J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2013 Jun;17(2):144-148. 10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.2.144.
Irreversible Hemorrhagic Complication of Recurrent Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. leehuijoong@knu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2099873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.2.144
Abstract
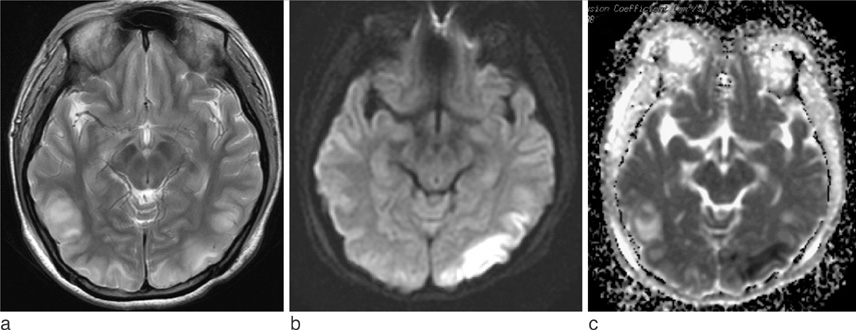
- Although most cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) are reversible, irreversible lesions as a form of hemorrhage or infarction have been described. PRES as a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (PRES-SLE) is associated with hypertension or use of immunosuppressive agents. We present a case of recurrent atypical PRES-SLE, which showed restricted diffusion in the first manifestation of SLE, resulted in parenchymal hemorrhagic transformations in the recurrent episode.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:494–500.2. Kinoshita T, Moritani T, Shrier DA, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a pictorial essay. Clin Imaging. 2003; 27:307–315.3. McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:904–912.4. Magnano MD, Bush TM, Herrera I, Altman RD. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 35:396–402.5. Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, Cruz LC, Wong JC, Engelter S, Barboriak DP. Quantitative assessment of diffusion abnormalities in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1455–1461.6. Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1038–1048.7. Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 2: controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1043–1049.8. Sweany JM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF. "Recurrent" posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: report of 3 cases--pres can strike twice. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007; 31:148–156.9. Thaipisuttikul I, Phanthumchinda K. Recurrent reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Neurol. 2005; 252:230–231.10. Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2008; 65:205–210.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Systemic Sclerosis Overlap Syndrome
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Lupus Nephritis
- Successful treatment with rituximab in a patient with lupus cerebritis and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case report
- Cyclophosphamide-induced Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Lupus Nephritis
- A Comprehensive Rehabilitation Approach in a Patient With Serious Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus