Korean J Perinatol.
2013 Dec;24(4):315-321. 10.14734/kjp.2013.24.4.315.
Vertically Transmitted Severe Coxsackievirus B Infection in Four Preterm Twins Presented
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. iamgawon@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2072310
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2013.24.4.315
Abstract
- During summer and fall months (from June to November), enteroviral infection is more common than group B streptococcal infection or herpes simplex viral infection in neonates. Enteroviruses are divided into polioviruses, coxsackieviruses A, coxsackieviruses B, and echoviruses. Enteroviruses can cause a wide spectrum of acute illnesses ranging from non-specific febrile illness, upper respiratory tract infection or gastroenteritis, to severe diseases such as myocarditis, and encephalitis. Coxsackieviruses B are important neonatal pathogens, which can cause meningoencephalitis, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and cardiomyopathy. Transplacental transmission of coxsackievirus or perinatal transmission by inhalation or swallowing of cervical secretion or feces during delivery causes more severe diseases than postnatal transmission by horizontal transmission in nursery or neonatal intensive care unit, due to larger load of viruses. Four preterm infants had severe coxsackieviral B infection with thrombocytopenia, meningitis, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and myocarditis within seven days of age during this June. Coxsackieviruses B were detected from their feces, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood. Viruses might be transmitted prenatally through placenta from mother to fetus, which caused severe disease. Coxsackieviruses B infections have to be considered in the neonates with sepsis-like illness during summer and fall months, or enteroviral seasons.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cardiomyopathies
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Deglutition
Encephalitis
Enterovirus
Enterovirus B, Human
Feces
Fetus
Gastroenteritis
Herpes Simplex
Humans
Infant, Newborn
Infant, Premature
Inhalation
Intensive Care, Neonatal
Meningitis
Meningoencephalitis
Mothers
Myocarditis
Nurseries
Placenta
Poliovirus
Respiratory Tract Infections
Seasons
Streptococcal Infections
Thrombocytopenia
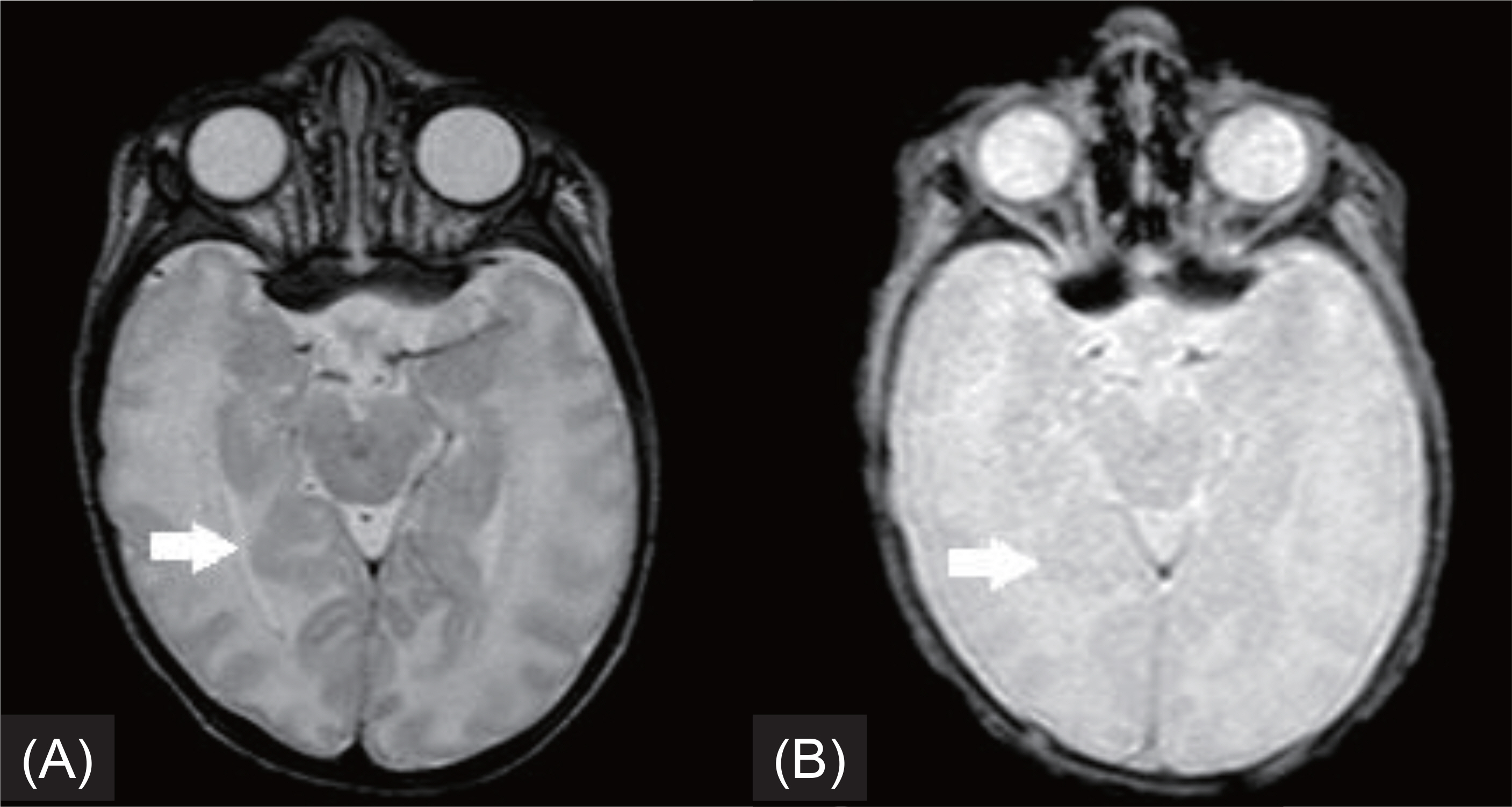
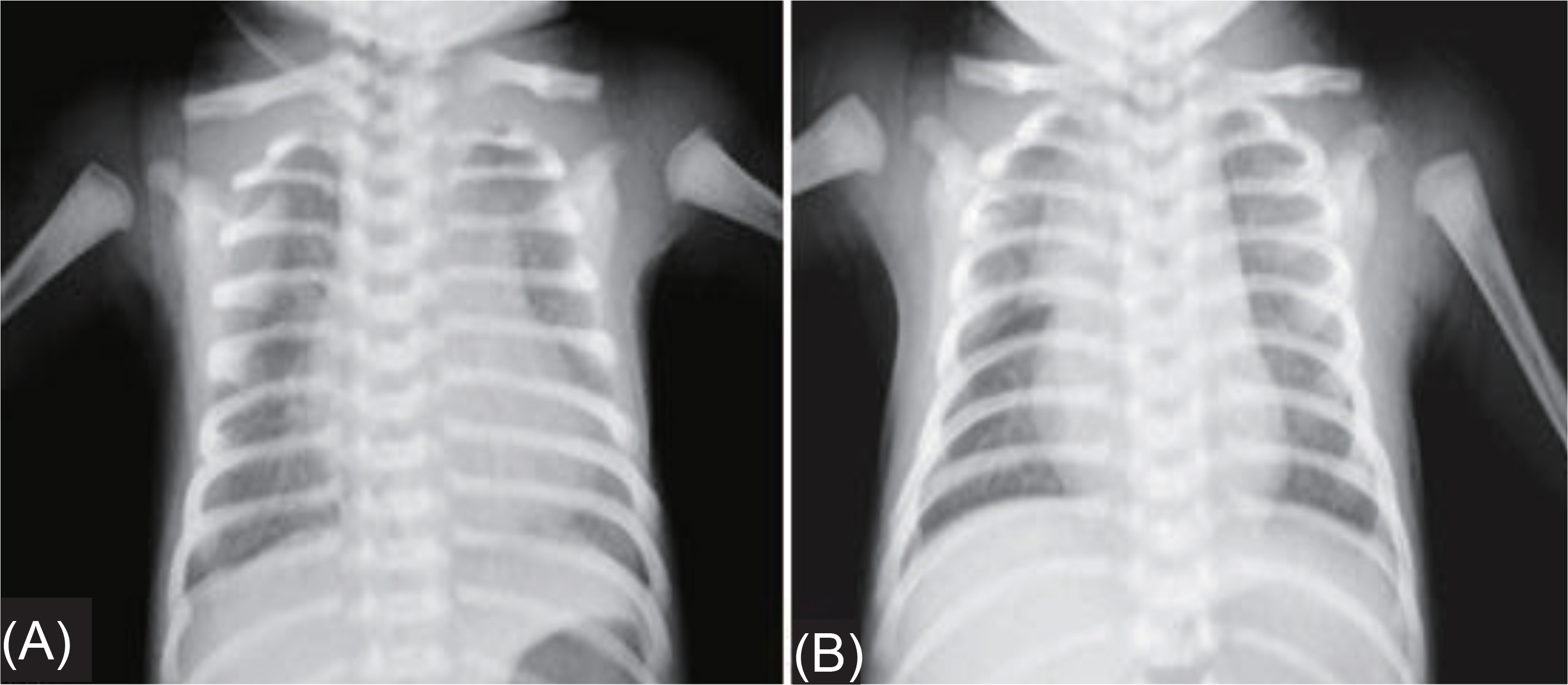
Figure
Reference
-
1). Tebruegge M., Curtis N. Enterovirus infections in neonates. Semin in Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009. 14:222–7.
Article2). Romero JR. Pediatric group B coxsackievirus infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. 323:223–39.
Article3). Modlin JF. Perinatal echovirus and group B coxsackievirus infections. Clin Perinatol. 1988. 15:233–46.4). Bryant PA., Tingay D., Darqaville PA., Starr M., Curtis N. Neonatal coxsakie B virus infection-a treatable disease? Eur J Pediatr. 2004. 163:223–8.5). Isacsohn M., Eidelman AI., Kaplan M., Goren A., Rudensky B., Handsher R, et al. Neonatal coxsackievirus group B infections: experience of a single department of neonatology. Isr J Med Sci. 1994. 30:371–4.6). Jenista JA., Powell KR., Menegus MA. Epidemiology of neonatal enterovirus infection. J Pediatr. 1984. 104:685–90.
Article7). Huebner RJ., Cole RM., Beeman EA., Bell JA., Peers JH. Herpangina; etiological studies of a specific infectious disease. J Am Med Assoc. 1951. 145:628–33.8). Bendig JW., Franklin OM., Hebden AK., Backhouse PJ., Clewley JP., Goldman AP, et al. Coxsackievirus B3 sequences in the blood of a neonate with congenital myocarditis, plus serological evidence of maternal infection. J Med Virol. 2003. 70:606–9.
Article9). Kaplan MH., Klein SW., McPhee J., Harper RG. Group B coxsackie virus infections in infants younger than three months of age: a serious childhood illness. Rev Infect Dis. 1983. 5:1019–32.10). Cheng LL., Ng PC., Chan PK., Wong HL., Cheng FW., Tang JW. Probable intrafamilial transmission of coxsackievirus b3 with vertical transmission, severe early-onset neonatal hepatitis, and prolonged viral RNA shedding. Pediatrics. 2006. 118:e929–33.
Article11). Khetsuriani N., Lamonte A., Oberste MS., Pallansch M. Neonatal enterovirus infections reported to the national enterovirus surveillance system in the United States, 1983-2003. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006. 25:889–93.
Article12). Lee HJ., Choi CW., Kim EK., Kim HS., Kim BI., Choi JH. A Case of Perinatal Echovirus 30 Infection in a Premature Infant. Korean J Perinatol. 2010. 21:81–5.13). Lin TY., Kao HT., Hsieh SH., Huang YC., Chiu CH., Chou YH, et al. Neonatal enterovirus infections: emphasis on risk factors of severe and fatal infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:889–94.
Article14). Abzug MJ., Levin MJ., Rotbart HA. Profile of enterovirus disease in the first two weeks of life. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993. 12:820–4.
Article15). Lu JC., Koay KW., Ramers CB., Milazzo AS. Neonate with coxsackie B1 infection, cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005. 97:1028–30.16). Wilfert CM., Thompson Jr RJ., Sunder TR., O'Quinn A., Zeller J., Blacharsh J. Longitudinal assessment of children with enteroviral meningitis during the first three months of life. Pediatrics. 1981. 67:811–5.
Article17). Rotbart HA., O'Connell JF., McKinlay MA. Treatment of human enterovirus infection. Antiviral Res. 1998. 38:1–14.18). Bauer S., Gottesman G., Sirota L., Litmanovitz I., Ashkenazi S., Levi I. Severe Coxsakie virus B infection in preterm newborns treated with pleoconaril. Eur J Pediatr. 2002. 161:491–3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thyroid Function of Preterm Twins Having Breastmilk from Their Mothers Consuming Seaweed Soup Might Be Variable between Siblings: A Case Series
- Growth and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Preterm Twins Conceived by In Vitro Fertilization
- Antepartum Use of Antibiotics
- A Case of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease Caused by Coxsackievirus A6
- A Case of Vertically Transmitted Neonatal Hepatitis B with Pancytopenia