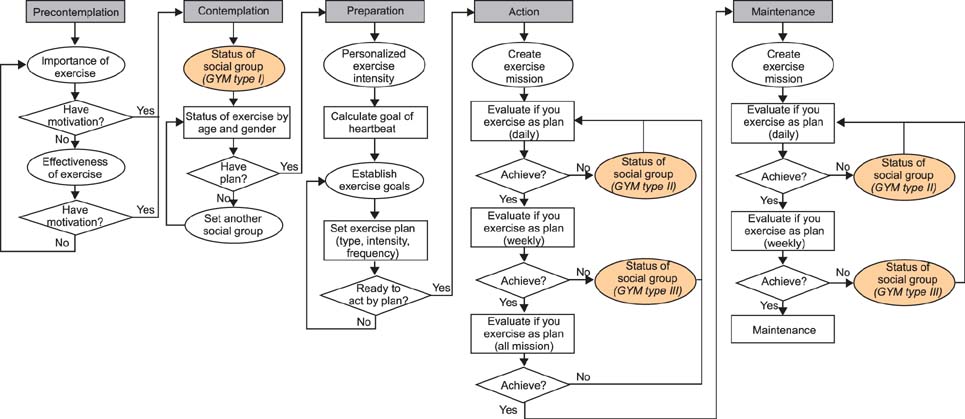
According to individual behavioral changes based on the Transtheoretical Model, we designed a non-drug intervention, including exercise, and applied it to a mobile based application. For effective data sharing between patients and physicians, we adopted an SNS function for our application in order to offer a social support environment.
RESULTS
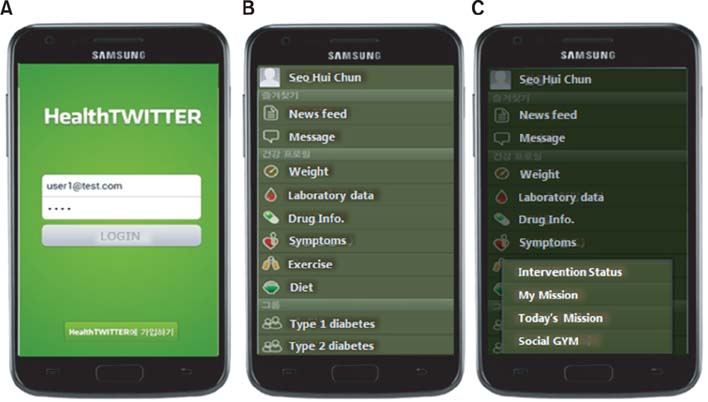
To induce continual and comprehensive care for diabetes, rigorous self-management is essential during the diabetic's life; this is possible through a collaborative patient-physician healthcare model. We designed and developed an SNS-based diabetes self-management mobile application that supports the use of social groups, which are present in three social GYM types. With simple testing of patients in their 20s and 30s, we were able to validate the usefulness of our application.
CONCLUSIONS
Mobile gadget-based chronic disease symptom management and intervention has the merit that health management can be conducted anywhere and anytime in order to cope with increases in the demand for health and medical services that are occurring due to the aging of the population and to cope with the surge of national medical service costs. This patient-driven and SNS-based intervention program is expected to contribute to promoting the health management habits of diabetics, who need to constantly receive health guidance.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Social Media in Clinical Practice
Mona Choi
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(2):138-140. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.2.138.Development of tailored nutrition information messages based on the transtheoretical model for smartphone application of an obesity prevention and management program for elementary-school students
Ji Eun Lee, Da Eun Lee, Kirang Kim, Jae Eun Shim, Eunju Sung, Jae-Heon Kang, Ji-Yun Hwang
Nutr Res Pract. 2017;11(3):247-256. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.3.247.
Reference
-
1. Statistics Korea. Causes of death statistics in 2012 [Internet]. Daejeon, Korea: Statistics Korea;2012. cited at 2014 Jan 14. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr.2. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27(5):1047–1053.
Article3. Wu JH, Wang SC, Lin LM. Mobile computing acceptance factors in the healthcare industry: a structural equation model. Int J Med Inform. 2007; 76(1):66–77.
Article4. Kim SI, Kim HS. Effectiveness of mobile and internet intervention in patients with obese type 2 diabetes. Int J Med Inform. 2008; 77(6):399–404.
Article5. Arsand E, Tatara N, Ostengen G, Hartvigsen G. Mobile phone-based self-management tools for type 2 diabetes: the few touch application. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010; 4(2):328–336.
Article6. Grajales FJ 3rd, Sheps S, Ho K, Novak-Lauscher H, Eysenbach G. Social media: a review and tutorial of applications in medicine and health care. J Med Internet Res. 2014; 16(2):e13.
Article7. Choi I, Kim S, Kwon YD. Key aspects of using Web-based diabetes telemedicine systems in multiple clinical settings. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2007; 13(4):375–383.
Article8. Plack K, Herpertz S, Petrak F. Behavioral medicine interventions in diabetes. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2010; 23(2):131–138.
Article9. Vallis M, Ruggiero L, Greene G, Jones H, Zinman B, Rossi S, et al. Stages of change for healthy eating in diabetes: relation to demographic, eating-related, health care utilization, and psychosocial factors. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26(5):1468–1474.10. Fava JL, Velicer WF, Prochaska JO. Applying the transtheoretical model to a representative sample of smokers. Addict Behav. 1995; 20(2):189–203.
Article11. Evers KE, Paiva AL, Johnson JL, Cummins CO, Prochaska JO, Prochaska JM, et al. Results of a transtheoretical model-based alcohol, tobacco and other drug intervention in middle schools. Addict Behav. 2012; 37(9):1009–1018.
Article12. Prochaska JO, Velicer WF. The transtheoretical model of health behavior change. Am J Health Promot. 1997; 12(1):38–48.
Article13. Di Noia J, Contento IR, Prochaska JO. Computer-mediated intervention tailored on transtheoretical model stages and processes of change increases fruit and vegetable consumption among urban African-American adolescents. Am J Health Promot. 2008; 22(5):336–341.
Article14. Seo HJ, Yim J, Lim JS, Kang KH, Kim EJ, Park IB, et al. Development of Incheon Chronic Disease Management System through Local Community Connection: an example of one Metropolitan City. J Korean Soc Health Inf Health Stat. 2008; 33(2):77–88.15. Prochaska JO, DiClemente CC. Towards a comprehensive model of change. In : Miller WR, Heather N, editors. Treating addictive behaviors: processes of change. New York (NY): Plenum Press;1986. p. 3–27.16. iCare-D app [Internet]. Seoul, Korea: Ubiquitous Health Care Research Center, Catholic University of Korea;2012. cited at 2014 Jan 15. Available from: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=tw.project.diabetes.17. Q-Care app [Internet]. Suwon, Korea: Gyeonggi Province;2013. cited at 2014 Jan 15. Available from: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.brenex.18. U-Care Note app [Internet]. Incheon, Korea: Gachon University Gil Medical Center;2014. cited at 2014 Jan 15. Available from: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.smartcare.19. Korean Diabetes Association. Camp for 2030 [Internet]. Seoul, Korea: Korean Diabetes Association;2012. cited at 2014 Jan 15. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/general/camp/index.php.20. Park SS, Oh SW. Strategy for the management of metabolic syndrome of Seoul citizen. Food Ind Nutr. 2010; 15(1):10–16.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Application of a Web-Based Tailored Nutrition Management Program and Change in Knowledge of Nutrition and Eating Habits in Elementary Students
- Understanding Psycho-Social Aspects and Social Welfare Information of Low-Income Diabetes Patients
- Social Support for Diabetes Patients
- The Role of Medical Social Worker Engaging in Diabetes Management
- Current interventions, strategies, and networking of adolescent suicide