Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2014 Dec;22(2):102-105. 10.12793/tcp.2014.22.2.102.
A bioequivalence study of two levofloxacin tablets in healthy male subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Seoul National University Hospital and College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. howardlee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Transdisciplinary Studies, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 3Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine and Hospital, Seoul 130-872, Korea.
- KMID: 2050943
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2014.22.2.102
Abstract
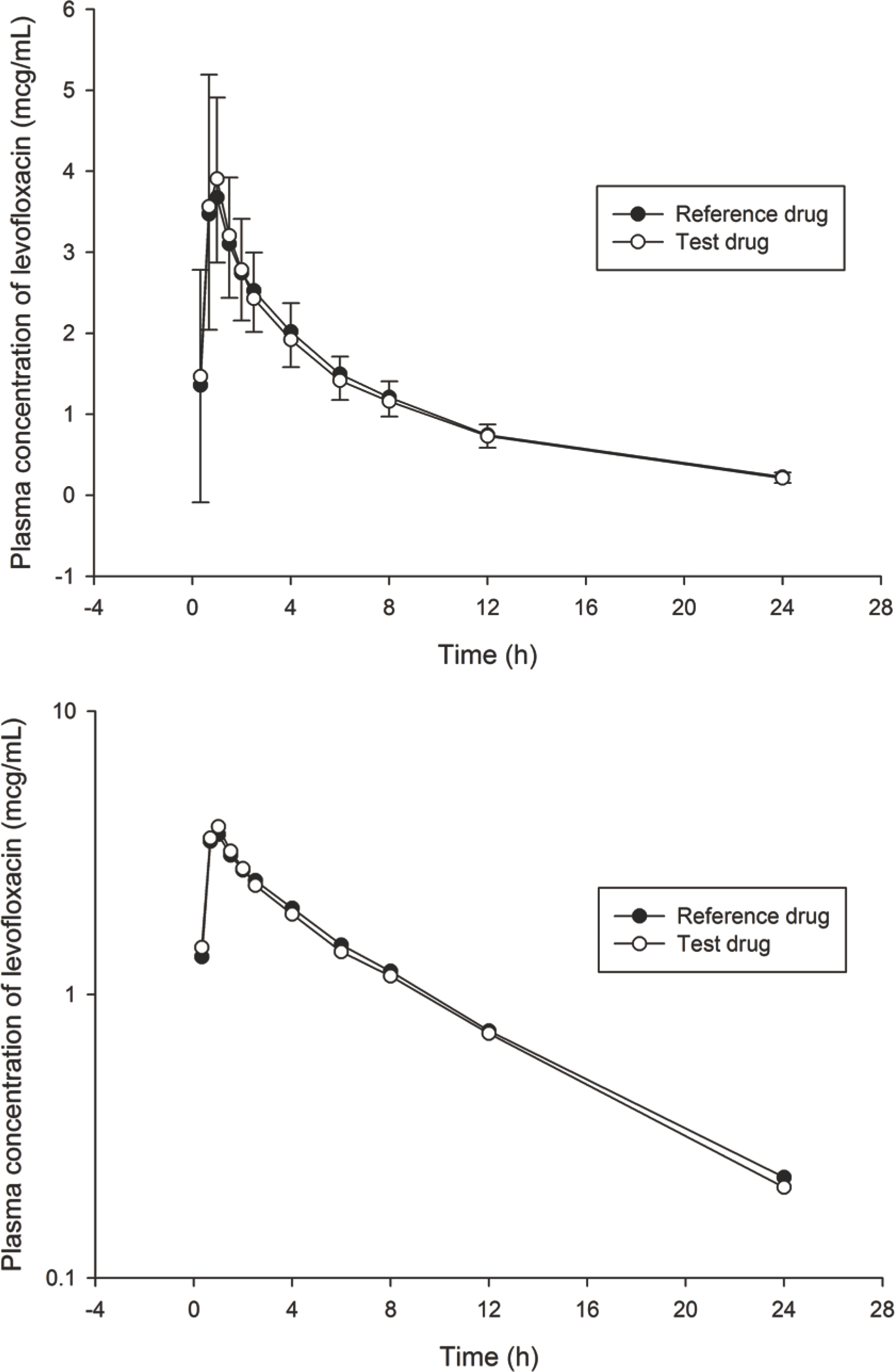
- Levofloxacin is a bactericidal broad spectrum antibiotic against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. A randomized, two-treatment, two-period, two-way crossover study was conducted to evaluate the bioequivalence of Lectacin 250 mg tablet, a generic levofloxacin, to its reference drug, Cravit 250 mg tablet. Each period was separated by a 7-day washout. Serial blood samples were collected until 24 h after dosing and plasma levofloxacin concentrations were determined using a high performance liquid chromatography. Pharmacokinetic parameters were analyzed using K-BE Test 2007 and BA calc 2007 (Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Cheongju-si, South Korea). The peak concentration (Cmax) and the area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from 0 to the last measurable concentration (AUC(0-t)) for the generic and reference levofloxacin were 4.48+/-0.89 mg/L and 4.46+/- 0.95 mg/L, and 25.33+/-4.12 mg*h/L and 25.77+/-4.01 mg*h/L, respectively, leading to a geometric mean ratio (90% confidence interval) of the generic to the reference levofloxacin of 1.0060 (0.9339-1.0842) and 0.9810 (0.9476-1.0159), respectively, for Cmax and AUC(0-t). Lectacin 250 mg tablet is bioequivalent to Cravit 250 mg tablet.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. North DS, Fish DN, Redington JJ. Levofloxacin, a second-generation fluoroquinolone. Pharmacotherapy. 1998; 18:915–935.2. Croom KF, Goa KL. Levofloxacin: a review of its use in the treatment of bacterial infections in the United States. Drugs. 2003; 63:2769–2802.3. Rafat C, Debrix I, Hertig A. Levofloxacin for the treatment of pyelonephritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013; 14:1241–1253. doi: 10.1517/14656566. 2013.792805.
Article4. Torres A, Liapikou A. Levofloxacin for the treatment of respiratory tract infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012; 13:1203–1212. doi: 10.1517/14 656566.2012.688952.
Article5. Anderson VR, Perry CM. Levofloxacin: a review of its use as a high-dose, short-course treatment for bacterial infection. Drugs. 2008; 68:535–565.6. Guidance Document for Bioequivalence Study. In: MFDS, editor. 2010.7. Tsaganos T, Kouki P, Digenis P, Giamarellou H, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Kanellakopoulou K. Pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin after single and multiple oral doses in patients undergoing intermittent haemodialysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008; 32:46–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.02.011.
Article8. Levaquin® (levofloxacin tablets, oral solution, injection): US prescribing information. In: Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical I, editor. 2008.9. Chien SC, Rogge MC, Gisclon LG, Curtin C, Wong F, Natarajan J, et al. Pharmacokinetic profile of levofloxacin following once-daily 500-milligram oral or intravenous doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997; 41:2256–2260.
Article10. Gao X, Yao G, Guo N, An F, Guo X. A simple and rapid high performance liquid chromatography method to determine levofloxacin in human plasma and its use in a bioequivalence study. Drug Discov Ther. 2007; 1:136–140.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fed and fasted bioequivalence assessment of two formulations of extended-release fixed-dose combination dapagliflozin/metformin (10/1,000 mg) tablets in healthy subjects
- Pharmacokinetic properties and bioequivalence of gefitinib 250 mg in healthy Korean male subjects
- Bioequivalence study of Donepezil hydrochloride in healthy Korean volunteers
- Comparative pharmacokinetic and tolerability evaluation of two simvastatin 20 mg formulations in healthy Korean male volunteers
- Pharmacokinetic comparison of two levofloxacin 100-mg tablet formulations and determination of time point appropriately reflecting its area under the curve