J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Feb;80(2):131-141. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.2.131.
Relationship of Serum Ferritin, Cholesterol, and Intimal Hyperplasia after Mechanical Injury to Carotid Artery in a Rat Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Vascular and Transplant Surgery, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ismoon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2117121
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.80.2.131
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Iron plays an important role in the process of oxidizing Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) in the arterial wall during the development of atherosclerosis, but the role of iron during the development of intimal hyperplasia has not been confirmed. Therefore, we evaluated the relationship of serum ferritin, serum cholesterol and intimal hyperplasia.
METHODS
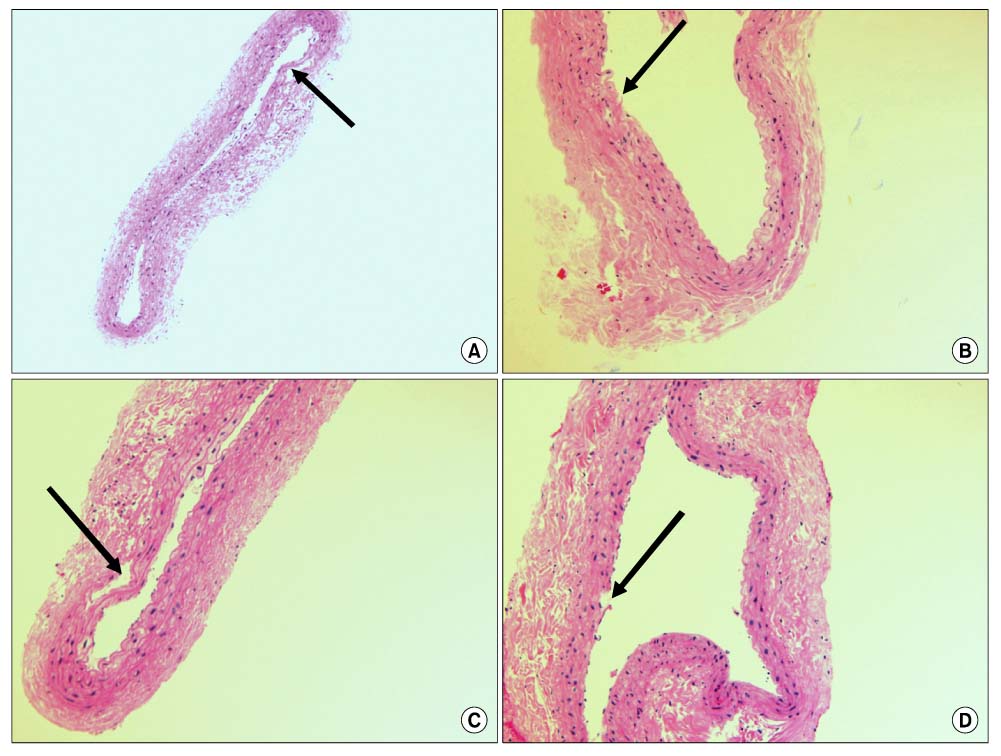
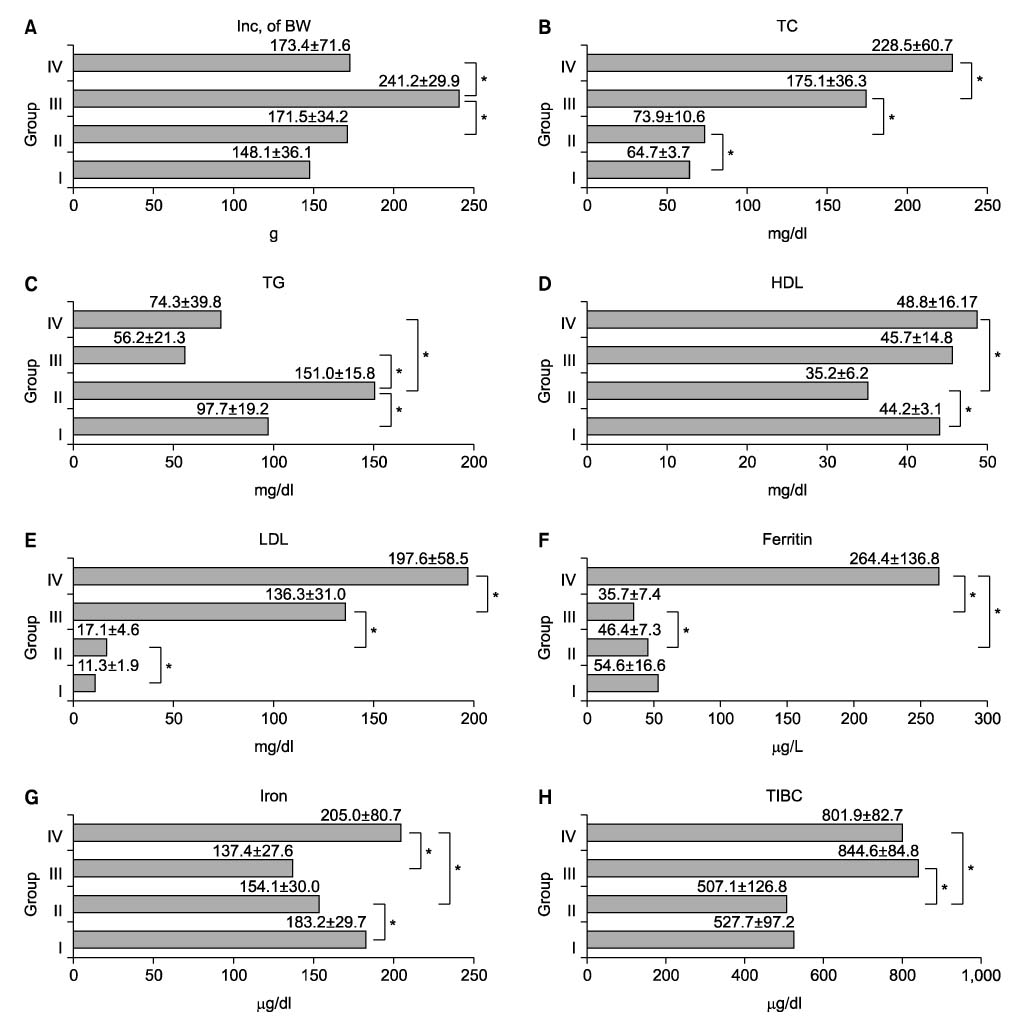
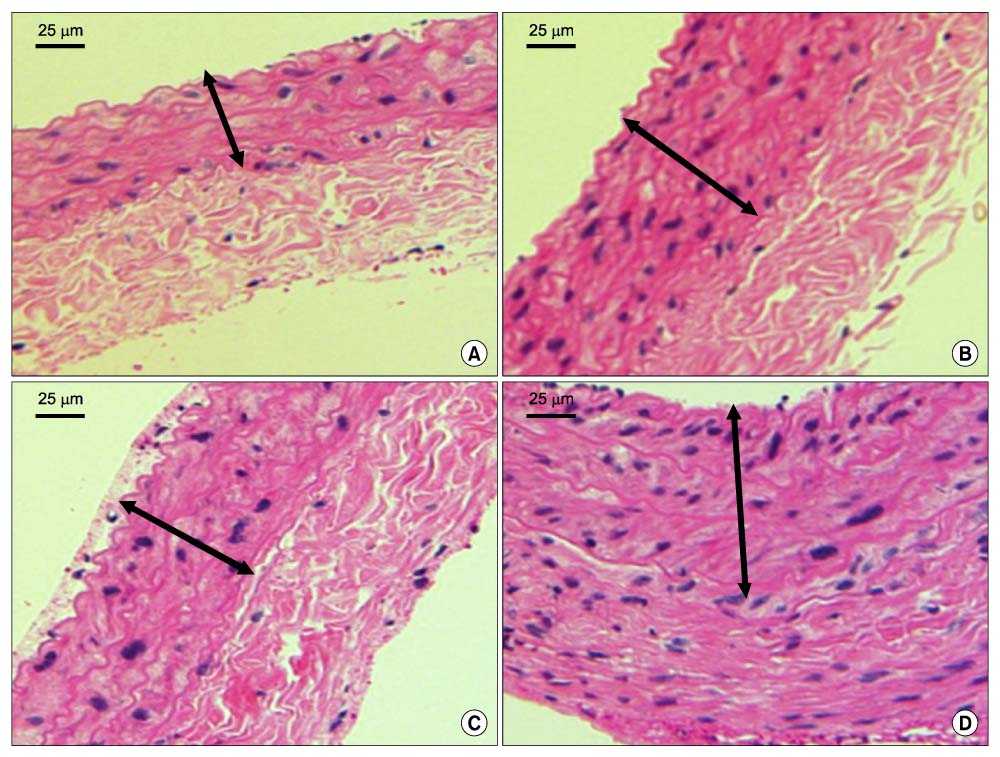
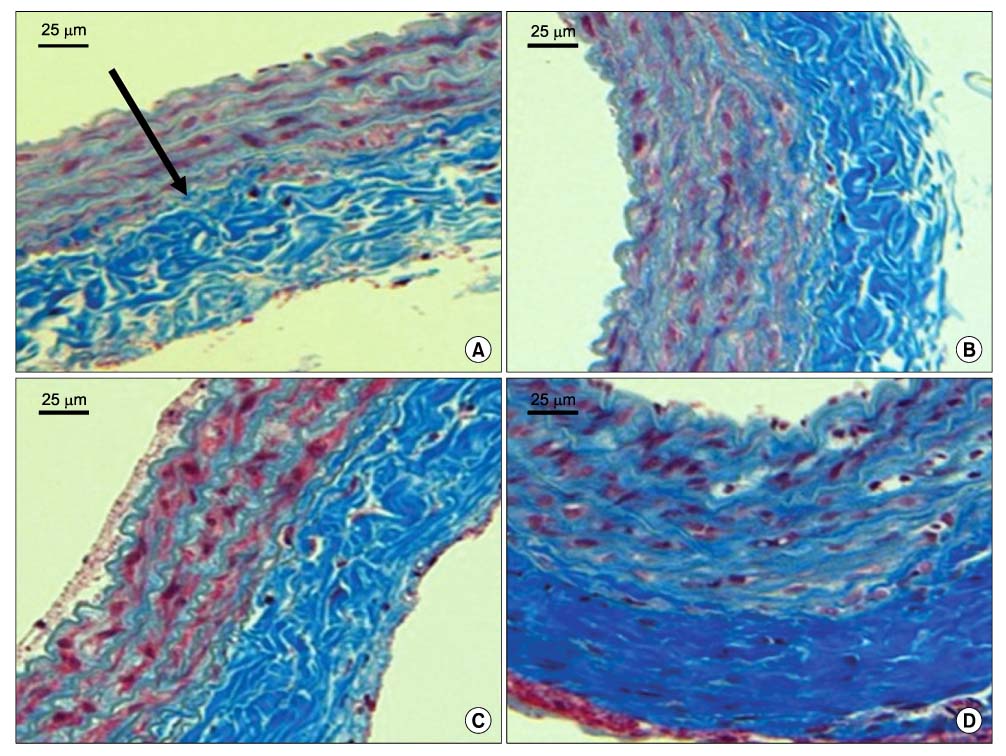
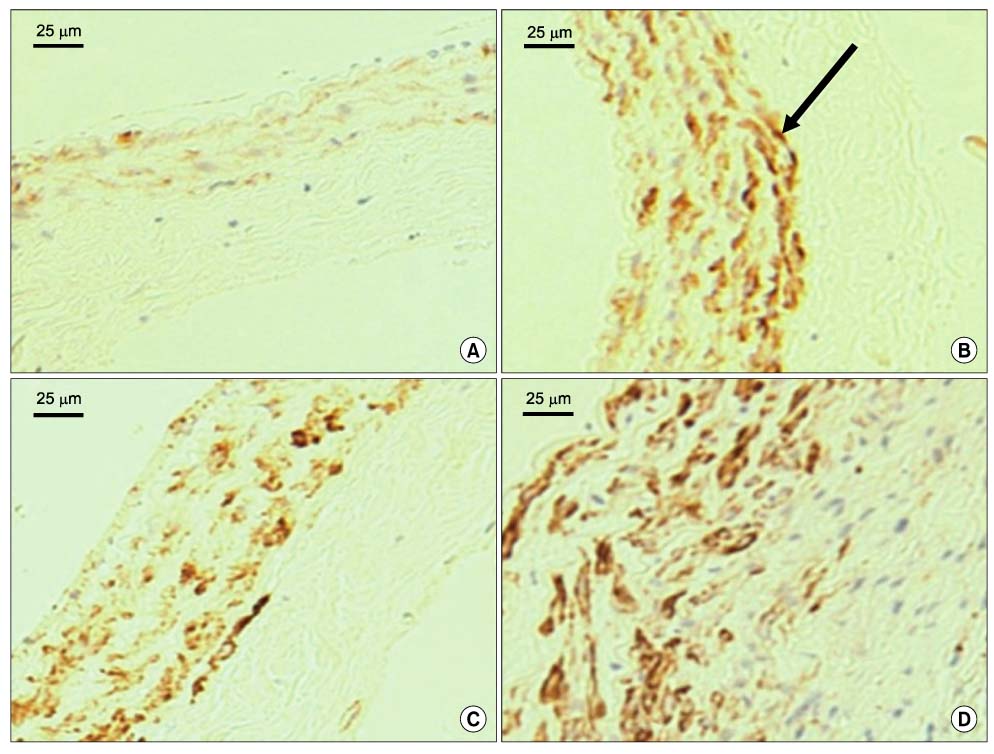
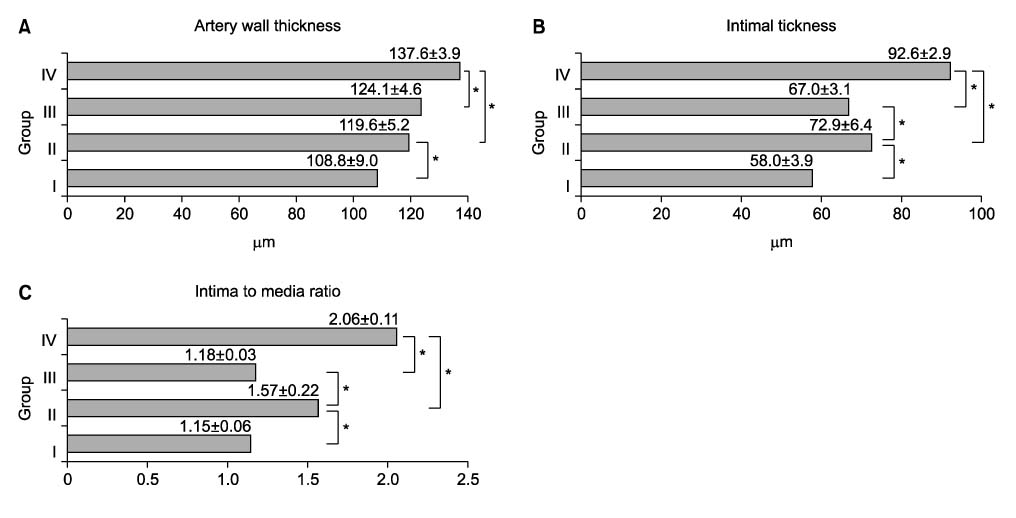
Forty rats were divided into four groups according to diet. Group I was the normocholesterol and normoferritin group, group II was the hypercholesterol and normoferritin group, group III was the hypercholesterol and hypoferritin group, and group IV was the hypercholesterol and hyperferritin group. At the sixth week, we induced clamping injury at the left common carotid artery of each rat. At the end of the eighth week, we obtained tissue of the left common carotid artery from each rat, and we performed staining. After that, we evaluated differences of the intima to media ratio (IMR) of arterial walls according to groups.
RESULTS
The IMR of group II was higher than that of group I (P<0.001). Among hypercholesterol groups (group II~IV), the IMR of group III was lower than that of group II (P<0.001), and the IMR of group IV was higher than that of group II (P=0.007).
CONCLUSION
We suggest the possibility that serum ferritin and serum cholesterol are proportionally related with intimal hyperplasia. But we think that large-volume experiments in animal models and prospective studies in humans are needed to confirm and expand on our results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heinecke JW. Oxidants and antioxidants in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: implications for the oxidized low density lipoprotein hypothesis. Atherosclerosis. 1998. 141:1–15.2. Sullivan JL. Iron and the sex difference in heart disease risk. Lancet. 1981. 1:1293–1294.3. Haidari M, Javadi E, Sanati A, Hajilooi M, Ghanbili J. Association of increased ferritin with premature coronary stenosis in men. Clin Chem. 2001. 47:1666–1672.4. Ramakrishna G, Rooke TW, Cooper LT. Iron and peripheral arterial disease: revisiting the iron hypothesis in a different light. Vasc Med. 2003. 8:203–210.5. You SA, Wang Q. Ferritin in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2005. 357:1–16.6. Chiang MT, Chen YC, Huang AL. Plasma lipoprotein cholesterol levels in rats fed a diet enriched in cholesterol and cholic acid. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1998. 68:328–334.7. Holbein BE. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980. 29:886–891.8. Han JG, Xu HM, Song WL, Jin ML, Gao JS, Wang ZJ, et al. Histologic analysis of acellular dermal matrix in the treatment of anal fistula in an animal model. J Am Coll Surg. 2009. 208:1099–1106.9. Yuan XM, Brunk UT, Olsson AG. Effects of iron- and hemoglobin-loaded human monocyte-derived macrophages on oxidation and uptake of LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995. 15:1345–1351.10. Lamb DJ, Leake DS. Iron released from transferring at acidic pH can catalyse the oxidation of low density lipoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1994. 352:15–18.11. Pratico D, Pasin M, Barry OP, Ghiselli A, Sabatino G, Iuliano L, et al. Iron-dependent human platelet activation and hydroxyl radical formation: involvement of protein kinase C. Circulation. 1999. 99:3118–3124.12. Salonen JT, Nyyssonen K, Korpela H, Tuomilehto J, Seppanen R, Salonen R. High stored iron levels are associated with excess risk of myocardial infarction in eastern Finnish men. Circulation. 1992. 86:803–811.13. Magnusson MK, Sigfusson N, Sigvaldason H, Johannesson GM, Magnusson S, Thorgeirsson G. Low iron-binding capacity as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1994. 89:102–108.14. Kiechl S, Willeit J, Egger G, Poewe W, Oberhollenzer F. Body iron stores and the risk of carotid atherosclerosis: prospective results from the Bruneck study. Circulation. 1997. 96:3300–3307.15. Wolff B, Völzke H, Lüdemann J, Robinson D, Vogelgesang D, Staudt A, et al. Association between high serum ferritin levels and carotid atherosclerosis in the study of health in Pomerania (SHIP). Stroke. 2004. 35:453–457.16. Hinagata J, Kakutani M, Fujii T, Naruko T, Inoue N, Fujita Y, et al. Oxidized LDL receptor LOX-1 is involved in neointimal hyperplasia after balloon arterial injury in a rat model. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. 69:263–271.17. Bennett MR, O'Sullivan M. Mechanisms of angioplasty and stent restenosis: implications for design of rational therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2001. 91:149–146.18. Aoyama T, Chen M, Fujiwara H, Masaki T, Sawamura T. LOX-1 mediates lysophosphatidylcholin-induces oxidized LDL uptake in smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 2000. 467:217–220.19. Moriwaki H, Kume N, Kataoka H, Murase T, Nishi E, Sawamura T, et al. Expression of lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 in human and murine macrophages: upregulated expression by TNF-alpha. FEBS Lett. 1998. 440:29–32.20. Chen M, Kakutani M, Naruko T, Ueda M, Narumiya S, Masaki T, et al. Activation-dependent surface expression of LOX-1 in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 282:153–158.21. Day SM, Duquaine D, Mundada LV, Menon RG, Khan BV, Rajagopalan S, et al. Chronic iron administration increases vascular oxidative stress and accelerates arterial thrombosis. Circulation. 2003. 107:2601–2606.22. Smith C, Mitchinson MJ, Aruoma OI, Halliwell B. Stimulation of lipid peroxidation and hydroxyl-radical generation by the contents of human atherosclerotic lesions. Biochem J. 1992. 286:901–905.23. Pang JH, Jiang MJ, Chen YL, Wang FW, Wang DL, Chu SH, et al. Increased ferritin gene expression in atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest. 1996. 97:2204–2212.24. Yuan XM, Anders WL, Olsson AG, Brunk UT. Iron in human atheroma and LDL oxidation by macrophages following erythrophagocytosis. Atherosclerosis. 1996. 124:61–73.25. Turbino-Ribeiro SM, Silva ME, Chianca DA Jr, De Paula H, Cardoso LM, Colombari E, et al. Iron overload in hypercholesterolemic rats affects iron homeostasis and serum lipids but not blood pressure. J Nutr. 2003. 133:15–20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intimal Hyperplasia in Loop-Injured Carotid Arteries Is Attenuated in Transglutaminase 2-Null Mice
- Inhibition of intimal hyperplasia by local perivascular application of rapamycin and imatinib mesilate after carotid balloon injury
- Retrovirus-Mediated Herpes Simplex Virus Thymidine Kinase Gene Therapy for the Prevention of Stenosis in Rat Carotid Artery Injury Model
- The Serum Lipid Level is Associated with Intimal Thickness of the Carotid Artery for Patients with Coronary Atherosclerosis
- Effect of High Dose External Irradiation on the Matrix Metalloprotease-2 Expression in a Rat Carotid Artery Injury Model