J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Jun;49(6):942-950. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.942.
Comparison of Stratus OCT and GDx VCC in Detecting Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Gangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kihopark@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2110875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.942
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To compare the abilities of optical coherence tomography (Stratus OCT) and scanning laser polarimetry with variable corneal compensation (GDx VCC) in detecting localized retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) defects of red free photography
METHODS
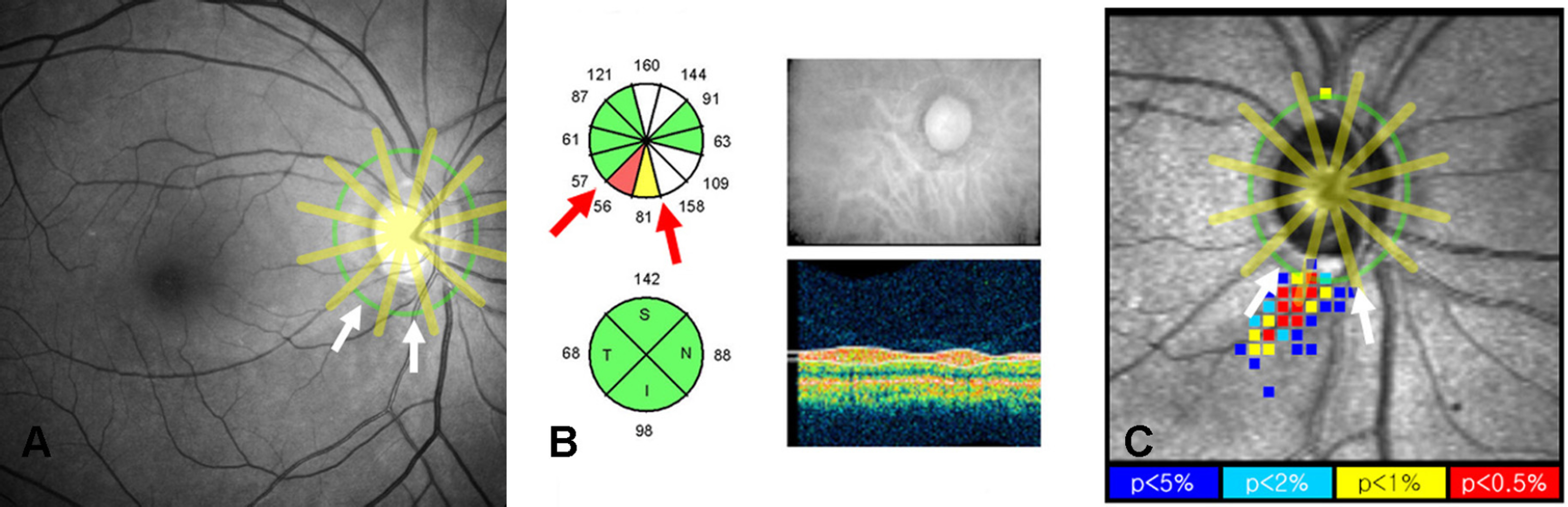
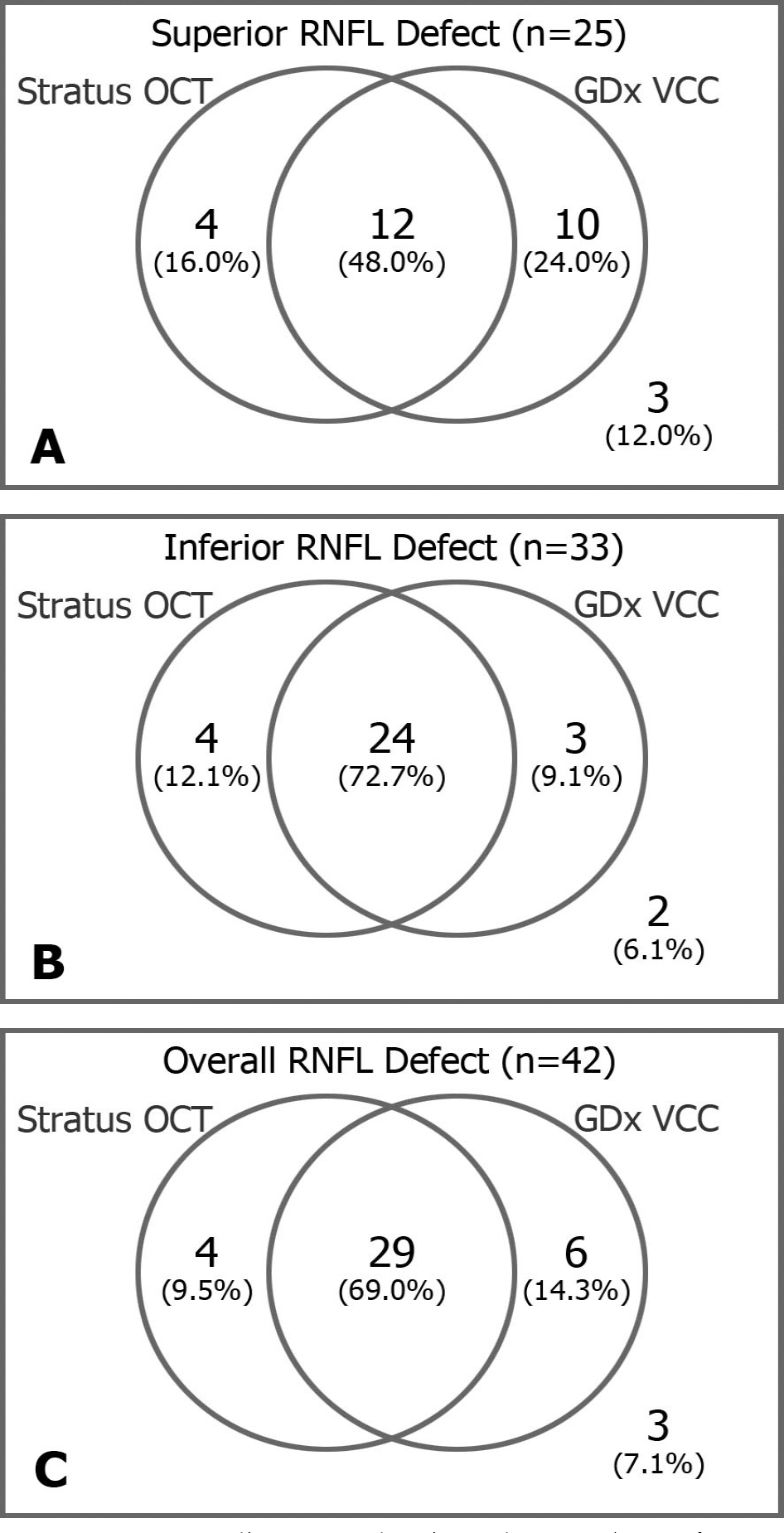
Thirty six normal subject and 50 patients with localized RNFL defects were included in this study. Only one eye per subject was considered. The peripapillary RNFL was divided into 12 clock-hour sectors and localized RNFL defects were evaluated in these 12 sectors. To compare the diagnostic performance of Stratus OCT and GDx VCC based on the findings of red-free photography, we calculated the sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of each analyzer using a criterion of 1 > or = clock hours abnormal at the <5% level.
RESULTS
The sensitivity (78.6%), specificity (94.4%), and AUC (0.872) of Stratus OCT were not significantly different from those of GDx VCC (83.3%, 94.4%, and 0.882, respectively) (McNemar test, p=0.75, 1.00, and 0.82, respectively). However, the sensitivity (64.0%) of Stratus OCT for superior RNFL defect was significantly lower than that (84.8%) for inferior defect (Fisher's exact test, p=0.02).
CONCLUSIONS
The sensitivity of the sector average of Stratus OCT and the deviation map of GDx VCC were fair in discriminating localized RNFL defects, and the specificity of those were excellent. In addition, the diagnostic performance was not significantly different between two analyzers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR, Maumenee AE. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:635–49.2. Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP. . Optical coherence tomography. Science. 1991; 254:1178–81.
Article3. Schuman JS, Hee MR, Puliafito CA. . Quantification of nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous eyes using optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995; 113:586–96.
Article4. Weinreb RN, Shakiba S, Zangwill L. Scanning laser polarimetry to measure the nerve fiber of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 119:627–36.5. Zhou Q, Weinreb RN. Individualized compensation of anterior segment birefringence during scanning laser polarimetry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43:2221–8.6. Schuman JS, Pedut-Kloizman T, Hertzmark E. . Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:1889–98.
Article7. Weinreb RN, Shakiba S, Zangwill L. Scanning laser polarimetry to measure the nerve fiber of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 119:627–36.8. Guedes V, Schuman JS, Hertzmark E. . Optical coherence tomography measurement of macular and nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous human eyes. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:177–89.
Article9. Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C. . Fourier analysis of scanning laser polarimetry measurements with variable corneal compensation in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:2606–12.
Article10. Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Weinreb RN. Comparison of the GDx VCC scanning laser polarimeter, HRT II confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope, and stratus OCT optical coherence tomograph for the detection of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:827–37.11. Leung CK, Chan WM, Chong KK. . Comparative study of retinal nerve fiber layer measurement by StratusOCT and GDx VCC, I: correlation analysis in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:3214–20.
Article12. Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M. . Comparison between GDx VCC scanning laser polarimetry and Stratus OCT optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis of chronic glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:650–5.
Article13. Kanamori A, Nagai-Kusuhara A, Escaño MF. . Comparison of confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, scanning laser polarimetry and optical coherence tomography to discriminate ocular hypertension and glaucoma at an early stage. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:58–68.
Article14. Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. III. Quantitative correlation of nerve fiber loss and visual field defect in glaucoma, ischemic neuropathy, papilledema, and toxic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:135–46.15. Sommer A, Katz J, Quigley HA. . Clinically detectable nerve fiber atrophy precedes the onset of glaucomatous field loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:77–83.
Article16. Mok KH, Lee VW. Disc‐ to‐ macula distance to disc- diameter ratio for optic disc size estimation. J Glaucoma. 2002; 11:392–5.17. Newcombe RG. Improved confidence intervals for the difference between binomial proportions based on paired data. Stat Med. 1998; 17:2635–50.
Article18. Odberg T, Riise D. Early diagnosis of glaucoma. The value of successive stereophotography of the optic disc. Acta Ophthalmol. 1985; 63:257–63.19. Quigley HA, Brown AE, Morrison JD, Drance SM. The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:51–7.
Article20. Seong GJ, Chung GW, Oh ST. Topographic measurements of the optic nerve head with confocal scanning laser tomography in normal Koreans. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:1834–41.21. Park SJ, Park KH, Yu YS. . Early detection of glaucoma with retinal nerve fiber layer photograph. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:180–6.22. Niessen AG, van den Berg TJ, Langerhorst CT, Bossuyt PM. Grading of retinal nerve fiber layer with a photographic reference set. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 120:577–86.
Article23. Quigley HA, Reacher M, Katz J. . Quantitative grading of nerve fiber layer photographs. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:1800–7.
Article24. Budenz DL, Michael A, Chang RT. . Sensitivity and specificity of the StratusOCT for perimetric glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:3–9.
Article25. Jeoung JW, Park KH, Kim TW. . Diagnostic ability of optical coherence tomography with a normative database to detect localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:2157–63.
Article26. Varma R, Skaf M, Barron E. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal human eyes. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:2114–9.
Article27. Poinoosawmy D, Fontana L, Wu JX. . Variation of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements with age and ethnicity by scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997; 81:350–4.28. Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Varma R. . Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1046–52.
Article29. Kim TW, Park UC, Park KH, Kim DM. Ability of Stratus OCT to identify localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects in patients with normal standard automated perimetry results. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:1635–41.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Scanning Laser Polarimetry and Optical Coherence Tomography for Detection of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects
- The Relationship between Optical Coherence Tomography and Scanning Laser Polarimetry Measurements in Glaucoma
- Usefulness of Table Parameters of Stratus OCT in Detection of Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects
- Relationship between the Retinal Thickness Analyzer and the GDx VCC Scanning Laser Polarimeter, Stratus OCT Optical Coherence Tomograph, and Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy
- Comparison of Time Domain OCT and Spectrum Domain OCT for Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Assessment