J Korean Endocr Soc.
2008 Feb;23(1):27-34. 10.3803/jkes.2008.23.1.27.
Effects of Alpha-lipoic Acid on SREBP-1c Expression in HepG2 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2063547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.1.27
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is common in patients with insulin resistance. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) is a member of a family of transcription factors that have been recognized as key regulators for lipid accumulation in the liver that activate enzymes involved in the fatty acid biosynthetic pathway. This study was designed to evaluate whether alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) inhibits insulin-stimulated SREBP-1c expression.
METHODS
We investigated the effects of ALA on insulin-stimulated SREBP-1c expression in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2 cells) using Northern and Western blot analysis. We also examined the effect of ALA on the promoter activity of the SREBP-1c gene to examine whether ALA can affect SREBP-1c expression at the transcriptional level. To discern the mechanism by which ALA inhibits SREBP-1c expression, we examined the role of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
RESULTS
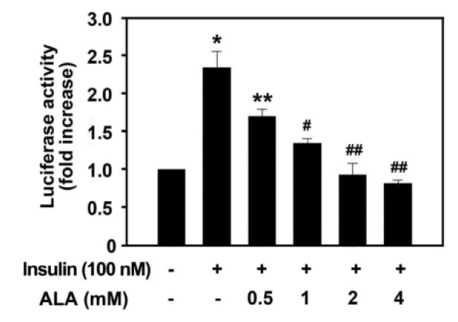
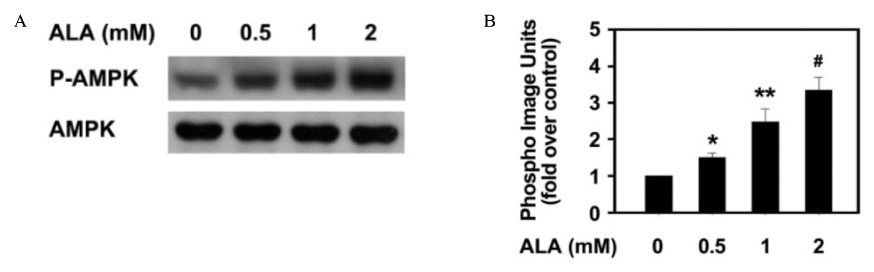
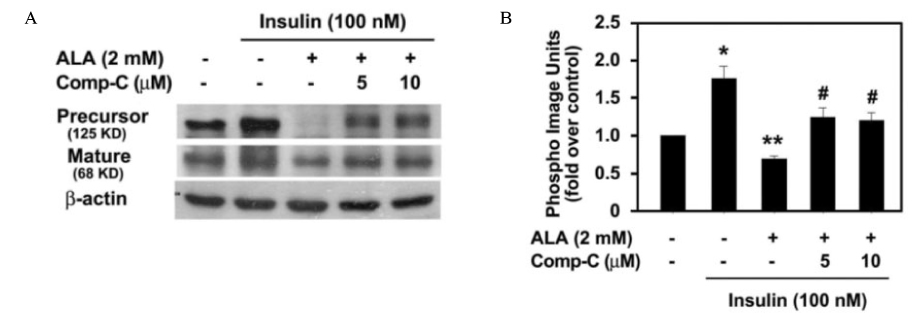
Insulin increased the expression of SREBP-1c mRNA and protein in HepG2 cells in a dose depended manner. Co-treatment with ALA inhibited the insulin increased SREBP-1c expression in a dose-dependent manner. ALA also inhibited insulin-stimulated activation of the SREBP-1c promoter activity, indicating that ALA inhibited SREBP-1c expression at the transcriptional level. ALA increased phosphorylation of AMPK in HepG2 cells. Inhibition of the AMPK activity by compound C markedly reversed the inhibitory effects of ALA for insulin-stimulated SREBP-1c expression. These results suggest that ALA-induced suppression of SREBP-1c expression is at least in part mediated via AMPK activation.
CONCLUSION
The present study suggests that ALA has an inhibitory effect on insulin-stimulated SREBP-1c expression. Therefore, further studies on the effects of ALA on hepatic steatosis in an animal model need to be performed.
MeSH Terms
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases
Biosynthetic Pathways
Blotting, Western
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular
Cell Line
Fatty Liver
Hep G2 Cells
Humans
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Liver
Models, Animal
Phosphorylation
RNA, Messenger
Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1
Thioctic Acid
Transcription Factors
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases
Fatty Liver
Insulin
RNA, Messenger
Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1
Thioctic Acid
Transcription Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of an aqueous extract of purple sweet potato on nonalcoholic fatty liver in high fat/cholesterol-fed mice
∗
You Jin Lee, Yang Yoon Kyoung, You Jin Kim, Oran Kwon
J Nutr Health. 2015;48(1):1-8. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2015.48.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002. 122:1649–1657.2. Angulo P. Nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:1221–1231.3. Marceau P, Biron S, Hould FS, Marceau S, Simard S, Thung SN, Kral JG. Liver pathology and the metabolic syndrome X in severe obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:1513–1517.4. Kim TH, Yoo K. Obesity and Fatty liver disease. Korean J Intern Med. 2005. 68:347–349.5. Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M, McCullough AJ, Natale S, Forlain G, Melchionda N. Nonalcholic fatty liver disease; a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2001. 50:1844–1850.6. Hillgartner FB, Salati LM, Goodridge AG. Physiological and molecular mechanisms involved in nutritional regulation of fatty acid synthase. Physiol Rev. 1995. 75:47–76.7. Horton JD, Bashmakov Y, Shimomura I, Shimano H. Regulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins in livers of fasted and refed mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:5987–5992.8. Foretz M, Pacot C, Dugail I, Lemarchand P, Guichard C, Lie'pvre XL, Berthelier-Lubrano C, Spiegelman B, Kim JB, Ferre P, Foufelle F. ADD1/SREBP-1c is required in the activation of hepatic lipogenic gene expression by glucse. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. 19:3760–3768.9. Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997. 89:331–340.10. Shimomura I, Shimano H, Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Differential expression of exons 1a and 1c in mRNAs for sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 in human and mouse organs and cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:838–845.11. Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 2002. 109:1125–1131.12. Shimomura I, Bashmakov Y, Horton JD. Increased levels of nuclear SREBP-1c associated with fatty livers in two mouse models of diabetes mellitus. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:30028–30032.13. Foretz M, Guichard C, Ferre P, Foufelle F. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999. 96:12737–12742.14. Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995. 269:543–546.15. Yahagi N, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka T, Ide T, Yoshikawa T, Amemiya-Kudo M, Tomita S, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Lizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J, Harada K, Gotoda T, Nagai R, Ishibashi S, Yamada N. Absence of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) ameliorates fatty livers but not obesity or insulin resistance in Lepob/Lepob mice. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:19353–19357.16. Biewenga GP, Haenen SR, Bast A. The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen pharmacol. 1997. 29:315–331.17. Packer K, Kraemer K, Rimbach G. Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications. Nutrition. 2001. 17:888–895.18. Lee WJ, Song KH, Koh EH, Won JC, Kim HS, Park HS, Kim MS, Kim SW, Lee KU, Park JY. Alpha-lipoic acid increases insulin sensitivity by activating AMPK in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. 332:885–891.19. Tarling E, Salter A, Bennett A. Transcriptional regulation of human SREBP-1c(sterol-regulataroy-element-bindingprotein -1c) : a key regulator of lipogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. 32:107–109.20. You M, Matsumoto M, Pacold CM, Cho WK, Crabb DW. The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the action of ethanol in the liver. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:1798–1808.21. Hardie DG. Minireview. The AMP-activated protein kinase cascade: the key sensor of cellular energy status. Endocrinology. 2003. 144:5179–5183.22. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, Musi N, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Moller DE. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2001. 108:1167–1174.23. Fryer LG, Parbu-Patel A, Carling D. The Anti- diabetic drugs rosiglitazone and metformin stimulate AMP -activated protein kinase through distinct signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:25226–25232.24. Saha AK. Pioglitazone treatment activates AMP-activated protein kinase through distinct signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:25226–25232.25. Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Wehmeier KR, Oliver D, Bacon BR. Improved nonalcoholic steatohepatitis after 48 weeks of treatment with the PPAR-gamma ligand rosiglitazone. Hepatology. 2003. 38:1008–1017.26. Lee WJ, Lee IK, Kim HS, Kim YM, Koh EH, Won JC, Han SM, Kim MS, Jo I, Oh GT, Park IS, Youn JH, Park SW, Lee KU, Park JY. alpha-lipoic acid prevents endothelial dysfunction in obese rats via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. 25:2488–2494.27. Shimomura I, bashmakov Y, Ikemoto S, Horton JD, Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Insulin selectively increases SREBP-1c mRNA in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999. 96:13656–13661.28. Azzout-Marniche D, Becard D, Guichard C, Foretz M, Ferre P, Foufelle F. Insulin effects on sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) transcriptional activity in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 2000. 50:389–393.29. Deng X, Cagen LM, Wilcox HG, Park EA, Raghow R, Elam MB. Regulation of the rat SREBP-1c promoter in primary rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 290:256–262.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Compounds from Physalis angulata on Fatty Acid Synthesis and Glucose Metabolism in HepG2 Cells via the AMP-activated Protein Kinase Pathway
- Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on cell proliferation and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cells
- Cilostazol inhibits insulin-stimulated expression of sterol regulatory binding protein-1c via inhibition of LXR and Sp1
- Efficacy and Safety of α-Lipoic Acid and Low Dose Pregabalin Combination in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
- Artemisia annua extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced fatty liver by activating AMPK