J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Sep;29(Suppl 2):S155-S163. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S155.
Effect of Bilirubin on Triglyceride Synthesis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. mednep@snubh.org
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Immunology, Seoul National University Postgraduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Renal Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2069807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S155
Abstract
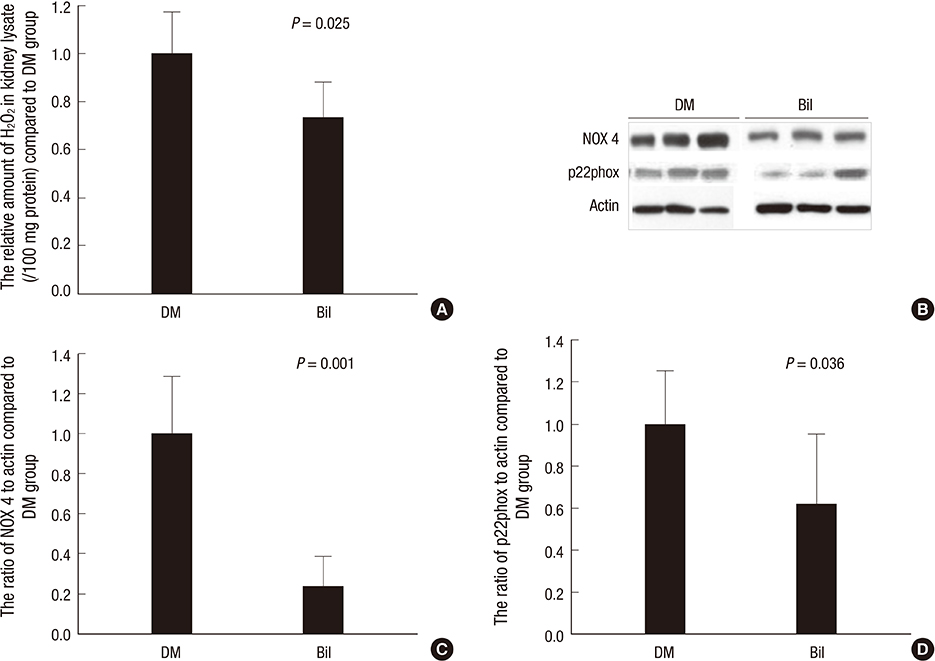
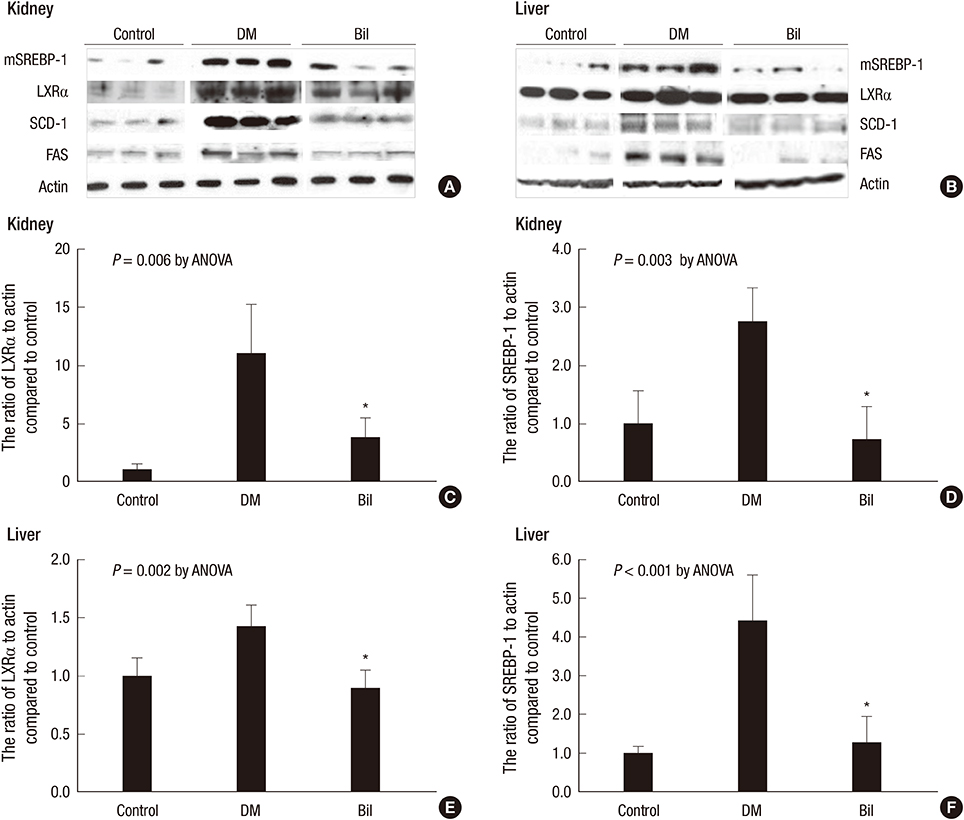
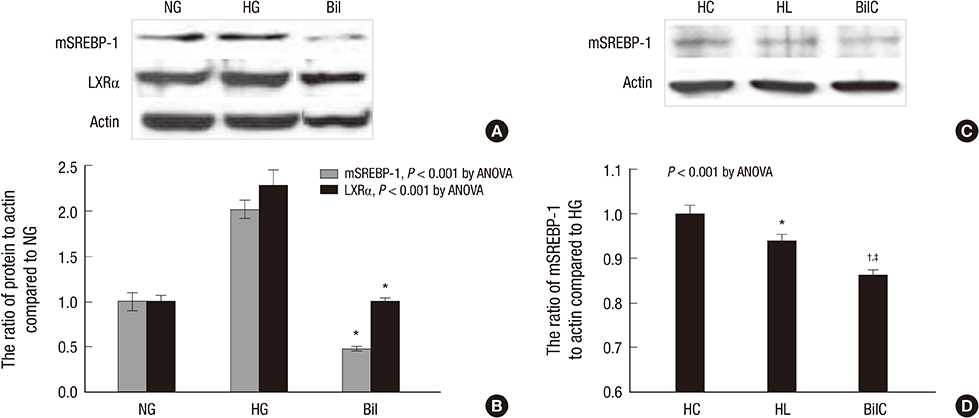
- We aimed to elucidate the effect of bilirubin on dyslipidemia and nephropathy in a diabetes mellitus (DM) type I animal model. Sprague-Dawley rats were separated into control, DM, and bilirubin-treated DM (Bil) groups. The Bil group was injected intraperitoneally with 60 mg/kg bilirubin 3 times per week and hepatoma cells were cultured with bilirubin at a concentration of 0.3 mg/dL. The Bil group showed lower serum creatinine levels 5 weeks after diabetes onset. Bilirubin treatment also decreased the amount of mesangial matrix, lowered the expression of renal collagen IV and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1, and reduced the level of apoptosis in the kidney, compared to the DM group. These changes were accompanied by decreased tissue levels of hydrogen superoxide and NADPH oxidase subunit proteins. Bilirubin decreased serum total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), free fatty acids, and triglycerides (TGs), as well as the TG content in the liver tissues. Bilirubin suppressed protein expression of LXRalpha, SREBP-1, SCD-1, and FAS, factors involved in TG synthesis that were elevated in the livers of DM rats and hepatoma cells under high-glucose conditions. In conclusion, bilirubin attenuates renal dysfunction and dyslipidemia in diabetes by suppressing LXRalpha and SREBP-1 expression and oxidative stress.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bilirubin/pharmacology/*therapeutic use
Cell Line, Tumor
Creatine/blood
Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental/chemically induced/complications/*pathology
Diabetic Nephropathies/*drug therapy/etiology
Disease Models, Animal
Kidney/pathology
Lipoproteins, HDL/blood
Liver/metabolism
Male
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
NADPH Oxidase/metabolism
Orphan Nuclear Receptors/antagonists & inhibitors/genetics/metabolism
Oxidative Stress/drug effects
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Reactive Oxygen Species/metabolism
Streptozocin/toxicity
Triglycerides/analysis/*biosynthesis/blood
Bilirubin
Creatine
Lipoproteins, HDL
Orphan Nuclear Receptors
Reactive Oxygen Species
Triglycerides
Streptozocin
NADPH Oxidase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Donovan A, Brownlie A, Zhou Y, Shepard J, Pratt SJ, Moynihan J, Paw BH, Drejer A, Barut B, Zapata A, et al. Positional cloning of zebrafish ferroportin1 identifies a conserved vertebrate iron exporter. Nature. 2000; 403:776–781.2. Dennery PA, McDonagh AF, Spitz DR, Rodgers PA, Stevenson DK. Hyperbilirubinemia results in reduced oxidative injury in neonatal Gunn rats exposed to hyperoxia. Free Radic Biol Med. 1995; 19:395–404.3. Fu YY, Kang KJ, Ahn JM, Kim HR, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim S, Chin HJ. Hyperbilirubinemia reduces the streptozotocin-induced pancreatic damage through attenuating the oxidative stress in the Gunn rat. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010; 222:265–273.4. Fujii M, Inoguchi T, Sasaki S, Maeda Y, Zheng J, Kobayashi K, Takayanagi R. Bilirubin and biliverdin protect rodents against diabetic nephropathy by downregulating NAD(P)H oxidase. Kidney Int. 2010; 78:905–919.5. Jenko-Pražnikar Z, Petelin A, Jurdana M, Žiberna L. Serum bilirubin levels are lower in overweight asymptomatic middle-aged adults: an early indicator of metabolic syndrome? Metabolism. 2013; 62:976–985.6. Hwang HJ, Kim SH. Inverse relationship between fasting direct bilirubin and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:1496–1501.7. Kwon KM, Kam JH, Kim MY, Kim MY, Chung CH, Kim JK, Linton JA, Eom A, Koh SB, Kang HT. Inverse association between total bilirubin and metabolic syndrome in rural Korean women. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2011; 20:963–969.8. Jung CH, Lee MJ, Kang YM, Hwang JY, Jang JE, Leem J, Park JY, Kim HK, Lee WJ. Higher serum bilirubin level as a protective factor for the development of diabetes in healthy Korean men: a 4 year retrospective longitudinal study. Metabolism. 2014; 63:87–93.9. Han SS, Na KY, Chae DW, Kim YS, Kim S, Chin HJ. High serum bilirubin is associated with the reduced risk of diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010; 221:133–140.10. Mashitani T, Hayashino Y, Okamura S, Tsujii S, Ishii H. Correlations between serum bilirubin levels and diabetic nephropathy progression among Japanese type 2 diabetic patients: a prospective cohort study (Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri [DDCRT 5]). Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:252–258.11. Chin HJ, Song YR, Kim HS, Park M, Yoon HJ, Na KY, Kim Y, Chae DW, Kim S. The bilirubin level is negatively correlated with the incidence of hypertension in normotensive Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:S50–S56.12. Chin HJ, Cho HJ, Lee TW, Na KY, Oh KH, Joo KW, Yoon HJ, Kim YS, Ahn C, Han JS, et al. The mildly elevated serum bilirubin level is negatively associated with the incidence of end stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:S22–S29.13. Schwertner HA, Jackson WG, Tolan G. Association of low serum concentration of bilirubin with increased risk of coronary artery disease. Clin Chem. 1994; 40:18–23.14. Kamisako T, Masuda S, Tanaka Y. Relationship between serum bilirubin and remnant lipoprotein cholesterol level. Clin Lab. 2013; 59:435–438.15. Shepherd RE, Moreno FJ, Cashore WJ, Fain JN. Effects of bilirubin on fat cell metabolism and lipolysis. Am J Physiol. 1979; 237:E504–E508.16. Degenhardt TP, Alderson NL, Arrington DD, Beattie RJ, Basgen JM, Steffes MW, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW. Pyridoxamine inhibits early renal disease and dyslipidemia in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Kidney Int. 2002; 61:939–950.17. Kraynak AR, Storer RD, Jensen RD, Kloss MW, Soper KA, Clair JH, DeLuca JG, Nichols WW, Eydelloth RS. Extent and persistence of streptozotocin-induced DNA damage and cell proliferation in rat kidney as determined by in vivo alkaline elution and BrdUrd labeling assays. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995; 135:279–286.18. Junod A, Lambert AE, Orci L, Pictet R, Gonet AE, Renold AE. Studies of the diabetogenic action of streptozotocin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967; 126:201–205.19. Zhang S, Yang J, Li H, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhang D, Zhang F, Zhou W, Chen X. Skimmin, a coumarin, suppresses the streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in wistar rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012; 692:78–83.20. Roy S, Metya SK, Sannigrahi S, Rahaman N, Ahmed F. Treatment with ferulic acid to rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: effects on oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and apoptosis in the pancreatic β cell. Endocrine. 2013; 44:369–379.21. Fang J, Wei H, Sun Y, Zhang X, Liu W, Chang Q, Wang R, Gong Y. Regulation of podocalyxin expression in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with Chinese herbs (Yishen capsule). BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013; 13:76.22. Bulmer AC, Verkade HJ, Wagner KH. Bilirubin and beyond: a review of lipid status in Gilbert's syndrome and its relevance to cardiovascular disease protection. Prog Lipid Res. 2013; 52:193–205.23. Boon AC, Hawkins CL, Bisht K, Coombes JS, Bakrania B, Wagner KH, Bulmer AC. Reduced circulating oxidized LDL is associated with hypocholesterolemia and enhanced thiol status in Gilbert syndrome. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 52:2120–2127.24. Sakamoto S, Kusuhara H, Miyata K, Shimaoka H, Kanazu T, Matsuo Y, Nomura K, Okamura N, Hara S, Horie K, et al. Glucuronidation converting methyl 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(3-ethylvaleryl)-4-hydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxy-2-naphthoate (S-8921) to a potent apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter inhibitor, resulting in a hypocholesterolemic action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007; 322:610–618.25. Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA, Brown MS. Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell. 2006; 124:35–46.26. Magaña MM, Osborne TF. Two tandem binding sites for sterol regulatory element binding proteins are required for sterol regulation of fatty-acid synthase promoter. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:32689–32694.27. Le Lay S, Lefrère I, Trautwein C, Dugail I, Krief S. Insulin and sterol-regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1C) regulation of gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Identification of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta as an SREBP-1C target. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:35625–35634.28. Yokoyama C, Wang X, Briggs MR, Admon A, Wu J, Hua X, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell. 1993; 75:187–197.29. Fleischmann M, Iynedjian PB. Regulation of sterol regulatory-element binding protein 1 gene expression in liver: role of insulin and protein kinase B/cAkt. Biochem J. 2000; 349:13–17.30. Yoshikawa T, Shimano H, Amemiya-Kudo M, Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, et al. Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 21:2991–3000.31. Steffensen KR, Gustafsson JA. Putative metabolic effects of the liver X receptor (LXR). Diabetes. 2004; 53:S36–S42.32. Schultz JR, Tu H, Luk A, Repa JJ, Medina JC, Li L, Schwendner S, Wang S, Thoolen M, Mangelsdorf DJ, et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2831–2838.33. Shimano H. SREBPs: physiology and pathophysiology of the SREBP family. FEBS J. 2009; 276:616–621.34. Ishigaki N, Yamamoto T, Shimizu Y, Kobayashi K, Yatoh S, Sone H, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Yamagata K, Yamada N, et al. Involvement of glomerular SREBP-1c in diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 364:502–508.35. Chin HJ, Fu YY, Ahn JM, Na KY, Kim YS, Kim S, Chae DW. Omacor, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, attenuated albuminuria and renal dysfunction with decrease of SREBP-1 expression and triglyceride amount in the kidney of type II diabetic animals. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25:1450–1457.36. Sun L, Halaihel N, Zhang W, Rogers T, Levi M. Role of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 in regulation of renal lipid metabolism and glomerulosclerosis in diabetes mellitus. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:18919–18927.37. Uttarwar L, Gao B, Ingram AJ, Krepinsky JC. SREBP-1 activation by glucose mediates TGF-β upregulation in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012; 302:F329–F341.38. Sato R. Sterol metabolism and SREBP activation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010; 501:177–181.39. Wellington CL, Brunham LR, Zhou S, Singaraja RR, Visscher H, Gelfer A, Ross C, James E, Liu G, Huber MT, et al. Alterations of plasma lipids in mice via adenoviral-mediated hepatic overexpression of human ABCA1. J Lipid Res. 2003; 44:1470–1480.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Anti-inflammatory Effect of Retinoid on Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Nephropathy
- Apoptosis and Ultrastructural Changes of Glomerular Endothelial Cells of Mice with Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Nephropathy
- Role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Protective Effect of Melatonin on Neuropathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Proliferation of Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells(VSMCs) Obtained from Aortas of Insulin Dependent Diabetic Rats