Electrolyte Blood Press.
2009 Dec;7(2):58-66. 10.5049/EBP.2009.7.2.58.
Altered Regulation of Renal Sodium Transporters in Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats Induced by Uninephrectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Laboratory of Molecular Nephrology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junephro@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2052320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2009.7.2.58
Abstract
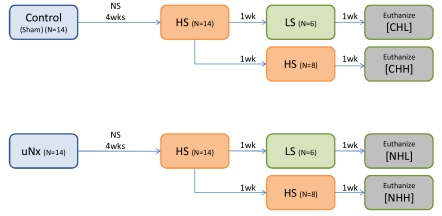
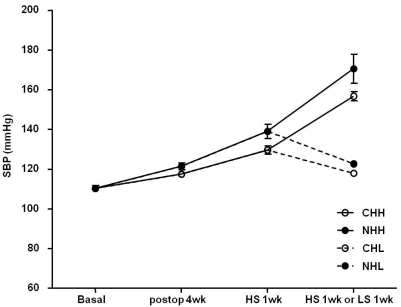
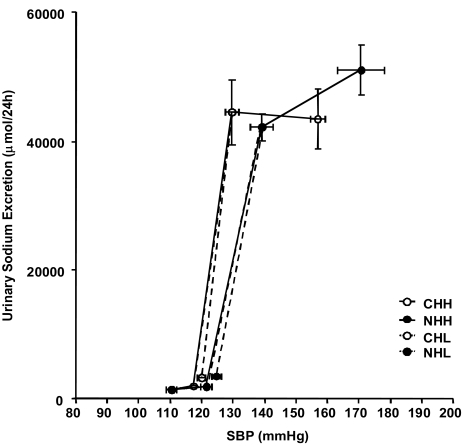
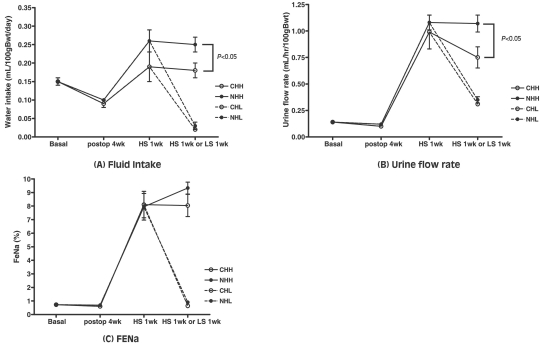
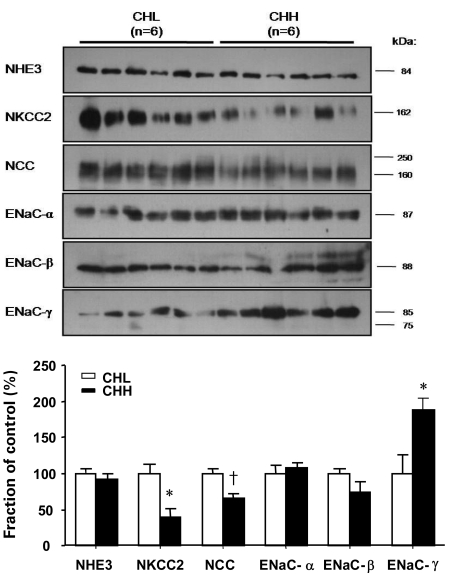
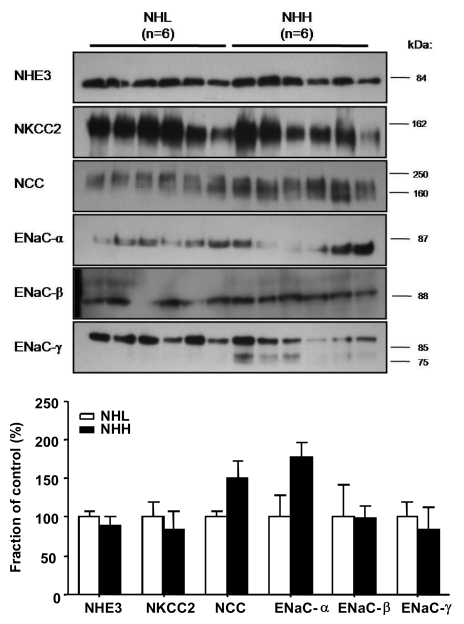
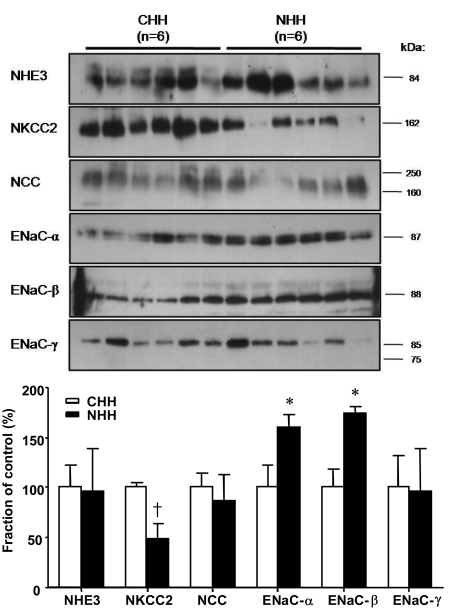
- Uninephrectomy (uNx) in young rats causes salt-sensitive hypertension (SSH). Alterations of sodium handling in residual nephrons may play a role in the pathogenesis. Therefore, we evaluated the adaptive alterations of renal sodium transporters according to salt intake in uNx-SSH rats. uNx or sham operations were performed in male Sprague-Dawley rats, and normal-salt diet was fed for 4 weeks. Four experimental groups were used: sham-operated rats raised on a high-salt diet for 2 weeks (CHH) or on a low-salt diet for 1 week after 1 week's high-salt diet (CHL) and uNx rats fed on the same diet (NHH, NHL) as the sham-operated rats were fed. Expression of major renal sodium transporters were determined by semiquantitative immunoblotting. Systolic blood pressure was increased in NHH and NHL groups, compared with CHH and CHL, respectively. Protein abundances of Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC2) and Na+/Cl- cotransporter (NCC) in the CHH group were lower than the CHL group. Expression of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)-gamma increased in the CHH group. In contrast, expressions of NKCC2 and NCC in the NHH group didn't show any significant alterations, compared to the NHL group. Expressions of ENaC-alpha and ENaC-beta in the NHH group were higher than the CHH group. Adaptive alterations of NKCC2 and NCC to changes of salt intake were different in the uNx group, and changes in ENaC-alpha and ENaC-beta were also different. These altered regulations of sodium transporters may be involved in the pathogenesis of SSH in the uNx rat model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blood Pressure
Diet
Diet, Sodium-Restricted
Epithelial Sodium Channels
Handling (Psychology)
Humans
Hypertension
Immunoblotting
Male
Nephrectomy
Nephrons
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Salicylamides
Social Control, Formal
Sodium
Sodium Chloride Symporters
Sodium-Potassium-Chloride Symporters
Epithelial Sodium Channels
Salicylamides
Sodium
Sodium Chloride Symporters
Sodium-Potassium-Chloride Symporters
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johnson RJ, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Nakagawa T, Kang DH, Feig DI, Herrera-Acosta J. Subtle renal injury Is likely a common mechanism for salt-sensitive essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2005; 45:326–330. PMID: 15655117.
Article2. Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J, Schreiner GF, Rodriguez-Iturbe B. Subtle acquired renal injury as a mechanism of salt-sensitive hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:913–923. PMID: 11907292.
Article3. Guyton AC, Coleman TG, Cowley AV Jr., Scheel KW, Manning RD Jr., Norman RA Jr.Arterial pressure regulation. Overriding dominance of the kidneys in long-term regulation and in hypertension. Am J Med. 1972; 52:584–594. PMID: 4337474.4. Elliott P, Stamler J, Nichols R, et al. Intersalt revisited: further analyses of 24 hour sodium excretion and blood pressure within and across populations. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. BMJ. 1996; 312:1249–1253. PMID: 8634612.5. MacGregor GA, Markandu ND, Best FE, et al. Double-blind randomised crossover trial of moderate sodium restriction in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1982; 1:351–355. PMID: 6120346.
Article6. Lifton RP. Molecular genetics of human blood pressure variation. Science. 1996; 272:676–680. PMID: 8614826.
Article7. Karet FE, Lifton RP. Mutations contributing to human blood pressure variation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997; 52:263–276. PMID: 9238856.8. Brenner BM, Garcia DL, Anderson S. Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am J Hypertens. 1988; 1:335–347. PMID: 3063284.
Article9. Curtis JJ, Luke RG, Dustan HP, et al. Remission of essential hypertension after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1983; 309:1009–1015. PMID: 6353230.
Article10. Boudville N, Prasad GV, Knoll G, et al. Meta-analysis: risk for hypertension in living kidney donors. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 145:185–196. PMID: 16880460.
Article11. Larsson L, Aperia A, Wilton P. Effect of normal development on compensatory renal growth. Kidney Int. 1980; 18:29–35. PMID: 7218658.
Article12. Carlstrom M, Sallstrom J, Skott O, Larsson E, Persson AE. Uninephrectomy in young age or chronic salt loading causes salt-sensitive hypertension in adult rats. Hypertension. 2007; 49:1342–1350. PMID: 17438306.
Article13. Kim GH, Ecelbarger C, Knepper MA, Packer RK. Regulation of thick ascending limb ion transporter abundance in response to altered acid/base intake. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:935–942. PMID: 10232678.
Article14. Kim GH, Ecelbarger CA, Mitchell C, Packer RK, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Vasopressin increases Na-K-2Cl cotransporter expression in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1999; 276:F96–F103. PMID: 9887085.15. Kim G, Masilamani S, Turner R, Mitchell C, Wade J, Knepper M. The thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter is an aldosterone-induced protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:14552–14557. PMID: 9826738.
Article16. Masilamani S, Kim GH, Mitchell C, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Aldosterone-mediated regulation of ENaC α, β, and γ subunit proteins in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:R19–R23. PMID: 10510339.
Article17. Guyton AC. Blood pressure control--special role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science. 1991; 252:1813–1816. PMID: 2063193.
Article18. Hoagland KM, Flasch AK, Dahly-Vernon AJ, dos Santos EA, Knepper MA, Roman RJ. Elevated BSC-1 and ROMK expression in Dahl salt-sensitive rat kidneys. Hypertension. 2004; 43:860–865. PMID: 14967839.
Article19. Hager H, Kwon TH, Vinnikova AK, et al. Immunocytochemical and immunoelectron microscopic localization of α-, β-, and γ-ENaC in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 280:F1093–F1106. PMID: 11352848.
Article20. Ecelbarger CA, Kim GH, Terris J, et al. Vasopressin-mediated regulation of epithelial sodium channel abundance in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 279:F46–F53. PMID: 10894786.
Article21. Masilamani S, Kim GH, Mitchell C, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Aldosterone-mediated regulation of ENaC alpha, beta, and gamma subunit proteins in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:R19–R23. PMID: 10510339.22. Loffing J, Pietri L, Aregger F, et al. Differential subcellular localization of ENaC subunits in mouse kidney in response to high-and low-Na diets. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 279:F252–F258. PMID: 10919843.23. Canessa CM, Schild L, Buell G, et al. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994; 367:463–467. PMID: 8107805.
Article24. Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM, et al. Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell. 1994; 79:407–414. PMID: 7954808.
Article25. Ecelbarger CA, Kim GH, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Regulation of the abundance of renal sodium transporters and channels by vasopressin. Exp Neurol. 2001; 171:227–234. PMID: 11573975.
Article26. Blazer-Yost BL, Liu X, Helman SI. Hormonal regulation of ENaCs: insulin and aldosterone. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:C1373–C1379. PMID: 9612225.
Article27. Morris M, Keller M, Sundberg DK. Changes in paraventricular vasopressin and oxytocin during the development of spontaneous hypertension. Hypertension. 1983; 5:476–481. PMID: 6862574.
Article28. Tahara A, Tsukada J, Tomura Y, et al. Alterations of renal vasopressin V1A and V2 receptors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacology. 2003; 67:106–112. PMID: 12566855.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Renal Sodium Transporters and Water Channels
- Pathophysiological Implications of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in the Kidney
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic regulation of sodium transporters and water channels in rat submandibular gland
- Effects of Thiazide on the Expression of TRPV5, Calbindin-D28K, and Sodium Transporters in Hypercalciuric Rats
- Contributory Roles of Distal Renal Sodium Transporters in NSAID-induced Sodium Retention