Korean J Pain.
2011 Dec;24(4):221-225. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.221.
Anaphylactic Shock Caused by the Epidurally-Administered Hyalurinidase
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hiitsme@snubh.org
- KMID: 2074017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.221
Abstract
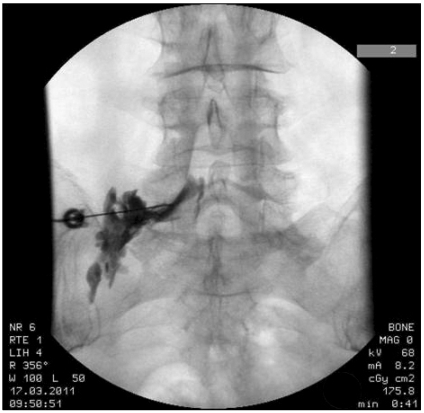
- Hyaluronidase is an enzyme that has temporary and reversible enzymatic effects on the matrix of connective tissue. When added to local anesthetics in pain treatments, it enhances their infiltration and dispersal into tissues. It is widely used in anesthesia for ocular, dental, and plastic surgery. Reports of drug hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase are rare and are usually confined to peribulbar or retrobulbar anesthesia during ophthalmic surgery. However, few reports exist on adverse drug reaction after epidural injection. We have observed two patients experiencing anaphylactic shock caused by hyaluronidase following epidural injection. Most of the patients with a hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase had one previous uneventful injection containing hyaluronidase, implying that sensitization had taken place. However, hypersensitivity occurring at the first administration is possible. A positive skin test can help establish the diagnosis. Although rare, the possibility of an allergic reaction to hyaluronidase should be considered even in patients with no known previous exposure.
MeSH Terms
-
Anaphylaxis
Anesthesia
Anesthetics, Local
Connective Tissue
Drug Hypersensitivity
Drug Toxicity
Humans
Hyaluronoglucosaminidase
Hypersensitivity
Hypogonadism
Injections, Epidural
Mitochondrial Diseases
Ophthalmoplegia
Skin Tests
Surgery, Plastic
Anesthetics, Local
Hyaluronoglucosaminidase
Hypogonadism
Mitochondrial Diseases
Ophthalmoplegia
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Review of Medical Dispute Cases in the Pain Management in Korea: A Medical Malpractice Liability Insurance Database Study
Yeon Dong Kim, Hyun Seog Moon
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(4):254-264. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.4.254.
Reference
-
1. Yocum RC, Kennard D, Heiner LS. Assessment and implication of the allergic sensitivity to a single dose of recombinant human hyaluronidase injection: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Infus Nurs. 2007; 30:293–299. PMID: 17895809.
Article2. Feighery C, McCoy EP, Johnston PB, Armstrong DK. Delayed hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase (Hyalase) used during cataract surgery. Contact Dermatitis. 2007; 57:343. PMID: 17937752.
Article3. Girish KS, Kemparaju K. The magic glue hyaluronan and its eraser hyaluronidase: a biological overview. Life Sci. 2007; 80:1921–1943. PMID: 17408700.
Article4. Stern R. Hyaluronidases in cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008; 18:275–280. PMID: 18485730.
Article5. Dunn AL, Heavner JE, Racz G, Day M. Hyaluronidase: a review of approved formulations, indications and off-label use in chronic pain management. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010; 10:127–131. PMID: 20420518.
Article6. Escolano F, Parés N, Gonzalez I, Castillo J, Valero A, Bartolomé B. Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase in cataract surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005; 22:729–730. PMID: 16163925.
Article7. Kim JH, Choi GS, Ye YM, Nahm DH, Park HS. Acute urticaria caused by the injection of goat-derived hyaluronidase. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2009; 1:48–50. PMID: 20224671.
Article8. Lee KJ, Han SG, Yoon SH, Kim JS, Lee YS. Nerve root block with corticosteroids, hyaluronidase, and local anesthetic in the failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS). J Korean Pain Soc. 1999; 12:191–194.9. Schulze C, Bittorf T, Walzel H, Kundt G, Bader R, Mittelmeier W. Experimental evaluation of hyaluronidase activity in combination with specific drugs applied in clinical techniques of interventional pain management and local anaesthesia. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:877–883. PMID: 19057633.10. Ahluwalia HS, Lukaris A, Lane CM. Delayed allergic reaction to hyaluronidase: a rare sequel to cataract surgery. Eye (Lond). 2003; 17:263–266. PMID: 12640426.
Article11. Kirby B, Butt A, Morrison AM, Beck MH. Type I allergic reaction to hyaluronidase during ophthalmic surgery. Contact Dermatitis. 2001; 44:52. PMID: 11156027.
Article12. Kempeneers A, Dralands L, Ceuppens J. Hyaluronidase induced orbital pseudotumor as complication of retrobulbar anesthesia. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 1992; 243:159–166. PMID: 1302146.13. King TP, Spangfort MD. Structure and biology of stinging insect venom allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000; 123:99–106. PMID: 11060481.
Article14. Eberhart AH, Weiler CR, Erie JC. Angioedema related to the use of hyaluronidase in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:142–143. PMID: 15234297.
Article15. Quhill F, Bowling B, Packard RB. Hyaluronidase allergy after peribulbar anesthesia with orbital inflammation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:916–917. PMID: 15093662.
Article16. Fisher MM, Bowey CJ. Intradermal compared with prick testing in the diagnosis of anaesthetic allergy. Br J Anaesth. 1997; 79:59–63. PMID: 9301390.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylactic shock caused by intramuscular injection of midazolam during the perioperative period: a case report
- Simultaneous hypersensitivity reactions to trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole and amoxicillinclavulanate in a dog
- Usefulness of Serum Mast Cell Tryptase Analysis in Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylactic Shock
- Anaphylactic shock to vaginal misoprostol: a rare adverse reaction to a frequently used drug
- Predictors of Anaphylactic Shock in Patients with Anaphylaxis after Exposure to Bee Venom