Korean J Urol.
2009 Jan;50(1):72-80. 10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.72.
Effects of alpha-Lipoic Acid on the Antioxidant System in Prostate Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. urokang@lycos.co.kr
- 2Paik Institute of Clinical Research, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2140118
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.72
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Overproduction of lipid peroxidation byproducts and disturbances in the antioxidant defense system have been implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including prostate cancer. Although several studies have investigated the level of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in prostate cancer, there are no reports on alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) in prostate cancer. Here we assessed the effects of ALA on the antioxidant system in prostate cancer cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
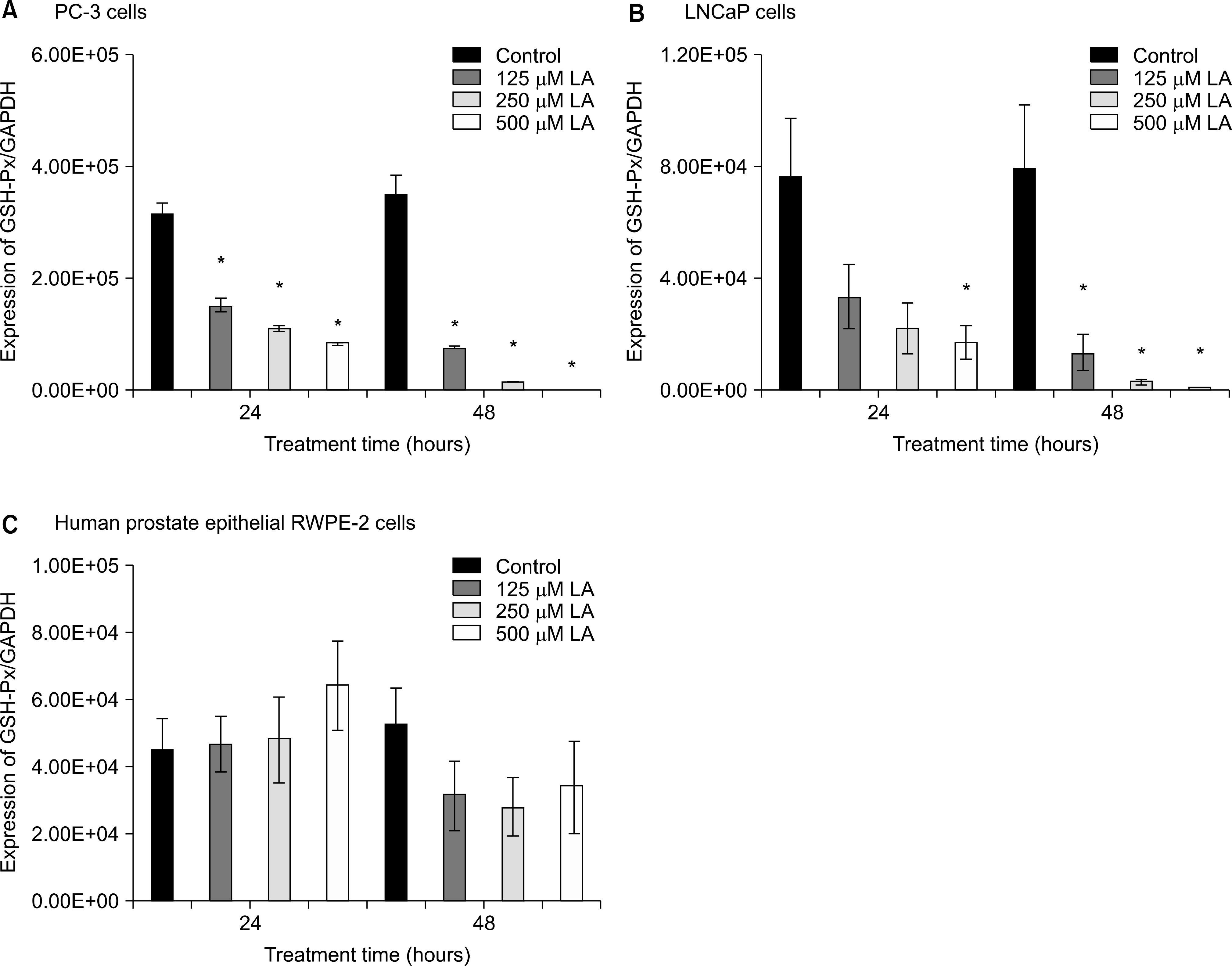
PC-3, LNCaP, and RWPE-2 cell lines were used in this study. Redox factor (Ref)-1 protein was measured by Western blot analysis after treatment with ALA. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to detect superoxide dismutase (SOD)-1 and -2, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) mRNA expression.
RESULTS
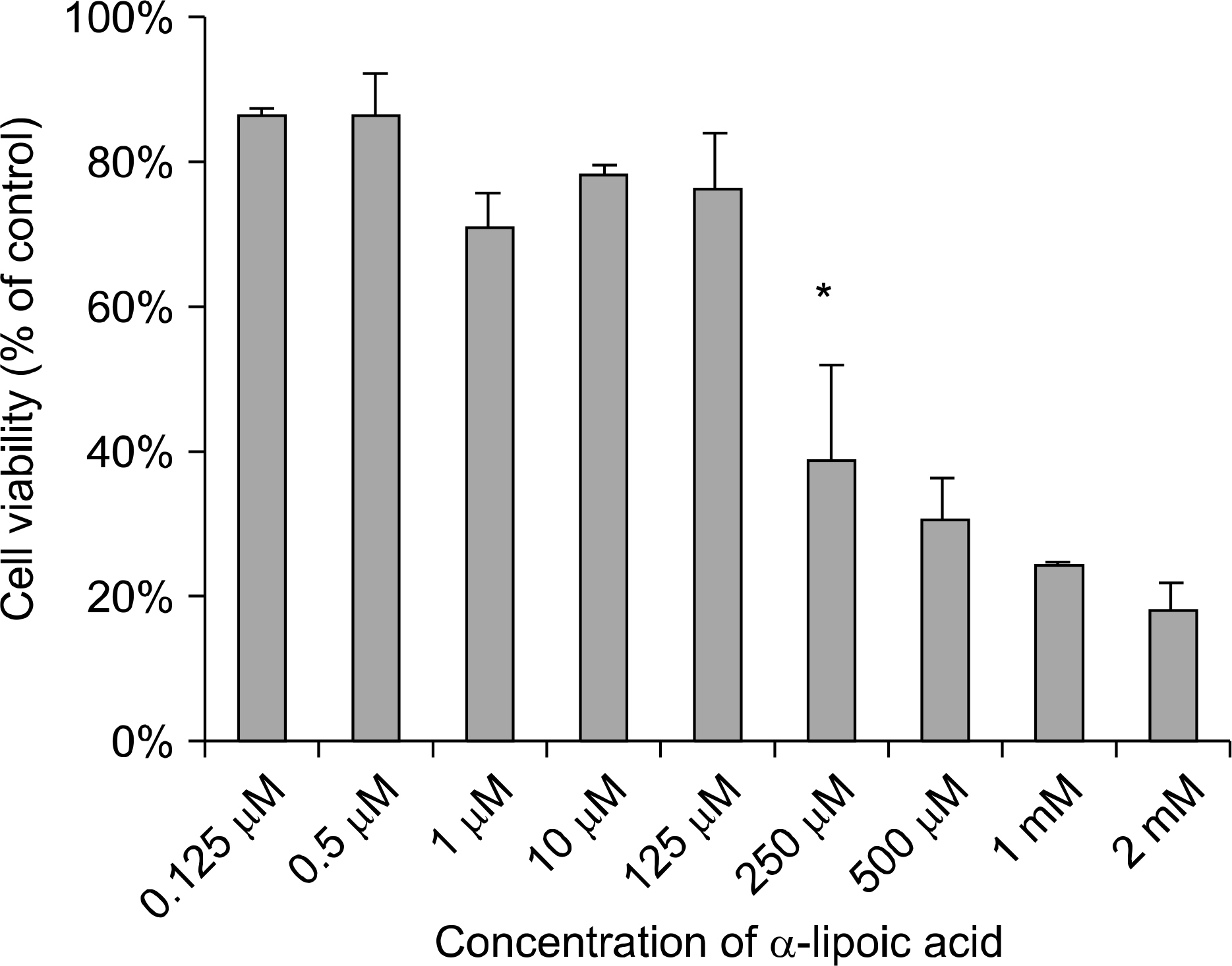
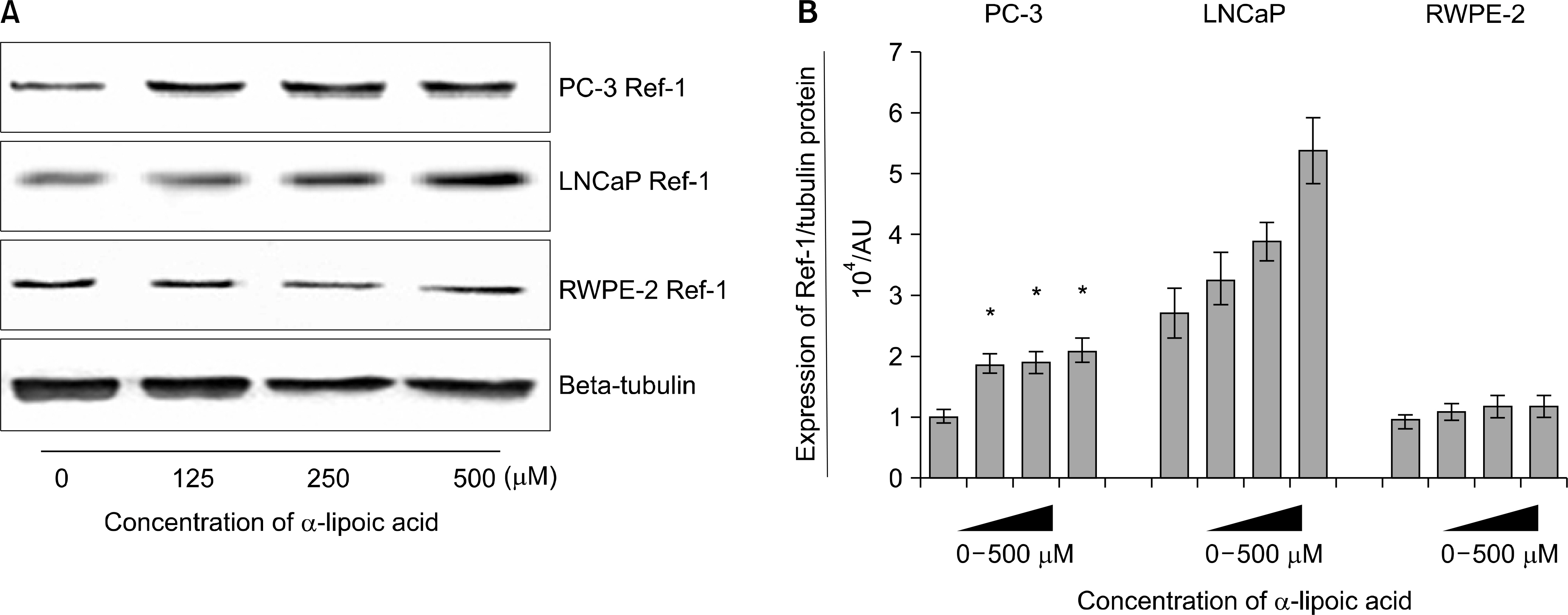
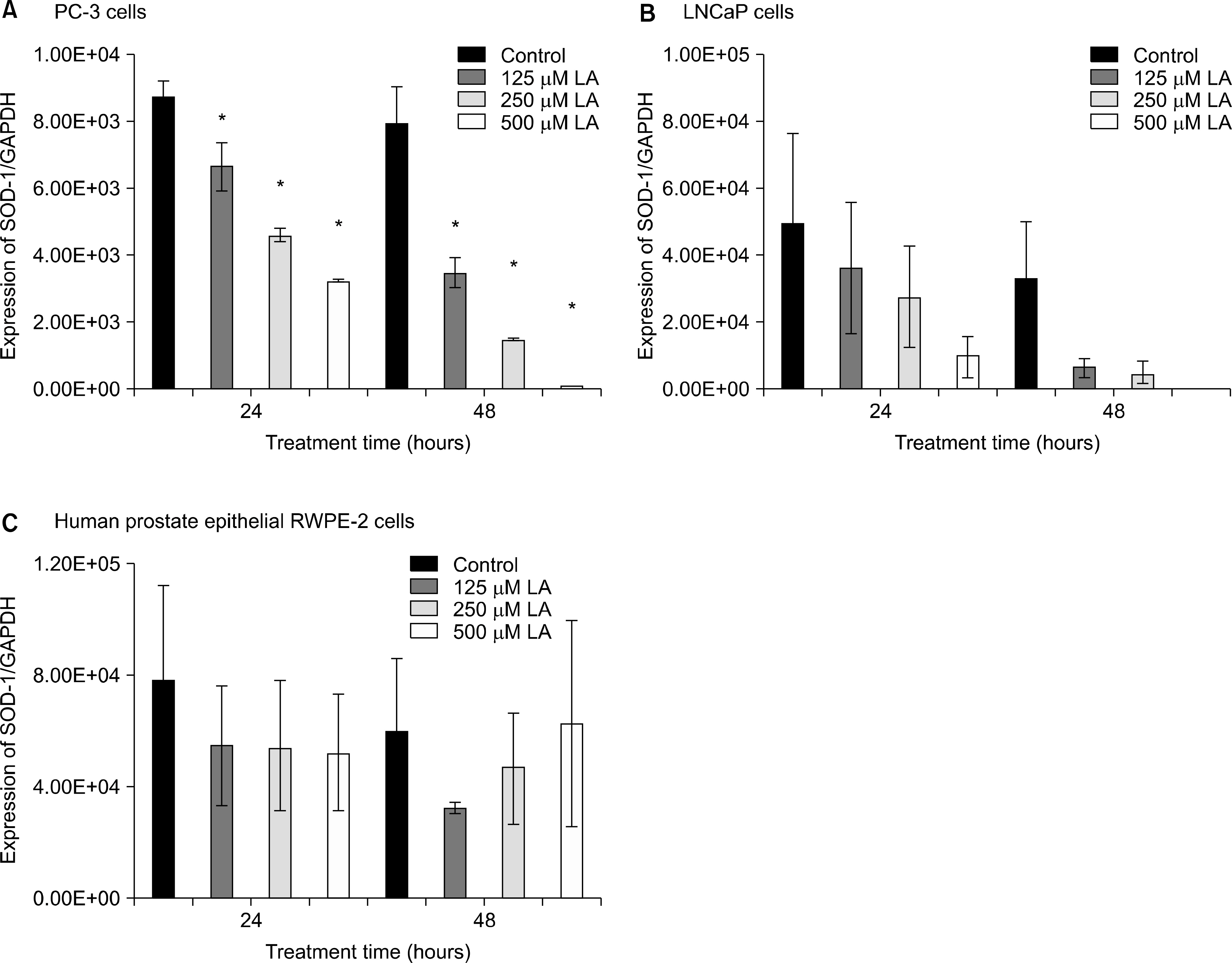
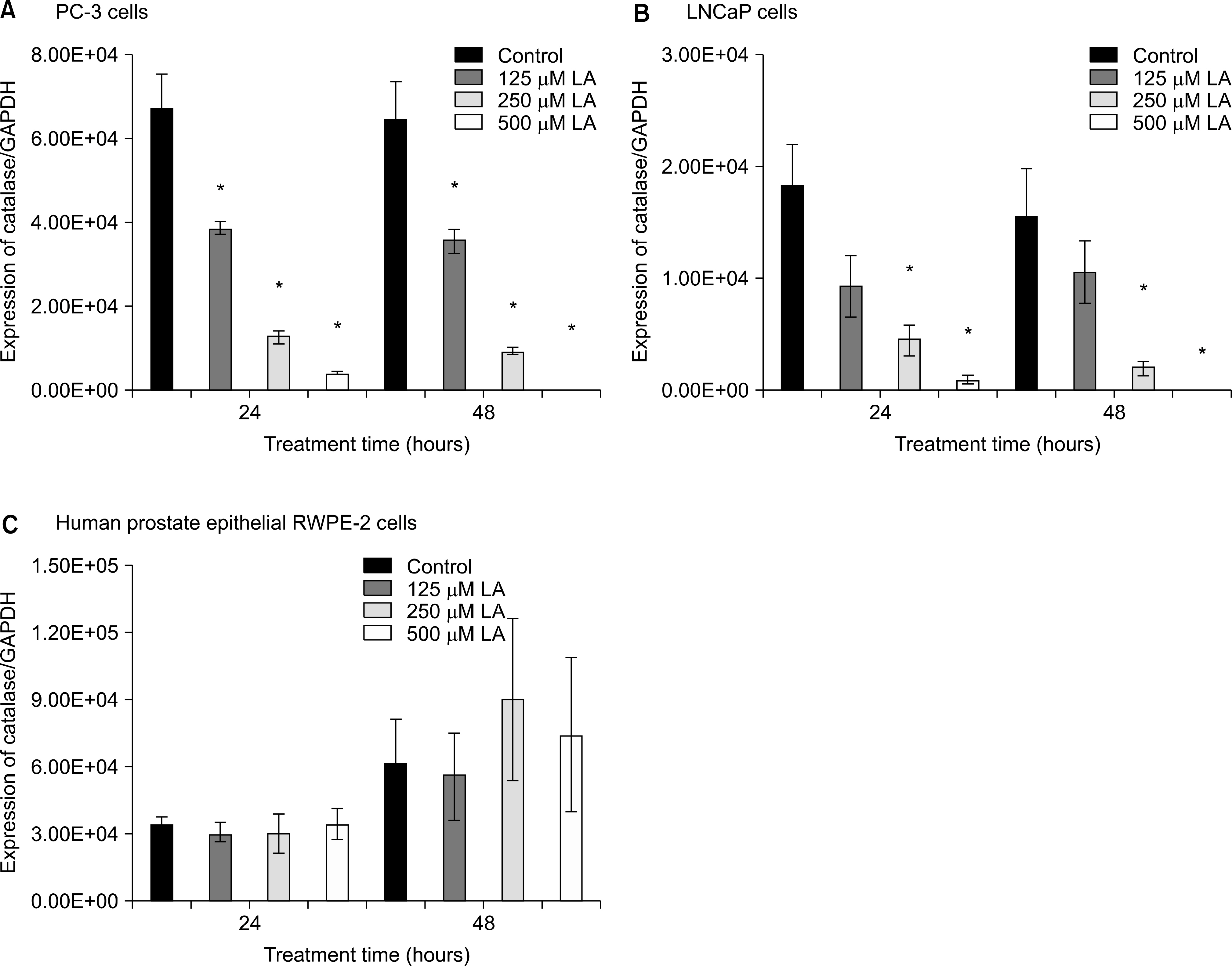
Ref-1 was expressed in the PC-3, LNCaP, and RWPE-2 cell lines. The expression of Ref-1 protein was increased after treatment with 125, 250, and 500 microM ALA in the PC-3 (p<0.05) and LNCaP (p>0.05) cells compared with the RWPE-2 cells at 48 hours. In PC-3 cells, the mRNA expression of SOD-1, SOD-2, catalase, and GSH-Px decreased at 24 and 48 hours dose-dependently compared with that in RWPE-2 cells (p<0.05). The mRNA expression of SOD-2, catalase, and GSH-Px in LNCaP cell decreased at 48 hours dose-dependently (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The expression of Ref-1 protein and antioxidant enzymes changed after ALA exposure in prostate cancer cells. Our findings suggest that ALA affects the antioxidant system in prostate cancer cells and may be related to compensatory changes in the antioxidant defense system of the cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antioxidants
Blotting, Western
Catalase
Cell Line
Glutathione Peroxidase
Lipid Peroxidation
Oxidation-Reduction
Prostate
Prostatic Neoplasms
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Superoxide Dismutase
Thioctic Acid
Antioxidants
Catalase
Glutathione Peroxidase
RNA, Messenger
Superoxide Dismutase
Thioctic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1.Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2002 Annual Report of the Korea central cancer registry. 2003. 11–24.2.Heinonen OP., Albanes D., Virtamo J., Taylor PR., Huttunen JK., Hartman AM, et al. Prostate cancer and supplementation with alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene: incidence and mortality in a controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998. 90:440–6.3.Clark LC., Dalkin B., Krongrad A., Combs GF Jr., Turnbull BW., Slate EH, et al. Decreased incidence of prostate cancer with selenium supplementation: results of a double-blind cancer prevention trial. Br J Urol. 1998. 81:730–4.
Article4.Chen JZ., Gokden N., Greene GF., Green B., Kadlubar FF. Simultaneous generation of multiple mitochondrial DNA mutations in human prostate tumors suggests mitochondrial hyper-mutagenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2003. 24:1481–7.
Article5.Moghadasian MH., Freeman HJ., Godin DV. Endogenous antioxidant status in neoplastic and adjacent tissues in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in rats: effects of olsalazine. Carcinogenesis. 1996. 17:983–7.6.Shi DY., Liu HL., Stern JS., Yu PZ., Liu SL. Alpha-lipoic acid induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells via the PTEN/Akt pathway. FEBS Lett. 2008. 582:1667–71.
Article7.Simbula G., Columbano A., Ledda-Columbano GM., Sanna L., Deidda M., Diana A, et al. Increased ROS generation and p53 activation in alpha-lipoic acid-induced apoptosis of hepatoma cells. Apoptosis. 2007. 12:113–23.8.Moungjaroen J., Nimmannit U., Callery PS., Wang L., Azad N., Lipipun V, et al. Reactive oxygen species mediate caspase activation and apoptosis induced by lipoic acid in human lung epithelial cancer cells through Bcl-2 down-regulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. 319:1062–9.
Article9.Surapaneni KM., Venkata GR. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in patients with carcinoma of prostate. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006. 50:350–4.10.Jung K., Seidel B., Rudolph B., Lein M., Cronauer MV., Henke W, et al. Antioxidant enzymes in malignant prostate cell lines and in primary cultured prostatic cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997. 23:127–33.
Article11.Reed LJ., DeBusk BG., Gunsalus IC., Hornberger CS Jr. Crystalline alpha-lipoic acid: a catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science. 1951. 114:93–4.12.Ziegler D. Thioctic acid for patients with symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: a critical review. Treat Endocrinol. 2004. 3:173–89.13.Wollin SD., Jones PJ. Alpha-lipoic acid and cardiovascular disease. J Nutr. 2003. 133:3327–30.14.Ho YS., Lai CS., Liu HI., Ho SY., Tai C., Pan MH, et al. Dihydrolipoic acid inhibits skin tumor promotion through anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. 73:1786–95.
Article15.Pathak SK., Sharma RA., Steward WP., Mellon JK., Griffiths TR., Gescher AJ. Oxidative stress and cyclooxygenase activity in prostate carcinogenesis: targets for chemopreventive strategies. Eur J Cancer. 2005. 41:61–70.
Article16.Yossepowitch O., Pinchuk I., Gur U., Neumann A., Lichtenberg D., Baniel J. Advanced but not localized prostate cancer is associated with increased oxidative stress. J Urol. 2007. 178:1238–43.
Article17.Evans AR., Limp-Foster M., Kelley MR. Going APE over ref-1. Mutat Res. 2000. 461:83–108.
Article18.Gaiddon C., Moorthy NC., Prives C. Ref-1 regulates the transactivation and pro-apoptotic functions of p53 in vivo. EMBO J. 1999. 18:5609–21.
Article19.Kelley MR., Cheng L., Foster R., Tritt R., Jiang J., Broshears J, et al. Elevated and altered expression of the multifunctional DNA base excision repair and redox enzyme Ape1/ref-1 in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. 7:824–30.20.Ramana CV., Boldogh I., Izumi T., Mitra S. Activation of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease in human cells by reactive oxygen species and its correlation with their adaptive response to genotoxicity of free radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:5061–6.
Article21.Lau JP., Weatherdon KL., Skalski V., Hedley DW. Effects of gemcitabine on APE/ref-1 endonuclease activity in pancreatic cancer cells, and the therapeutic potential of antisense oligonucleotides. Br J Cancer. 2004. 91:1166–73.
Article22.Karihtala P., Soini Y. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant mechanisms in human tissues and their relation to malignancies. APMIS. 2007. 115:81–103.
Article23.Powolny AA., Singh SV. Plumbagin-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is associated with modulation of cellular redox status and generation of reactive oxygen species. Pharm Res. 2008. 25:2171–80.
Article24.Asaumi H., Watanabe S., Taguchi M., Tashiro M., Nagashio Y., Nomiyama Y, et al. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatech-in-3-gallate inhibits ethanol-induced activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006. 36:113–22.
Article25.Siddiqui IA., Raisuddin S., Shukla Y. Protective effects of black tea extract on testosterone induced oxidative damage in prostate. Cancer Lett. 2005. 227:125–32.
Article26.Chowdhury SK., Raha S., Tarnopolsky MA., Singh G. Increased expression of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and antioxidant enzymes in prostate cancer cell lines/cancer. Free Radic Res. 2007. 41:1116–24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on cell proliferation and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cells
- Effect of 12-week Oral Treatment with alpha-lipoic acid on the Nerve Conduction in Symptomatic Diabetic Neuropathy
- Letter: Effects of alpha-lipoic Acid on Differentiation of Thyroid Cancer Cells
- The Efficacy of alpha-lipoic Acid on the Endotoxin-induced Acute Lung Injury
- Antioxidant Effects of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids