Cancer Res Treat.
2009 Sep;41(3):155-163.
Leptin and Leptin Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. heesung1.kim@samsung.com
Abstract
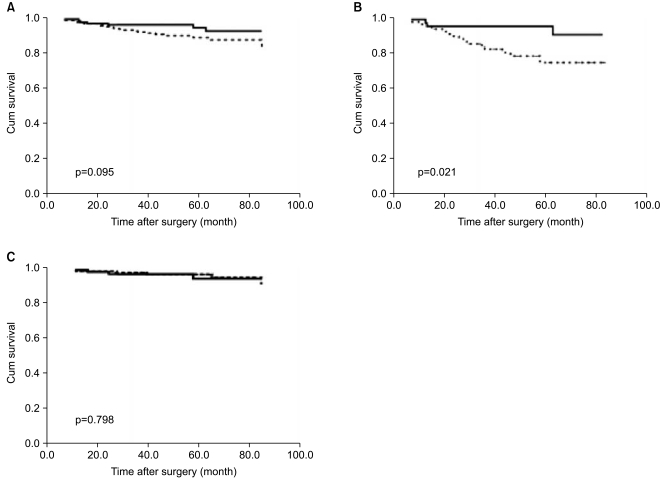
- PURPOSE
Leptin is a multifunctional hormone that's produced by adipose tissue and leptin is involved in the regulation of food intake and energy balance. The aims of this study were to determine the leptin and leptin receptor (Ob-R) expressions in human breast cancer and their corresponding influence on the prognosis of patients with breast cancer. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We examined the correlations between the leptin and Ob-R expressions and the breast cancer-related pathobiologic markers by performing immunohistochemistry in 517 patients with breast cancer. We analyzed the leptin and Ob-R expressions with respect to overall survival and relapse-free survival (RFS). RESULTS: Positive cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for leptin was noted in 39% of the patients and 79% of the patients showed positive cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for Ob-R. The expression of leptin in breast cancer was correlated with a high Ki-67 labeling index (p=0.019). Based on the univariate survival analysis, the clinicopathologic variables with prognostic value included the histologic grade, the T stage, the N stage, the HER2 status, the Bcl-2, p53 and Ki-67 expressions (p<0.05). The patients with leptin-positive breast cancers and a negative hormone receptor status had a significantly longer overall survival (p=0.021). Multivariate survival analysis showed that a positive expression of leptin was an independent prognostic marker for overall survival (hazard ratio, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.04~0.99; p=0.05). CONCLUSION: A leptin expression in breast cancer is significantly associated with the Ki-67 labeling index, and this suggests there is an association of a leptin expression with the proliferation activity. In addition, a leptin expression is an indicator of better survival for breast cancer patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reinier KS, Vacek PM, Geller BM. Risk factors for breast carcinoma in situ versus invasive breast cancer in a prospective study of pre- and post-menopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 103:343–348. PMID: 17063272.
Article3. Garofalo C, Surmacz E. Leptin and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2006; 207:12–22. PMID: 16110483.
Article4. Garofalo C, Koda M, Cascio S, Sulkowska M, Kanczuga-Koda L, Golaszewska J, et al. Increased expression of leptin and the leptin receptor as a marker of breast cancer progression: possible role of obesity-related stimuli. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:1447–1453. PMID: 16533767.
Article5. Ishikawa M, Kitayama J, Nagawa H. Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB-R) in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:4325–4331. PMID: 15240518.
Article6. Saxena NK, Sharma D, Ding X, Lin S, Marra F, Merlin D, et al. Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:2497–2507. PMID: 17363567.
Article7. Rose DP, Gilhooly EM, Nixon DW. Adverse effects of obesity on breast cancer prognosis, and the biological actions of leptin (review). Int J Oncol. 2002; 21:1285–1292. PMID: 12429979.
Article8. Bahrenberg G, Behrmann I, Barthel A, Hekerman P, Heinrich PC, Joost HG, et al. Identification of the critical sequence elements in the cytoplasmic domain of leptin receptor isoforms required for Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription activation by receptor heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol. 2002; 16:859–872. PMID: 11923481.
Article9. Bjorbaek C, Uotani S, da Silva B, Flier JS. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:32686–32695. PMID: 9405487.10. Yin N, Wang D, Zhang H, Yi X, Sun X, Shi B, et al. Molecular mechanisms involved in the growth stimulation of breast cancer cells by leptin. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:5870–5875. PMID: 15313931.
Article11. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. Part VII Breast. 2002. 6th ed. p. 221–240.12. Onuma M, Bub JD, Rummel TL, Iwamoto Y. Prostate cancer cell-adipocyte interaction: leptin mediates androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:42660–42667. PMID: 12902351.13. Rouet-Benzineb P, Aparicio T, Guilmeau S, Pouzet C, Descatoire V, Buyse M, et al. Leptin counteracts sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer HT-29 cells via NF-kappaB signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:16495–16502. PMID: 14752104.14. Bouloumie A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, Busse R. Leptin, the product of Ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circ Res. 1998; 83:1059–1066. PMID: 9815153.15. Tessitore L, Vizio B, Jenkins O, De Stefano I, Ritossa C, Argiles JM, et al. Leptin expression in colorectal and breast cancer patients. Int J Mol Med. 2000; 5:421–426. PMID: 10719061.
Article16. Hu X, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ, Cleary MP. Leptin--a growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94:1704–1711. PMID: 12441326.
Article17. Vona-Davis L, Rose DP. Adipokines as endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine factors in breast cancer risk and progression. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007; 14:189–206. PMID: 17639037.
Article18. Revillion F, Charlier M, Lhotellier V, Hornez L, Giard S, Baranzelli MC, et al. Messenger RNA expression of leptin and leptin receptors and their prognostic value in 322 human primary breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12(7 Pt 1):2088–2094. PMID: 16609020.
Article19. Jarde T, Caldefie-Chezet F, Damez M, Mishellany F, Penault-Llorca F, Guillot J, et al. Leptin and leptin receptor involvement in cancer development: a study on human primary breast carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008; 19:905–911. PMID: 18357374.
Article20. Caldefie-Chezet F, Damez M, de Latour M, Konska G, Mishellani F, Fusillier C, et al. Leptin: a proliferative factor for breast cancer? Study on human ductal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 334:737–741. PMID: 16009333.21. Miyoshi Y, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Shimomura I, et al. High expression of leptin receptor mRNA in breast cancer tissue predicts poor prognosis for patients with high, but not low, serum leptin levels. Int J Cancer. 2006; 118:1414–1419. PMID: 16206269.
Article22. Paik SS, Jang SM, Jang KS, Lee KH, Choi D, Jang SJ. Leptin expression correlates with favorable clinicopathologic phenotype and better prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:297–303. PMID: 19050975.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Leptin, Leptin Receptor, Adiponectin, and Adiponectin Receptor in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ and Invasive Breast Cancer
- Effects of the Expression of Leptin and Leptin Receptor (OBR) on the Prognosis of Early-stage Breast Cancers
- Identification and cDNA Cloning of the Leptin Receptor Long from ( OB-Rb ) from Rat Splenocytes
- p53 signaling is involved in leptin-induced growth of hepatic and breast cancer cells
- Leptin as a Potential Target for Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer