Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 May;74(5):231-234. 10.4046/trd.2013.74.5.231.
A Case of Endobronchial Aspergilloma Associated with Foreign Body in Immunocompetent Patient without Underlying Lung Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Tuberculosis and Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. prince-yoonbk11@nate.com
- KMID: 2050892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.5.231
Abstract
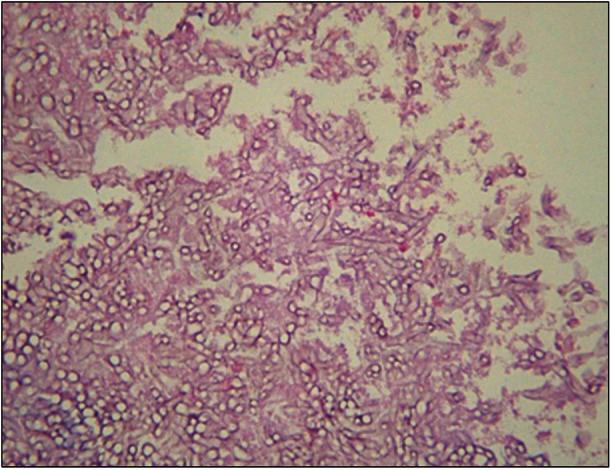
- Aspergillus causes a variety of clinical syndromes in the lung including tracheobronchial aspergillosis, invasive aspergillosis, chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and aspergilloma. Aspergilloma usually results from ingrowths of colonized Aspergillus in damaged bronchial tree, pulmonary cyst or cavities of patients with underlying lung diseases. There are a few reports on endobronchial aspergilloma without underlying pulmonary lesion. We have experienced a case of endobronchial aspergilloma associated with foreign body developed in an immunocompetent patient without underlying lung diseases. A 59-year-old man is being hospitalized with recurring hemoptysis for 5 months. X-ray and computed tomography scans of chest showed a nodular opacity in superior segment of left lower lobe. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed an irregular, mass-like, brownish material which totally obstructed the sub-segmental bronchus and a foreign body in superior segmental bronchus of the lower left lobe. Histopathologic examinations of biopsy specimen revealed fungal hyphae, characteristic of Aspergillus species.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Martin TR, King TE, Schraufnagel DE, Murray JF, et al. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2010.2. Glimp RA, Bayer AS. Pulmonary aspergilloma: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Intern Med. 1983; 143:303–308. PMID: 6824396.
Article3. Kim JS, Rhee Y, Kang SM, Ko WK, Kim YS, Lee JG, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:422–425. PMID: 10957902.
Article4. Kim TH, Yong BJ, Kim YK, Lee YM, Kim KU, Uh ST, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma with massive hemoptysis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2004; 57:589–593.
Article5. Eom WY, Kim NI, Kim SW, Lee BH, Kim SH, Ahn YS, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma in patient with collapse of right middle lobe. Korean J Med. 2006; 70:221–225.6. Kim SJ, Lee EJ, Lee TH, Yoo KH, Lee KY. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006; 61:60–64.
Article7. Lee SH, Lee BJ, Jung DY, Kim JH, Sohn DS, Shin JW, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes of pulmonary aspergilloma. Korean J Intern Med. 2004; 19:38–42. PMID: 15053042.
Article8. Ma JE, Yun EY, Kim YE, Lee GD, Cho YJ, Jeong YY, et al. Endobronchial aspergilloma: report of 10 cases and literature review. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:787–792. PMID: 21786444.
Article9. Quoix E, Gasser B, Apprill M, Gourdon C, Pauli G, Roegel E. Endobronchial aspergillosis associated with a carcinoid tumor. Rev Mal Respir. 1990; 7:609–612. PMID: 2270353.10. Ham HS, Lee SJ, Cho YJ, Jeon KN, Jeong YY, Kim HC, et al. A case of lung cancer obscured by endobronchial aspergilloma. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006; 61:157–161.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endobronchial Aspergilloma: Report of 10 Cases and Literature Review
- A case of endobronchial aspergilloma with massive hemoptysis
- Mycobacterium avium Infection Presenting as Endobronchial Lesions in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Pulmonary and Endobronchial Mycobacterium avium Infection Presenting as an Acute Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Endobronchial Aspergilloma