Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Jul;61(1):60-64.
A Case of Endobronchial Aspergilloma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Hospital School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Korea. kyleemd@kuh.ac.kr
Abstract
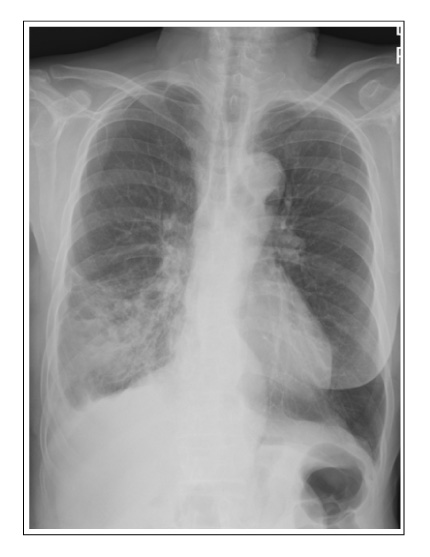
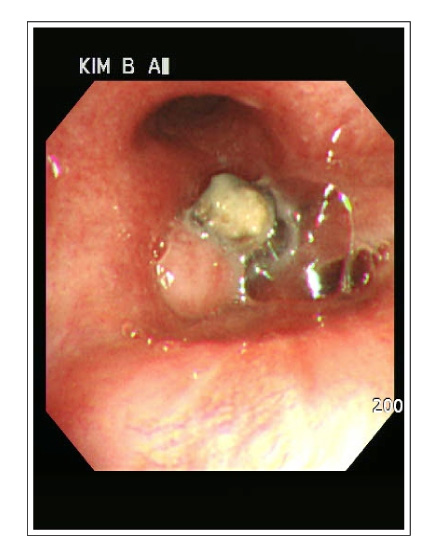
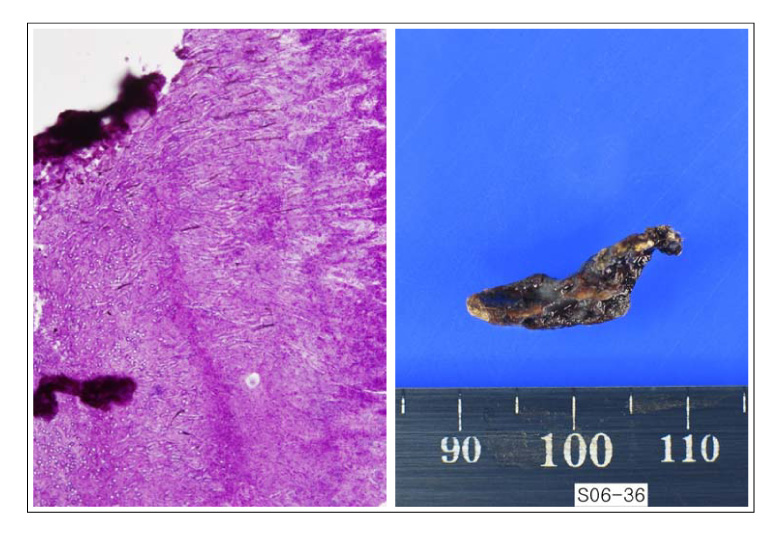
- Pulmonary aspergillosis presents as the following three different types depending on the immune status of the host: invasive aspergillosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), and aspergilloma. Aspergilloma develops as a result of an aspergillus growth inside a pre-existing lung cavity. However, endobronchial aspergilloma without a lung parenchymal lesion is quite rare. We encountered a case of endobronchial aspergilloma that developed in a healthy 75 year-old woman that led to necrotizing pneumonia of the right lower lobe. The chief complaints were fever, cough and yellowish sputum. The chest film revealed haziness with cavity-like shadows on the right lower lobe, and the chest CT scan showed endobronchial calcified density in the basal bronchus of the right lower lobe with peribronchial lymph node enlargement. Bronchoscopy revealed an obstruction of the basal orifice of the right lower lobe by blackish stone-like material, and the aspergilloma was confirmed by the bronchoscopic biopsy. The pneumonia improved after bronchoscopic removal of this lesion. We report this case along with a review of the relevant literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002. 121:1988–1999.2. Greene R. The pulmonary aspergilloses: three distinct entities or a spectrum of disease. Radiology. 1981. 140:527–530.3. Kim JS, Rhee Y, Kang SM, Ko WK, Kim YS, Lee JG, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:422–425.4. Kim TH, Yong BJ, Kim YK, Lee YM, Kim KU, Uh ST, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma with massive hemoptysis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2004. 57:589–593.5. Eom WY, Kim NI, Kim SW, Lee BH, Kim SH, Ahn YS, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma in patient with collapse of right middle lobe. Korean J Med. 2006. 70:221–225.6. Rinaldi MG. Invasive aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983. 5:1061–1077.7. Hinson KF, Moon AJ, Plummer NS. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis: a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952. 7:317–333.8. Gefter WB, Weingrad TR, Epstein DM, Ochs RH, Miller WT. "Semi-invasive"pulmonary aspergillosis: a new look at the spectrum of aspergillus infections of the lung. Radiology. 1981. 140:313–321.9. Franquet T, Muller NL, Gimenez A, Guembe P, de la Torre J, Bague S. Spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis: histologic, clinical, and radiologic findings. Radiographics. 2001. 21:825–837.10. Quoix E, Gasser B, Apprill M, Gourdon C, Pauli G, Roegel E. Endobronchial aspergillosis associated with a carcinoid tumor. Rev Mal Respir. 1990. 7:609–612.11. le Rochais JP, Icard P, Simon T, Poirier P, Evrard C. Bronchial stump aspergillosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000. 70:302–304.12. Kwon MY, Oh YJ, Ryu JS, Kwak SM, Lee HL, Cho CH, et al. A case of broncholithiasis caused by aspergillus. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1999. 46:136–141.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of endobronchial aspergilloma with massive hemoptysis
- A case of endobronchial aspergilloma
- A Case of Endobronchial Aspergilloma Associated with Foreign Body in Immunocompetent Patient without Underlying Lung Disease
- A case of endobronchial aspergilloma in patient with collapse of right middle lobe
- A Case of Lung Cancer Obscured by Endobronchial Aspergilloma