Lab Anim Res.
2010 Dec;26(4):361-367. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.4.361.
Dangyuja (Citrus grandis Osbeck) Peel Improves Lipid Profiles and Alleviates Hypertension in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. yjlee3@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Citrus Research Station, National Institute of Horticultural & Herbal Science, Rural Development Administration, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2114704
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.4.361
Abstract
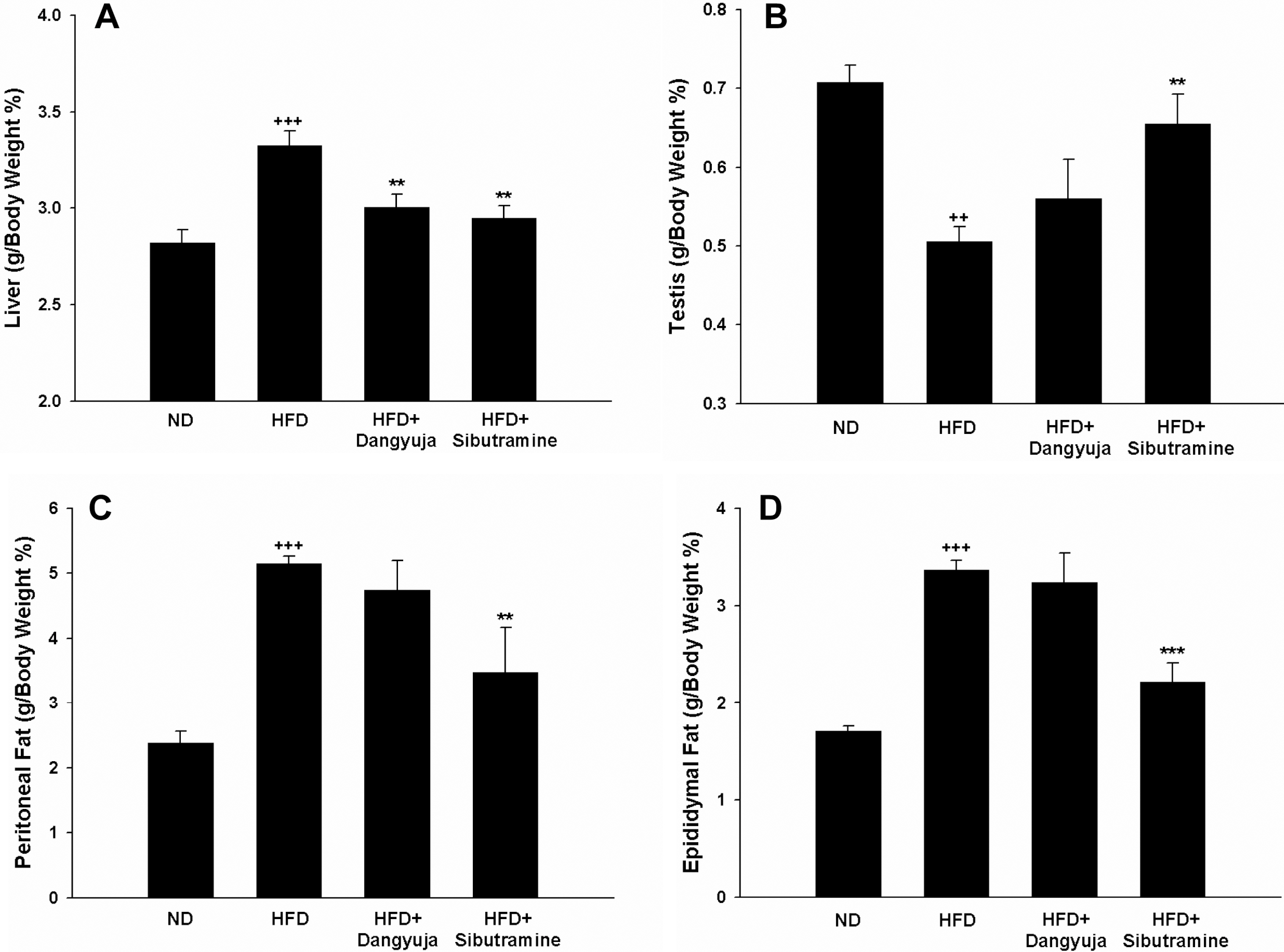
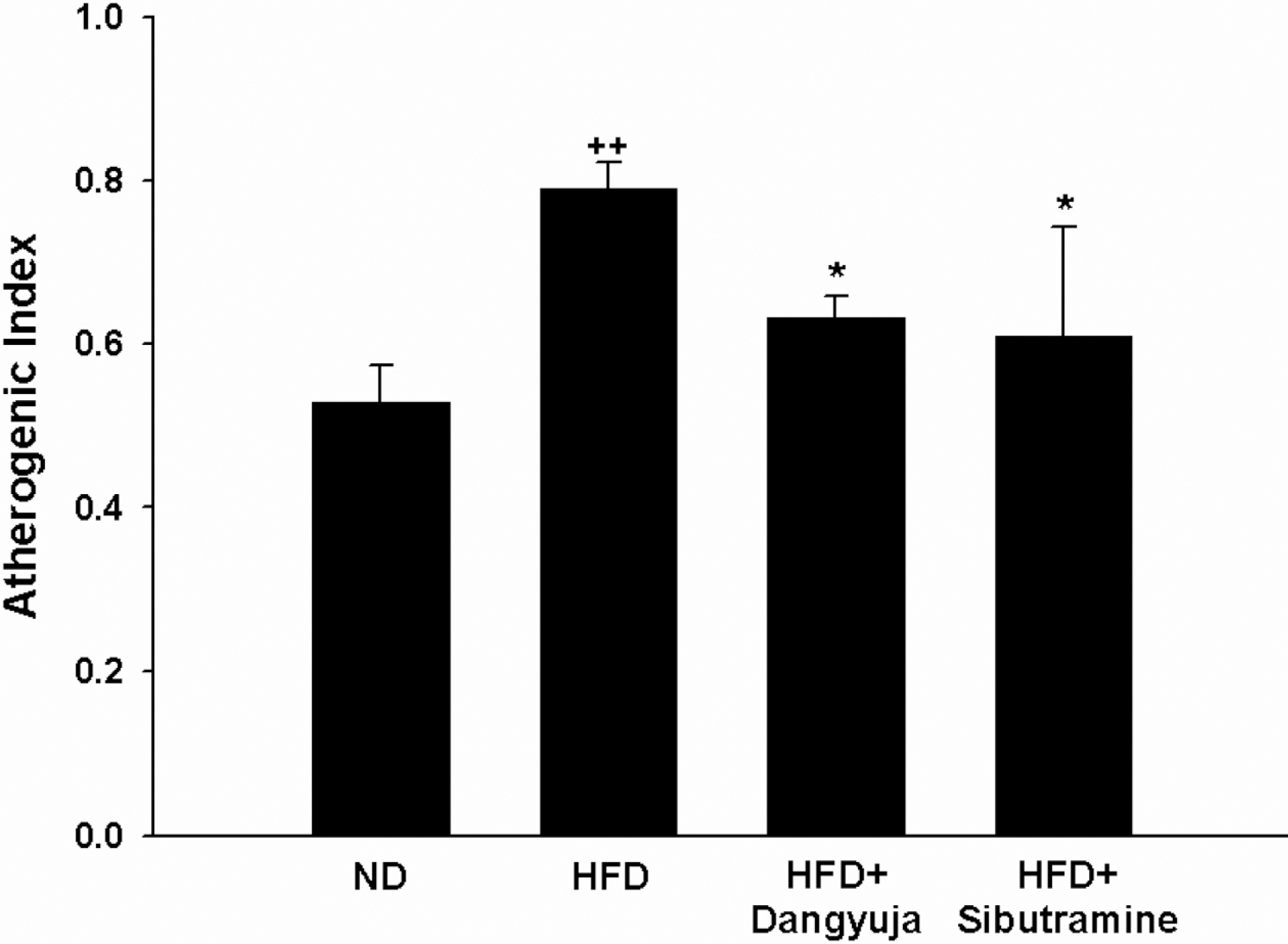
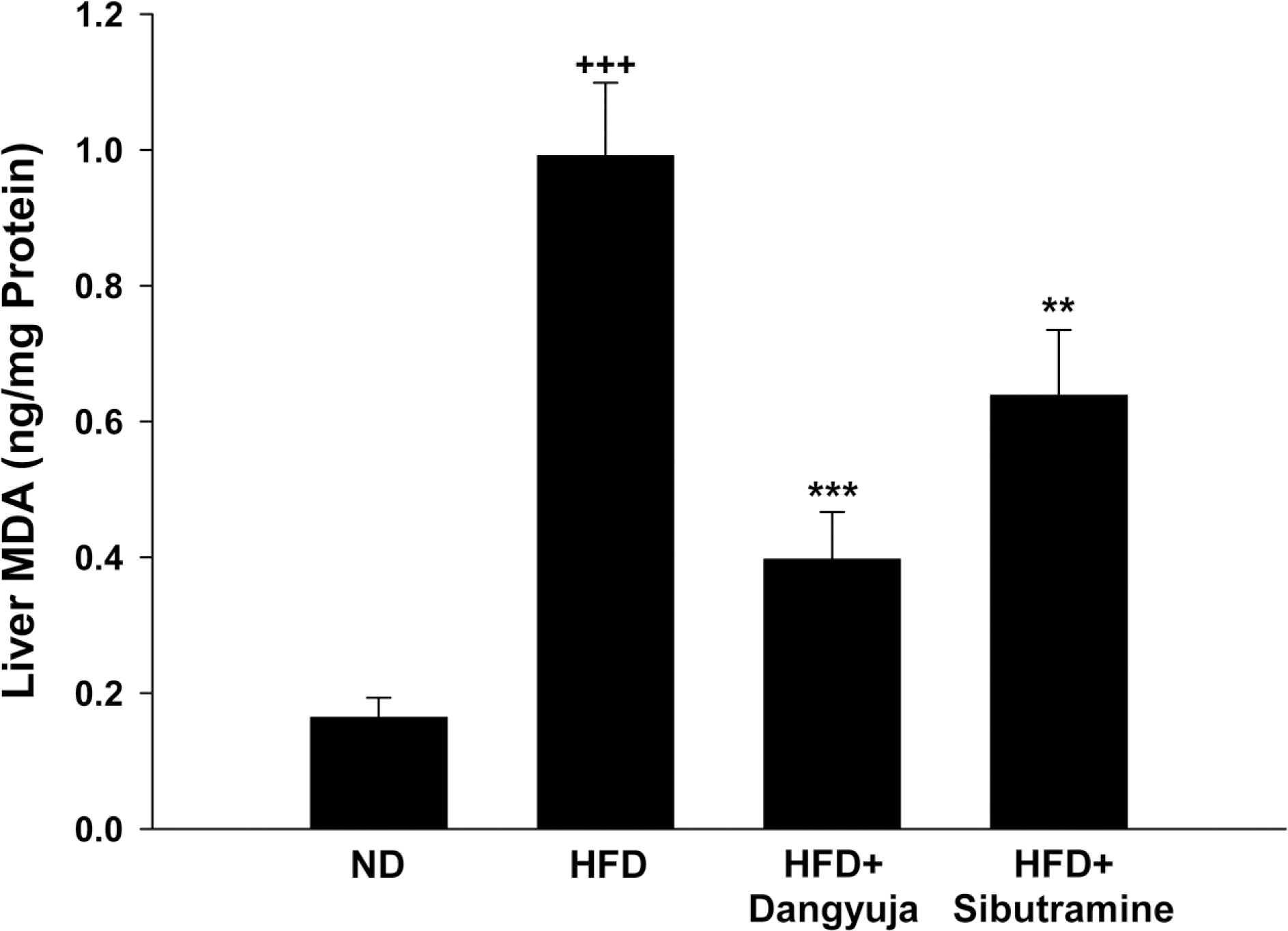
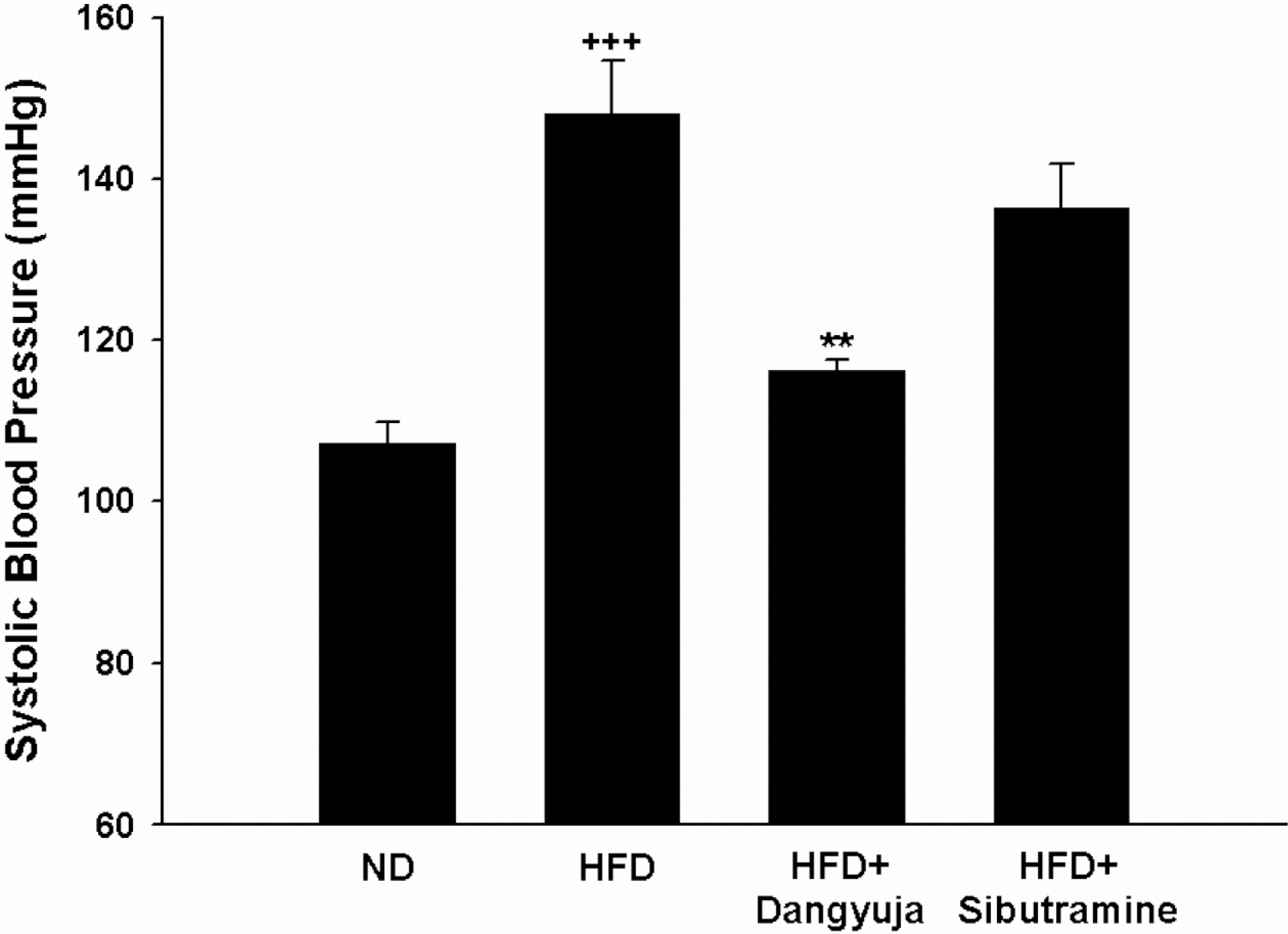
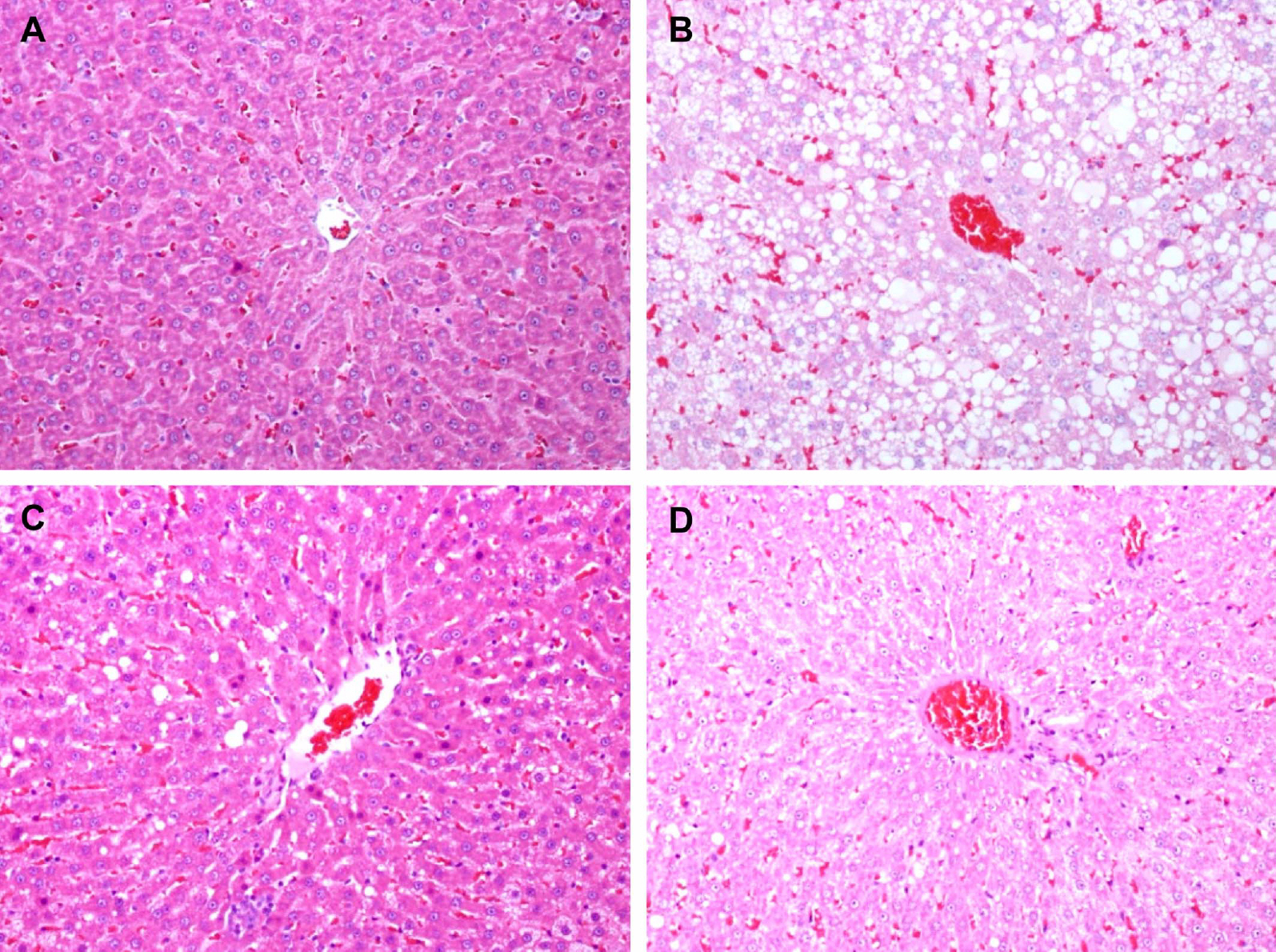
- Obesity is a major public health problem and significant risk factor for many serious diseases including coronary artery disease, cancer, and diabetes. This study was performed to investigate the hypolipidemic effects and anti-hypertensive effect of Dangyuja (Citrus grandis Osbeck) peel, which is bred on Jeju island, in rats fed a high-fat diet. This study was conducted on 4 equal rat groups which were fed as follows; normal diet group (ND), high fat diet group (HFD), high fat diet supplemented with powdered peel of Dangyuja (1%, wt/wt) group (HFD+Dangyuja), and high fat diet treated with sibutramine simultaneously at a dose of 10 mg/kg group (HFD+Sibutramine). After feeding the high fat diet, body weight gain and relative weight of adipose tissues and liver significantly increased in HFD group, but Dangyuja peel supplementation protected these HFD-induced changes. The levels of serum triglyceride, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, and the atherogenic index significantly decreased in the HFD+Dangyuja peel group compared with the HFD group. The systolic blood pressure was significantly increased by feeding the high fat diet, whereas the supplementation of Dangyuja peel effectively prevented the elevation of blood pressure. Therefore, these results suggest that Dangyuja exerts a beneficial effect on obesity by improving lipid metabolism and alleviating obesity-related hypertension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
Apfelbaum, M.D., Vague, P., Ziegler, O., Hanotin, C., Thomas, F. and Leutenegger, E. (. 1999. ). Long-term maintenance of weight loss after a very-low-calorie diet a randomized blinded trial of the efficacy and tolerability of sibutramine. Am. J. Med. 106(2):179–184.Buege, J.A. and Aust, S.D. (. 1978. ). Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 52:302–310.Cho, J.H., Lee, N.J., Hong, S.H., Kim, D.K., Shin, S., Park, J.H., Kang, J.K., Kim, Y.B. and Hwang, S.Y. (. 2005. ). Effect of HGD-201 on obesity induced by high-fat diet in Zucker rats. Lab. Anim. Res. 21(2):158–163.Cuevas, P., Garcia-Calvo, M., Carceller, F, Reimers, D., Zazo, M., Buevas, B., Munoz-Willery, I., Martinez-Coso, V., Lamas, S. and Gimenez-Gallego, G. (. 1996. ). Correction of hypertension by normalization of endothelial levels of fibroblast growth factor and nitric oxide synthase in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93(21):11996–12001.Festi, D., Colecchia, A., Sacco, T., Bondi, M., Roda, E. and Marchesini, G. (. 2004. ). Hepatic steatosis in obese patients: clinical aspects and prognostic significance. Obesity Rev. 5(1):27–42.Fujioka, K., Seaton, T.B., Rowe, E., Jelinek, C.A., Raskin, P., Levovitz, H.E. and Weinstein, S.P. (. 2000. ). Weight loss with sibutramine improves glycaemic control and other metabolic parameters in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2(3):175–187.Hill, J.O., Peters, J.C. and Wyatt, H.R. (. 2007. ). The role of public policy in treating the epidemic of global obesity. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 81(5):772–775.Hsu, C.L. and Yen, G.C. (. 2007. ). Effect of gallic acid on high fat diet-induced dyslipidaemia, hepatosteatosis and oxidative stress in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 98:727–735.Hsu, C.L., Wu, C.H., Huang, S.L. and Yen G.C. (. 2009. ). Phenolic compounds rutin and O-coumaric acid ameliorate obesity induced by high-fat diet in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(2):425–431.Jayakumar, S.M., Nalini, N. and Venugopal, P.M. (. 1991. ). Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) on lipids in rats fed atherogenic diet. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 27(2):79–82.Kim, M.H., Jang, S.Y. and Lee, Y.S. (. 2006. ). Effect of dietary fat and genistein on lipid metabolism and antioxidant activity in hyperlipidemic male rats induced high fat diet. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 39(2):100–108.Kim, S.J., Jung, J.Y., Kim, H.W. and Park, T.S. (. 2008. ). Anti-obesity effects of Juniperus chinensis extract are associated with increased AMP-activated protein kinase expression and phosphorylation in the visceral adipose tissue of rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 31(7):1415–1421.Kopelman, P.G. (. 2000. ). Obesity as a problem. Nature. 404(6778):635–643.Laurent, A., Nicco, C., Tran, V.N.J., Borderie, D., Chereau, C., Conti, F., Jaffray, P., Soubrane, O., Calmus, Y., Beill, B. and Batteux, F. (. 2004. ). Pivotal role of superoxide anion and beneficial effect of antioxidant molecules in murine steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 39(5):1277–1285.Lavie, C.J. and Milani, R.V. (. 2003. ). Obesity and cardiovascular disease: the Hippocrates paradox? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 42(4):677–679.Lee, H.J., Kang, G.J., Yoon, W.J., Kang, H.K., Kim, Y.S., Kim, S.M. and Yoo, E.S. (. 2006. ). Anti-inflammatory effect of Unripe fruit of Citrus grandis Osbeck in RAW264.7 and HaCaT cells. Kor. J. Pharmacogn. 37(2):74–80.Lim, H.K., Yoo, E.S., Moon, J.Y., Jeon, Y.J. and Cho, S.M.K. (. 2006. ). Antioxidant activity of extracts from Dangyuja (Citrus grandis Osbeck) fruits produced in Jeju island. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 15(2):312–316.Leung, W.Y.S., Thomas, G.N., Chan, J.C.N. and Tomlinson, B. (. 2003. ). Weight management and current options in pharmacotherapy: Orlistat and sibutramine. Clin. Ther. 25(1):58–80.McMahon, F.G., Fujioka, K., Singh, B.N, Mendel, C.M., Rowe, E., Rolston, K., Johnson, F. and Mooradian, A.D. (. 2000. ). Efficacy and safety of sibtramine in obese white and African American patients with hypertension: a 1-year, double-blind, placebocontrolled, multicenter trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 160(14):2185–2191.Moon, J.Y., Kim, H.N., Cho, M.J., Chang, W.Y., Kim, C.T. and Cho, S.M.K. (. 2009. ). Induction of apoptosis in SNU-16 human gastric cancer cells by the chloroform fraction of an extract of Dangyuja (Citrus grandis) leaves. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 52(2):168–175.Nakayama, T., Suzuki, S., Kudo, H., Sassa, S., Nomura, M. and Sakamoto, S. (. 2007. ). Effects of three Chinese herbal medicines on plasma and liver lipids in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 109:236–240.Park, S.H., Ko, S.K. and Chung, S.H. (. 2005. ). Euonymus alatus prevents the hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia induced by high-fat diet in ICR mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 102:326–335.Pessayre, D., Fromenty, B. and Mansouri, A. (. 2004. ). Mitochondrial injury in steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16(11):1095–1105.Roberts, C.K., Vaziri, N.D., Ni, Z. and Barnard, R.J. (. 2002. ). Correction of longterm diet-induced hypertension and nitrotyrosine accumulation by diet modification. Atherosclerosis. 163(2):321–327.Smith Jr, S.C., Jackson, R., Pearson, T.A., Fuster, V., Yusuf, S., Faergeman, O., Wood, D.A., Alderman, M., Horgan, J., Home, P., Hunn, M. and Grundy, S.M. (. 2004. ). Principles for national and regional guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention: a scientific statement from the World Heart and Stroke Forum, Circulation. 109(25):3112–3121.Song, E.Y., Choi, Y.H., Kang, K.H. and Koh, J.S. (. 1998. ). Free sugar, organic acid, hesperidin, naringin and inorganic elements changes of cheju citrus fruits according to harvest dat. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 30(2):306–312.Vasselli, J.R. and Weindruch, R. (. 2005. ). Intentional weight loss reduces mortality rate in a rodent model of dietary obesity. Obesity Res. 13(4):693–702.Walsh, K.M., Leen, E. and Leen, M.E. (. 1999. ). The effect of sibutramine on resting energy expenditure and adrenaline-induced thermogenesis in obese females. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 23(10):1009–1015.Yang, Y., Zhou, L., Gu, Y., Zhang, Y., Tang, J., Li, F., Shang, W., Jiang, B., Yue, X. and Chen, M. (. 2007. ). Dietary chickpeas reverse visceral adiposity, dyslipidemia and insulin resistance in rats induced by a chronic high-fat diet. Br. J. Nutr. 98(4):720–726.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Soyoligosaccharide on Lipid Metabolism in Rats Fed the High Fat or Low Fat Diet
- Effects of Genistein Supplementation on Fatty Liver and Lipid Metabolism in Rats Fed High Fat Diet
- Effect of Dietary Grape Pomace on Lipid Oxidation and Related Enzyme Activities in Rats Fed High Fat Diet
- Effects of Liquid Culture of Coriolus Versicolor on Lipid Metabolism and Enzyme Activities in Rats Fed High Fat Diet
- alpha-Lipoic acid reduced weight gain and improved the lipid profile in rats fed with high fat diet