Korean J Hematol.
2006 Jun;41(2):83-91. 10.5045/kjh.2006.41.2.83.
Clinical Efficacy of Thalidomide Containing Regimens as a Primary Therapy in Patients with Multiple Myeloma
- Affiliations
-
- 1NUHSK Group, Department of Hematology-Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Jeonnam, Korea. drjejung@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Hematology-Oncology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Hematology-Oncology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2083481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2006.41.2.83
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and toxicity of thalidomide-containing regimens as the first-line therapy for patients with multiple myeloma.
METHODS
A total of 60 patients were initially treated with thalidomide-containing regimens at three institutions. Thalidomide was given with two different regimens: the TD regimen (thalidomide and dexamethasone) and the TCD regimen (thalidomide, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone). Autologous peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC) were collected after mobilizing with G-CSF with or without cyclophosphamide.
RESULTS
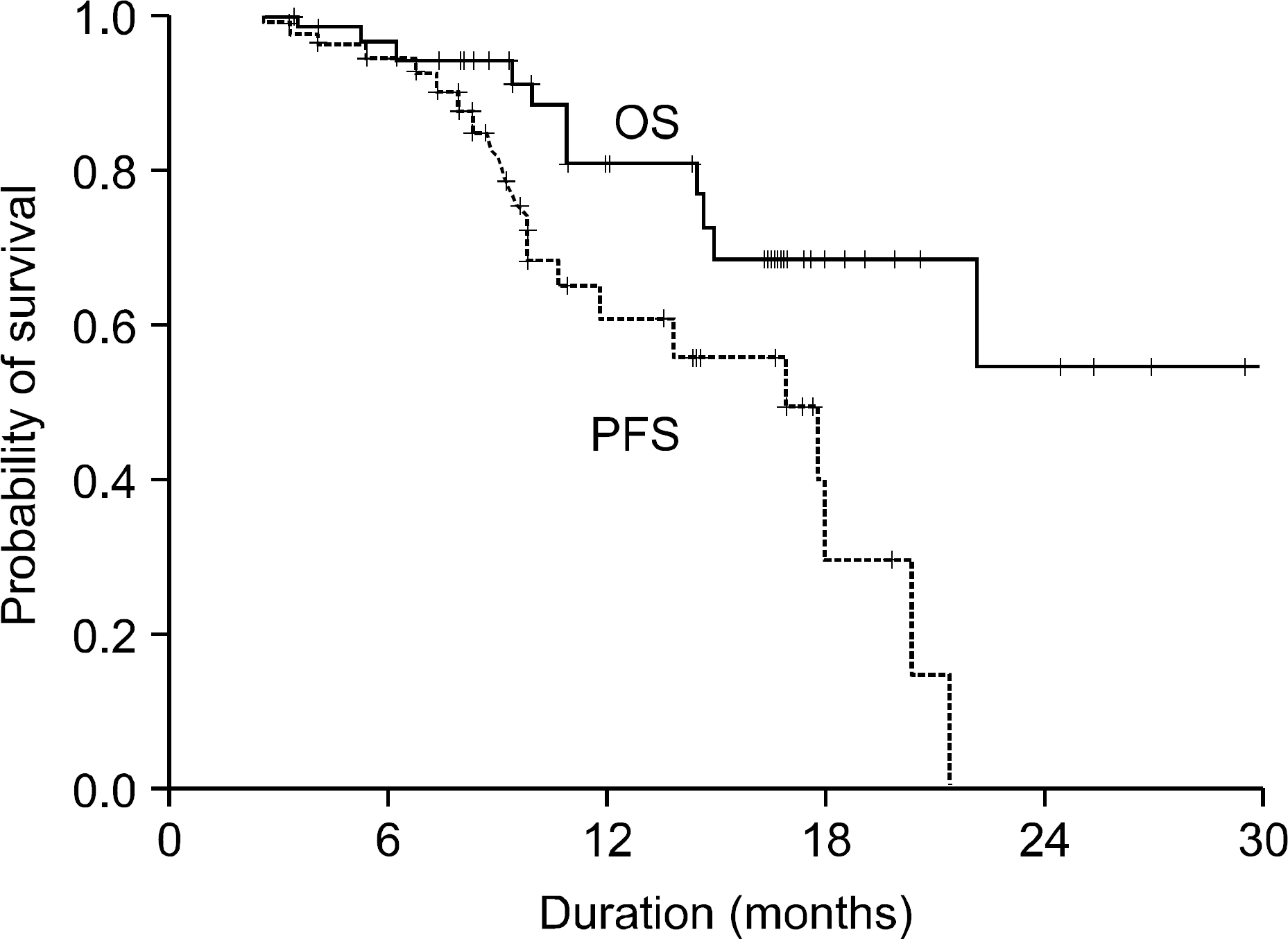
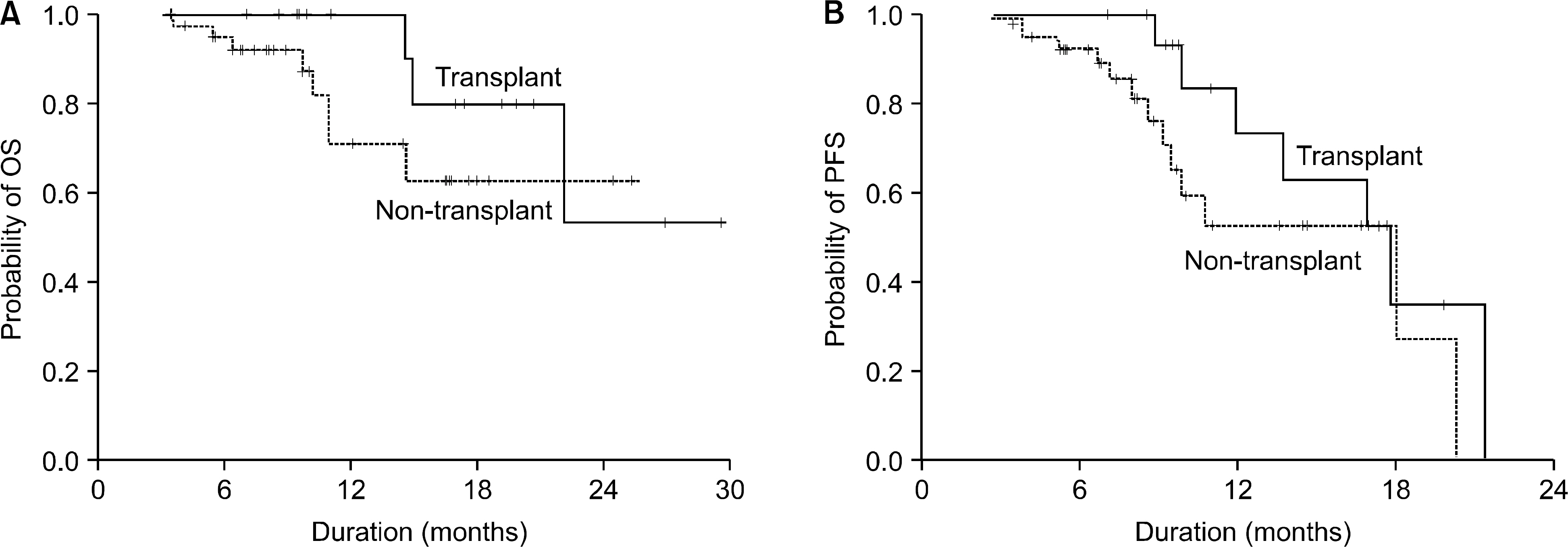
Of all the patients, 56 patients (TD regimen: 12 patients, TCD regimen: 44 patients) who received at least 4 cycles or more were evaluated for response and toxicity. The median age of the patients was 65.5 years (age range: 39~80 years). The overall response rate for the thalidomide-containing regimens was 85.5%. There were 3 (25%) complete responses and 6 (50%) partial responses for the TD regimen and there were 17 (38.6%) complete responses and 21 (47.7%) partial responses for the TCD regimen, respectively. The toxicity, according to the NCI-CTC (grade 3/4) included neutropenia in 7 patients (12.5%), thrombocytopenia in 4 patients (7.1%), infection in 6 patients (10.7%) and neuropathy in 10 patients (17.8%). In addition, there were 2 patients (3.6%) with thrombosis. Thirteen patients, who achieved more than a partial response to the thalidomide-containing regimen, proceeded to PBSC collection and the median number of CD34+ cells collected was 3.8 x 106/kg.
CONCLUSION
Thalidomide-based combination chemotherapy is a safe, well tolerated and effective regimen for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, and it showed a high response rates, relatively low toxicity and sufficient collection of PBSCs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Kyle RA., Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1860–73.
Article2). Sirohi B., Powles R. Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 2004. 363:875–87.
Article3). Galton DA., Peto R. A progress report on the Medical Research Council's therapeutic trial in myelomatosis. Br J Haematol. 1968. 15:319–20.4). Barlogie B., Jagannath S., Desikan KR, et al. Total therapy with tandem transplants for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood. 1999. 93:55–65.
Article5). Samson D., Gaminara E., Newland A, et al. Infusion of vincristine and doxorubicin with oral dexamethasone as first-line therapy for multiple myeloma. Lancet. 1989. 2:882–5.
Article6). Singhal S., Mehta J., Desikan R, et al. Antitumor activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1565–71.
Article7). Palumbo A., Giaccone L., Bertola A, et al. Low-dose thalidomide plus dexamethasone is an effective salvage therapy for advanced myeloma. Haematologica. 2001. 86:399–403.8). Tosi P., Zamagni E., Cellini C, et al. Salvage therapy with thalidomide in patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 2002. 87:408–14.
Article9). Rajkumar SV., Kyle RA. Multiple myeloma: diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005. 80:1371–82.
Article10). Cavo M., Zamagni E., Tosi P, et al. Superiority of thalidomide and dexamethasone over vincristine-doxorubicindexamethasone (VAD) as primary therapy in preparation for autologous transplantation for multiple myeloma. Blood. 2005. 106:35–9.
Article11). Dimopoulos MA., Hamilos G., Zomas A, et al. Pulsed cyclophosphamide, thalidomide and dexamethasone: an oral regimen for previously treated patients with multiple myeloma. Hematol J. 2004. 5:112–7.
Article12). Palumbo A., Bertola A., Musto P, et al. Oral melphalan, prednisone, and thalidomide for newly diagnosed patients with myeloma. Cancer. 2005. 104:1428–33.
Article13). Oken MM., Pomeroy C., Weisdorf D., Bennett JM. Prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of early infection in multiple myeloma. Am J Med. 1996. 100:624–8.
Article14). Blade J., Samson D., Reece D, et al. Criteria for evaluating disease response and progression in patients with multiple myeloma treated by high-dose therapy and haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Myeloma subcommittee of the EBMT. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplant. Br J Haematol. 1998. 102:1115–23.15). Greipp PR., San Miguel J., Durie BG, et al. International staging system for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:3412–20.
Article16). Rajkumar SV., Hayman S., Gertz MA, et al. Combination therapy with thalidomide plus dexamethasone for newly diagnosed myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:4319–23.
Article17). Weber D., Rankin K., Gavino M., Delasalle K., Alexani-an R. Thalidomide alone or with dexamethasone for previously untreated multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:16–9.
Article18). Rajkumar SV. Thalidomide: tragic past and promising future. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004. 79:899–903.
Article19). Garcia-Sanz R., Gonzalez-Porras JR., Hernandez JM, et al. The oral combination of thalidomide, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone (ThaCyDex) is effective in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2004. 18:856–63.
Article20). Bruno B., Rotta M., Giaccone L, et al. New drugs for treatment of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2004. 430–42.
Article21). Ghobrial IM., Rajkumar SV. Management of thalidomide toxicity. J Support Oncol. 2003. 1:194–205.22). Dimopoulos MA., Anagnostopoulos A., Weber D. Treatment of plasma cell dyscrasias with thalidomide and its derivatives. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:4444–54.
Article23). Zangari M., Siegel E., Barlogie B, et al. Thrombogenic activity of doxorubicin in myeloma patients receiving thalidomide: implications for therapy. Blood. 2002. 100:1168–71.
Article24). Osman K., Comenzo R., Rajkumar SV. Deep venous thrombosis and thalidomide therapy for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:1951–2.
Article25). Tricot G., Jagannath S., Vesole D, et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma: identification of favorable variables for rapid engraftment in 225 patients. Blood. 1995. 85:588–96.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cutaneous Plasmacytoma Treated with Thalidomide
- Diagnosis and therapy of multiple myeloma
- A Case of Extramedullary Progression Despite of Serologic Improvement in a Patient Treated with Thalidomide for Multiple Myeloma
- Salvage Therapy with Thalidomide in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma
- Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B During Thalidomide Therapy for Multiple Myeloma: A Case Report