Electrolyte Blood Press.
2006 Nov;4(2):66-71. 10.5049/EBP.2006.4.2.66.
Hypernatemia:Successful Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. skimw@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2052273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2006.4.2.66
Abstract
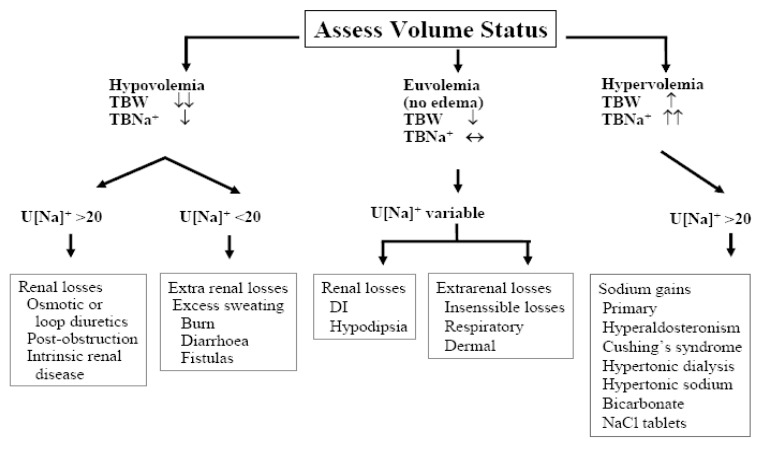
- Hypernatremia reflects a net water loss or a hypertonic sodium gain, with inevitable hyperosmolality. Severe symptoms are usually evident only with acute and large increases in plasma sodium concentrations to above 158-160 mmol/l. Importantly, the sensation of intense thirst that protects against severe hypernatremia in health may be absent or reduced in patients with altered mental status or with hypothalamic lesions affecting their sense of thirst and in infants and elderly people. Non-specific symptoms such as anorexia, muscle weakness, restlessness, nausea, and vomiting tend to occur early. More serious signs follow, with altered mental status, lethargy, irritability, stupor, and coma. Acute brain shrinkage can induce vascular rupture, with cerebral bleeding and subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, in the vast majority of cases, the onset of hypertonicity is low enough to allow the brain to adapt and thereby to minimize cerebral dehydration. Organic osmolytes accumulated during the adaptation to hypernatremia are slow to leave the cell during rehydration. Therefore, if the hypernatremia is corrected too rapidly, cerebral edema results as the relatively more hypertonic ICF accumulates water. To be safe, the rate of correction should not exceed 12 mEq/liter/day.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Hypernatremia. New Engl J Med. 2000; 342:1493–1499. PMID: 10816188.2. Petis LD, Luchitti A, Emma F. Cell volume regulation and transport mechanisms across the blood-brain barrier: implications for the management of hypernatremic states. Eur J Pediatrics. 2001; 160:71–77.3. McManus ML, Strange K. Acute volume regulation of brain cells in response to hypertonic challenge. Anesthesiology. 1993; 78:1132–1137. PMID: 8512106.
Article4. McDowell ME, Wolf AV, Steer A. Osmotic volumes of distribution: idiogenic changes in osmotic pressure associated with administration of hypertonic solutions. Am J Physiol. 1955; 180:545–558. PMID: 14376538.5. Strange K. Regulation of solute and water balance and cell volume in the central nervous system. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992; 3:12–27. PMID: 1391705.
Article6. Heilig CW, Stromski ME, Blumenfeld JB, Lee JP, Gullan SR. Characterization of the major brain osmolytes that accumulate in salt-loaded rats. Am J Physiol. 1989; 257:F1108–F1116. PMID: 2603957.
Article7. Lien YH, Shapiro JI, Chan L. Effect of hypernatremia on organic brain osmoles. J Clin Invest. 1990; 85:1427–1435. PMID: 2332498.8. Paredes A, McManus M, Kwon HM, Strange K. Osmoregulation of Na+-inositol cotransporter activity and mRNA levels in brain glial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992; 263:C1282–C1288. PMID: 1476169.9. Lee JH, Arcinue E, Ross BD. Brief report : Organic osmolytes in the brain of an infant with hypernatremia. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:439–442. PMID: 8035840.10. Strange K, Morrison R, Shrode L, Putnam R. Mechanism and regulation of swelling-activated inositol efflux in brain glial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993; 265:C244–C256. PMID: 8393281.
Article11. Gennari FJ. Davison AM, Cameron JS, Grünfeld J-P, Kerr DNS, Ritz E, Winearls CG, editors. Hypo-hypernatraemia: disorders of water balance. Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology. 1998. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press;p. 175–200.12. Finberg L, Harrison HE. Hypernatremia in infants: an evaluation of the clinical and biochemical findings accompanying this state. Pediatrics. 1955; 16:1–14. PMID: 14394733.13. Bruck E, Abal G, Aceto T Jr. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of hypertonic dehydration with diarrhea: a clinical study of 59 infants with observations of respiratory and renal water metabolism. Am J Dis Child. 1968; 115:122–144. PMID: 5636494.14. Phillips PA, Bretherton M, Johnston CI, Gray L. Reduced osmotic thirst in healthy elderly men. Am J Physiol. 1991; 261:R166–R171. PMID: 1858944.
Article15. Snyder NA, Feigal DW, Arieff AI. Hypernatremia in elderly patients: a heterogeneous, morbid, and iatrogenic entity. Ann Intern Med. 1987; 107:309–319. PMID: 3619220.16. Arieff AI, Guisado R. Effects on the central nervous system of hypernatremic and hyponatremic states. Kidney Int. 1976; 10:104–116. PMID: 7702.
Article17. Morris-Jones PH, Houston IB, Evans RC. Prognosis of the neurological complications of acute hypernatraemia. Lancet. 1967; 2:1385–1389. PMID: 4170055.18. Hogan GR, Dodge PR, Gill SR, Master S, Sotos JF. Pathogenesis of seizures occurring during restoration of plasma tonicity to normal in animals previously chronically hypernatremic. Pediatrics. 1969; 43:54–64. PMID: 5764069.
Article19. Hiromatsu K, Kobayashi T, Fujii N, Itoyama Y, Goto I, Murakami J. Hypernatremic myopathy. J Neurol Sci. 1994; 122:144–147. PMID: 8021697.
Article20. De Villota ED, Cavanilles JM, Stein L, Shubin H, Weil MH. Hyperosmolal crisis following infusion of hypertonic sodium chloride for purposes of therapeutic abortion. Am J Med. 1973; 55:116–122. PMID: 4715929.
Article21. Lien YH, Shapiro JI, Chan L. Effects of hypernatremia on organic brain osmoles. J Clin Invest. 1990; 85:1427–1435. PMID: 2332498.
Article22. Kahn A, Brachet E, Blum D. Controlled fall in natremia and risk of seizures in hypertonic dehydration. Intensive Care Med. 1979; 5:27–31. PMID: 35558.
Article23. Palevsky PM. Hypernatremia. Semin Nephrol. 1998; 18:20–30. PMID: 9459286.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The study on Non-successful Cases of ESWL in the Upper Urinary Tract Stone using Wolf Piezolith 2300 Lithotriptor(R)
- Psychosocial Stress, Memory, and Successful Aging of the Community-Residing Elderly
- Successful Management of Spontaneous Intraperitoneal Hemorrhage Occurred after Superior Mesenteric Artery Stenting
- Successful Aging: Concept and Strategies
- Risk Factors Associated with the Recurrence of Amblyopia after Successful Treatment